Taking user input boolean (True/False) values in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Taking user input boolean (True/False) values in Python
To take user input boolean values:
- Use the
input()function to take input from the user. - Check if the provided value is equal to the strings
TrueorFalse. - Perform an action if either condition is met.
user_input = '' while True: user_input = input('Subscribe to newsletter? True / False: ') if user_input.capitalize() == 'True': print('The user typed in True') break elif user_input.capitalize() == 'False': print('The user typed in False') break else: print('Enter True or False') continue
We used a while loop to iterate until the
user enters a True or False value.
The input() function takes an optional prompt
argument and writes it to standard output without a trailing newline.
The function then reads the line from the input, converts it to a string and returns the result.
input() function is guaranteed to return a string even if the user enters a boolean value.Converting any non-empty string to a boolean returns True.
print(bool('a')) # 👉️ True print(bool('False')) # 👉️ True print(bool('')) # 👉️ False
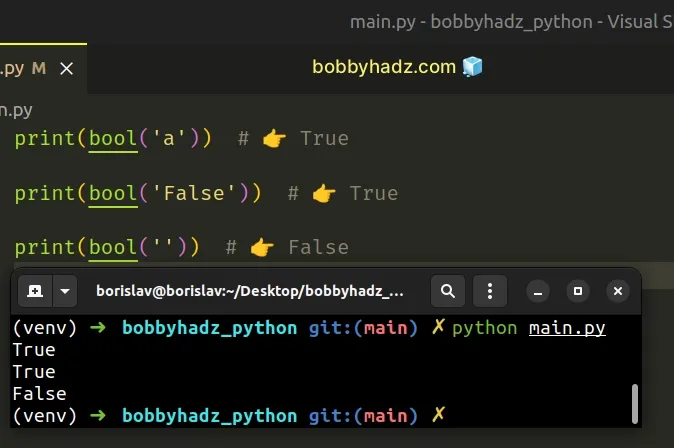
This is why we compare the user input value to the strings True and False
instead.
user_input = '' while True: user_input = input('Subscribe to newsletter? True / False: ') if user_input.capitalize() == 'True': print('The user typed in True') break elif user_input.capitalize() == 'False': print('The user typed in False') break else: print('Enter True or False') continue
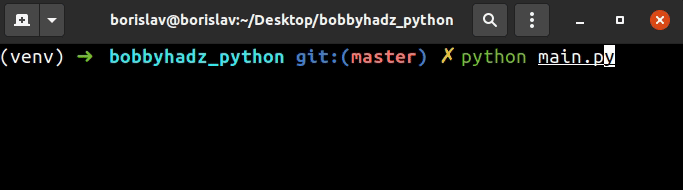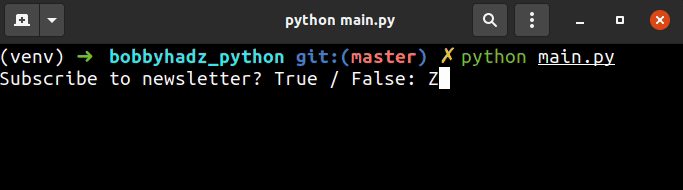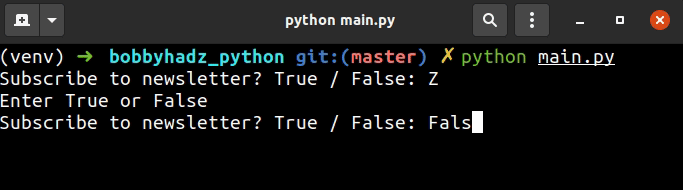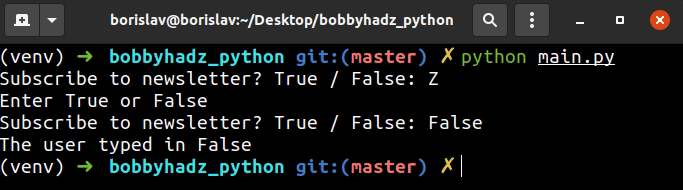
The if statement checks if the user input value is equal to the string True.
If the condition is met, we print the value and break out of the while loop.
The break statement breaks out of the innermost enclosing for or while loop.
The str.capitalize() function returns a copy of the string with the first character capitalized and the rest lowercased.
print('true'.capitalize()) # 👉️ 'True' print('FALSE'.capitalize()) # 👉️ 'False'
The str.capitalize method makes sure the first letter of the input value is
uppercase and the rest are lowercase.
If the provided value is neither True nor False, we use the
continue statement to
prompt the user again.
The continue statement continues with the next iteration of the loop.
while loop, we use the continue statement when the input is invalid, e.g. in an except block or an if statement.If the input is valid, we use the break statement to exit out of the while
loop.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Creating a Tuple or a Set from user Input in Python
- How to Validate user input in Python
- Yes/No question with user input in Python
- How to Create a Date from user Input in Python
- Taking a file path from user input in Python
- How to take Float user input in Python
- Multiple lines user Input in Python
- Only accept a single character from user Input in Python

