How to take a List from user input in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·7 min

# Table of Contents
- Add user input to a list in Python
- Take a list of integers from user Input in Python
- Take list user input using str.split()
- Take a list of integers from user Input using str.split()
- Take list user input using a while loop
- Take a list of integers from user Input using a while loop
- Take a list of lists user input
- Take a two-dimensional list of integers from user input
# Add user input to a list in Python
To add user input to a list in Python:
- Declare a variable that stores an empty list.
- Use the
range()class to loop N times in aforloop. - On each iteration, append the input value to the list.
shopping_list = [] list_length = 3 for idx in range(list_length): item = input('Enter item to buy: ') shopping_list.append(item) print(shopping_list) # 👉️ ['apple', 'banana', 'kiwi']
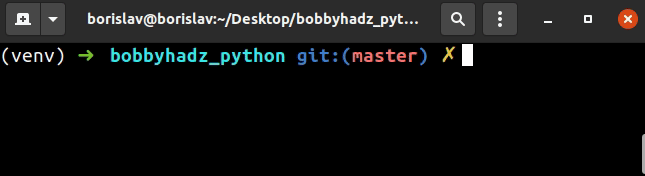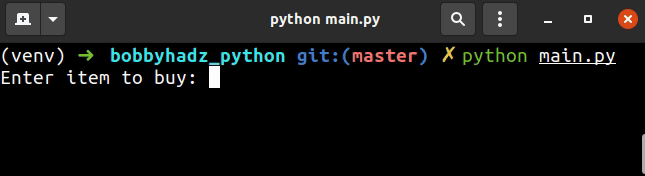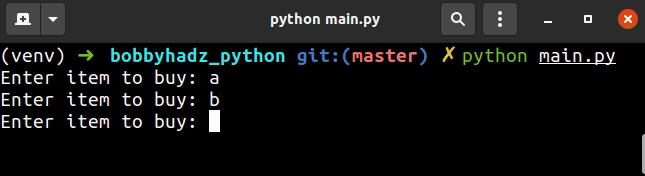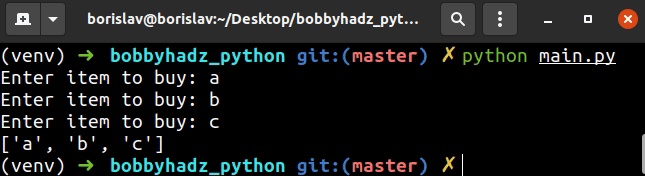
The code sample prompts the user for input 3 times and adds each value to the list.
The list.append() method adds an item to the end of the list.
The example uses the range() class, but you can
also use a while loop if you want to make sure the list has a length of at
least N items.
shopping_list = [] max_length = 3 while len(shopping_list) < max_length: item = input('Enter item to buy: ') shopping_list.append(item) print(shopping_list) # 👉️ ['apple', 'banana', 'kiwi']
If the list has a length of less than 3, we keep prompting the user for input.
shopping_list = [] max_length = 3 while len(shopping_list) < max_length: item = input('Enter item to buy: ') # 👇️ Make sure item is not in the list before appending if item not in shopping_list: shopping_list.append(item) print(shopping_list) # 👉️ ['apple', 'banana', 'kiwi']
We used an if statement to check if the value the user entered isn't in the
list before appending it.
The in operator tests
for membership. For example, x in l evaluates to True if x is a member of
l, otherwise it evaluates to False.
x not in l returns the negation of x in l.
user_input = '' while user_input.count(' ') < 2: user_input = input('Enter at least 3 space-separated shopping items: ') shopping_list = user_input.split(' ') print(shopping_list) # 👉️ ['apple', 'banana', 'kiwi']
Note that this approach is a bit harder to validate.
The str.split() method splits the string into a list of substrings using a delimiter.
The method takes the following 2 parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| separator | Split the string into substrings on each occurrence of the separator |
| maxsplit | At most maxsplit splits are done (optional) |
If the separator is not found in the string, a list containing only 1 element is returned.
Here is another example of taking a list from user input.
my_list = [] for _ in range(3): my_list.append(input('Enter a country: ')) print(my_list)
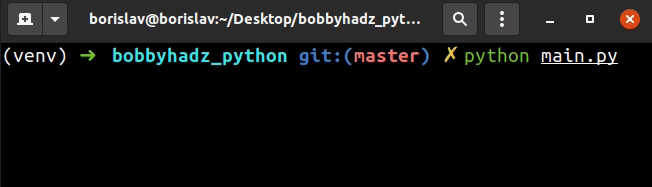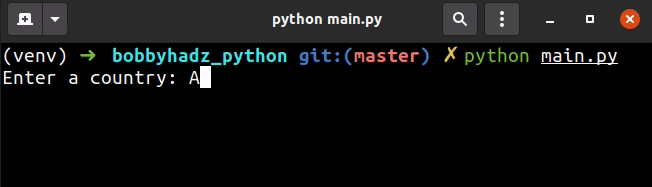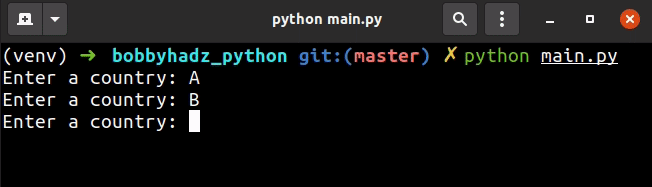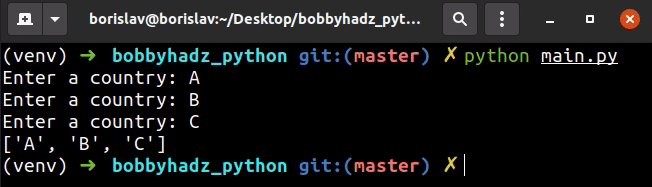
The code snippet loops 3 times, takes input from the user and appends it to a list.
The list.append() method adds an item to the end of the list.
# Take a list of integers from user Input in Python
If you need to store integer values in a list, use the int() class to convert the input strings to integers.
my_list = [] for _ in range(3): try: my_list.append(int(input('Enter a number: '))) except ValueError: print('The provided value is not an integer.') print(my_list)
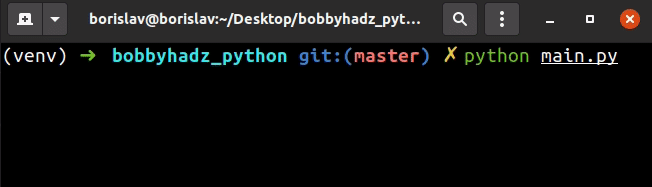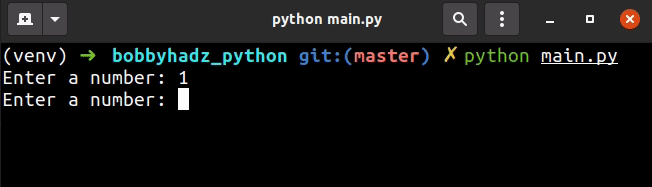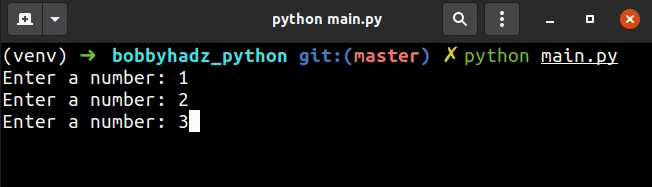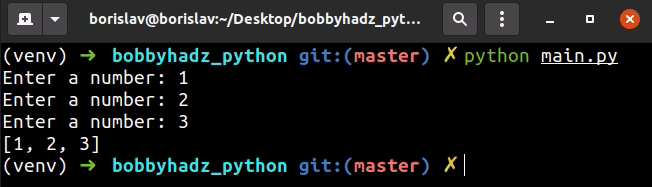
The input() function takes an optional prompt
argument and writes it to standard output without a trailing newline.
The function then reads the line from the input, converts it to a string and returns the result.
input() function is guaranteed to return a string, even if the user enters an integer.We used a try/except
statement to handle the ValueError that is raised if the int() class is
called with a value that is not a valid integer.
An alternative approach is to ask the user to enter multiple, space or comma-separated words and split the string on the separator.
# Take list user input using str.split()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
input()function to take input from the user. - Use the
str.split()method to split the string on each whitespace. - The
split()method will return a list containing the words the user entered.
user_input = input('Enter space-separated shopping items: ') shopping_list = user_input.split() print(shopping_list) # 👉️ ['apple', 'banana', 'kiwi']
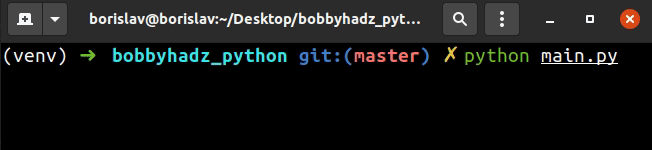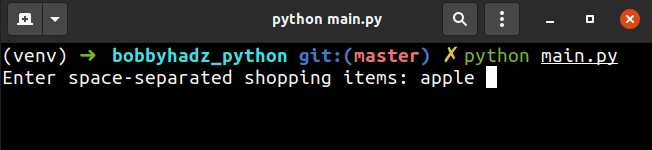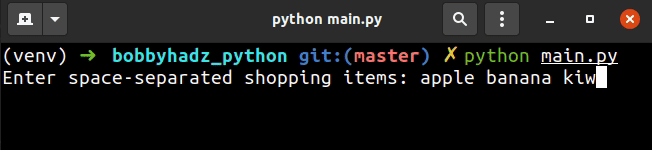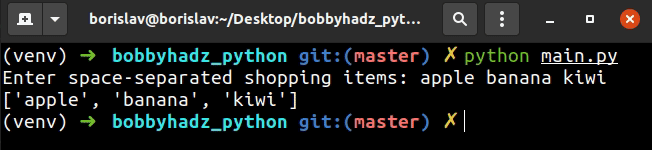
The str.split() method splits the string into a list of substrings using a delimiter.
str.split() method, it splits the input string on one or more whitespace characters.# Take a list of integers from user Input using str.split()
If you need to convert the values to numbers, use a list comprehension.
user_input = input('Enter space-separated integers: ').split() list_of_integers = [int(item) for item in user_input] print(list_of_integers) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3]
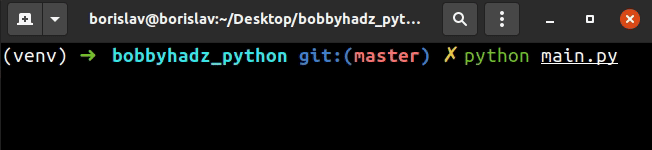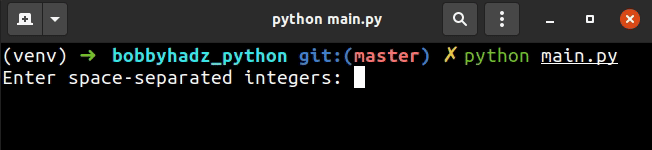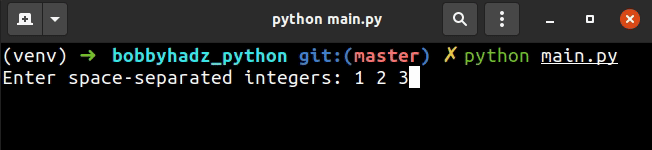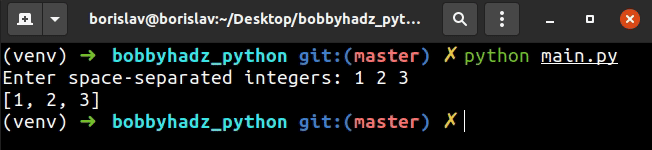
On each iteration, we pass the current list item to the int() class to convert
it to an integer.
# Take list user input using a while loop
This is a three-step process:
- Declare a new variable and initialize it to an empty list.
- Use a
whileloop to iterate as long as a condition is met. - On each iteration, append the input value to the list.
my_list = [] user_input = '' while len(my_list) < 3: user_input = input('Enter a word: ') my_list.append(user_input) print(my_list)
The example uses a while loop to ask the user for input until the list
contains at least 3 items.
# Take a list of integers from user Input using a while loop
You can also use this approach to make sure the list contains at least N integers.
my_list = [] user_input = '' while len(my_list) < 3: try: user_input = int(input('Enter an integer: ')) my_list.append(user_input) except ValueError: print('Enter a valid integer') continue print(my_list)
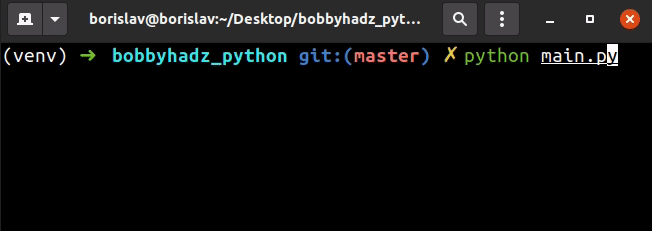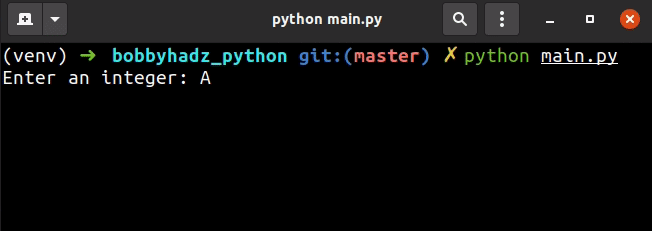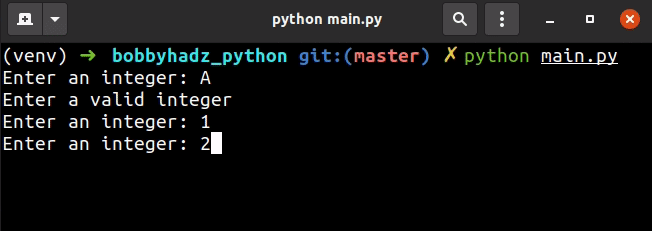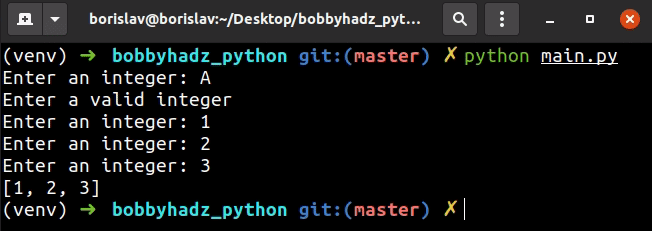
The example uses a while loop to iterate until the list contains at least 3
integers taken from user input.
The continue statement is used to continue to the next iteration of the loop.
try block raises a ValueError, the except block runs, where we use the continue statement to continue to the next iteration.When validating user input in a while loop,
we use the continue statement when the input is invalid, e.g. in an except
block or an if statement.
Alternatively, you can use a while True loop with a break statement.
my_list = [] user_input = '' while True: if len(my_list) >= 3: break try: user_input = int(input('Enter an integer: ')) my_list.append(user_input) except ValueError: print('Enter a valid integer') continue print(my_list)
The if statement checks if the length of the list is equal to or greater
than 3.
If the condition is met, we use the break statement to exit out of the loop.
The break statement breaks out of the
innermost enclosing for or while loop.
# Take a List of Lists user input
To take a list of lists user input:
- Use a
forloop to iterate N times. - Use the
input()function to take multiple inputs from the user. - Add the input values to a list and append the list to the original list.
list_of_lists = [] user_input = '' for _ in range(2): user_input_1 = input('Enter a word: ') user_input_2 = input('Enter another word: ') list_of_lists.append([user_input_1, user_input_2]) print(list_of_lists)
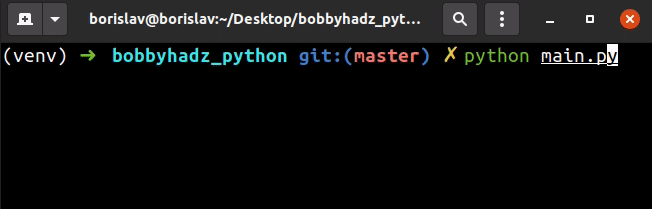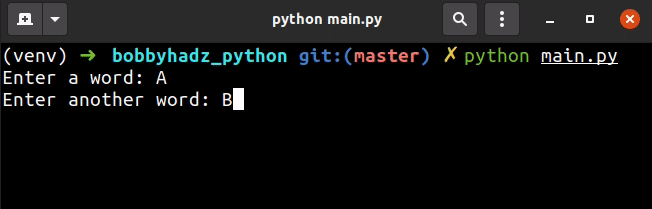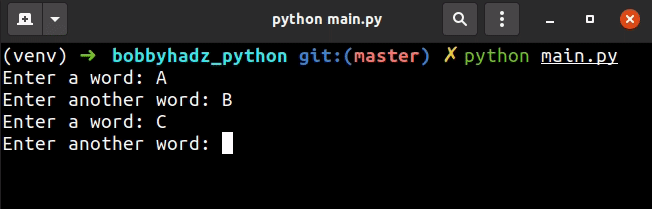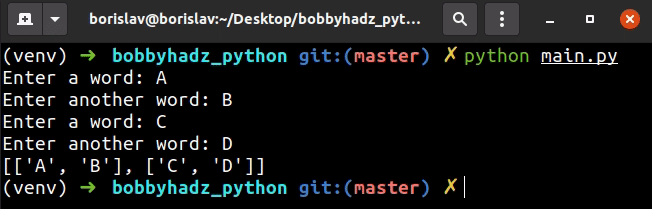
We used a for loop to iterate 2 times.
On each iteration, we take user input 2 times, place the values in a list and append the list to another list.
# Take a two-dimensional list of integers from user input
To take a two-dimensional list of integers from user input:
- Use a
forloop to iterate N times. - Use the
input()function to take multiple inputs from the user. - Use the
int()class to convert the values to integers. - Add the input values to a list and append the list to the original list.
list_of_lists = [] user_input = '' for _ in range(2): user_input_1 = int(input('Enter an integer: ')) user_input_2 = int(input('Enter another integer: ')) list_of_lists.append([user_input_1, user_input_2]) print(list_of_lists)
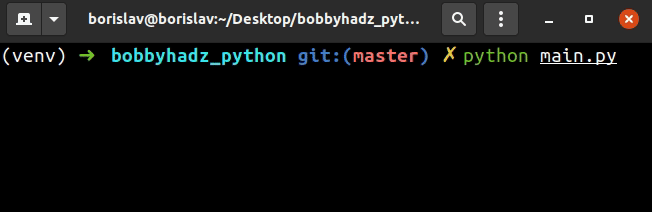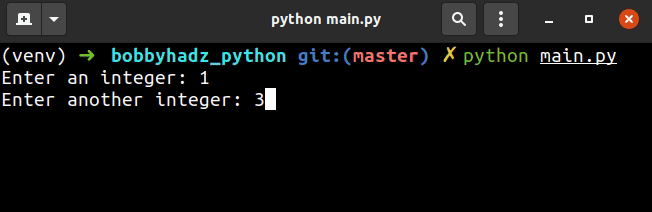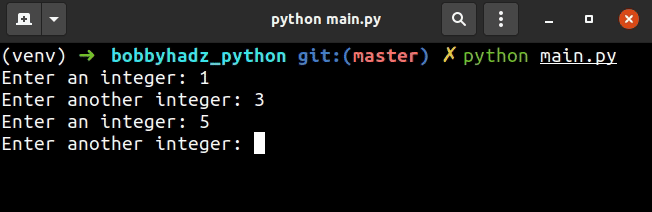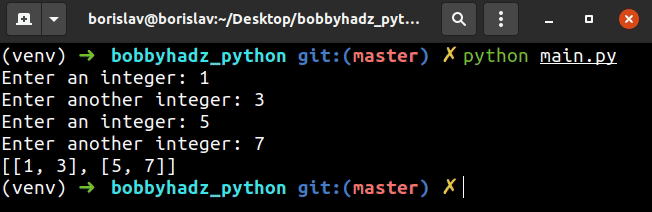
We used a for loop to iterate 2 times.
On each iteration, we take user input 2 times and convert the values to integers.
Lastly, we place the values in a list and append the list to another list.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to Add user input to a Dictionary in Python
- How to check if User Input is Empty in Python
- Using a For or While Loop to take user input in PythonTaking user input boolean (True/False) values in Python
- How to Create a Date from user Input in Python
- Taking a file path from user input in Python
- How to take Float user input in Python
- Multiple lines user Input in Python
- Only accept a single character from user Input in Python
- Creating a Tuple or a Set from user Input in Python
- How to Validate user input in Python
- Yes/No question with user input in Python
- How to save user input to a File in Python
- Using user input to Select an Option from a List in Python
- How to shift (rotate) a List in Python [5 Ways]
- How to keep a Python script output Window open

