Panda: Using fillna() with specific columns in a DataFrame
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Panda: Using fillna() with a specific column in a DataFrame
- Panda: Using fillna() with multiple specific columns in a DataFrame
- Panda: Using fillna() with specific columns in a DataFrame using a dict
# Panda: Using fillna() with a specific column in a DataFrame
To use the fillna() method with only specific columns in a Pandas
DataFrame:
- Select the
DataFramecolumn(s) using bracket notation. - Call the
fillna()method on the selected column(s).
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': [1, 1, None, 2, 2, None], 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', None, 'Dog', 'Dog', None], 'Max Speed': [25, 35, None, 55, 65, None] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df['Animal'] = df['Animal'].fillna(value='Anonymous') print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
ID Animal Max Speed 0 1 Cat 25.0 1 1 Cat 35.0 2 1 None NaN 3 2 Dog 55.0 4 2 Dog 65.0 5 2 None NaN -------------------------------------------------- ID Animal Max Speed 0 1 Cat 25.0 1 1 Cat 35.0 2 1 Anonymous NaN 3 2 Dog 55.0 4 2 Dog 65.0 5 2 Anonymous NaN
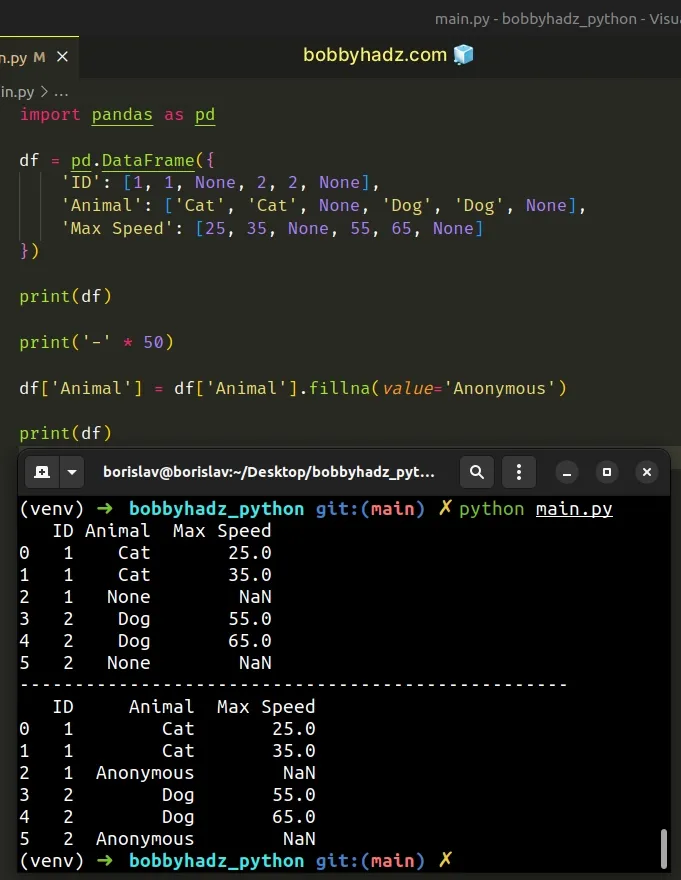
We used bracket notation [] to select the "Animal" column and used the
DataFrame.fillna
method to fill the NA/NaN values in the column with the string "Anonymous".
df['Animal'] = df['Animal'].fillna(value='Anonymous')
The value you pass to the fillna() method is the replacement for each NA/NaN
value in the specified column.
# Panda: Using fillna() with multiple specific columns in a DataFrame
If you need to use the fillna() method with multiple specific columns, use two
sets of square brackets when selecting them.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': [1, 1, None, 2, 2, None], 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', None, 'Dog', 'Dog', None], 'Max Speed': [25, 35, None, 55, 65, None] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df[['Animal', 'Max Speed']] = df[[ 'Animal', 'Max Speed']].fillna(value='NOT_AVAILABLE') print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
ID Animal Max Speed 0 1.0 Cat 25.0 1 1.0 Cat 35.0 2 NaN None NaN 3 2.0 Dog 55.0 4 2.0 Dog 65.0 5 NaN None NaN -------------------------------------------------- ID Animal Max Speed 0 1.0 Cat 25.0 1 1.0 Cat 35.0 2 NaN NOT_AVAILABLE NOT_AVAILABLE 3 2.0 Dog 55.0 4 2.0 Dog 65.0 5 NaN NOT_AVAILABLE NOT_AVAILABLE
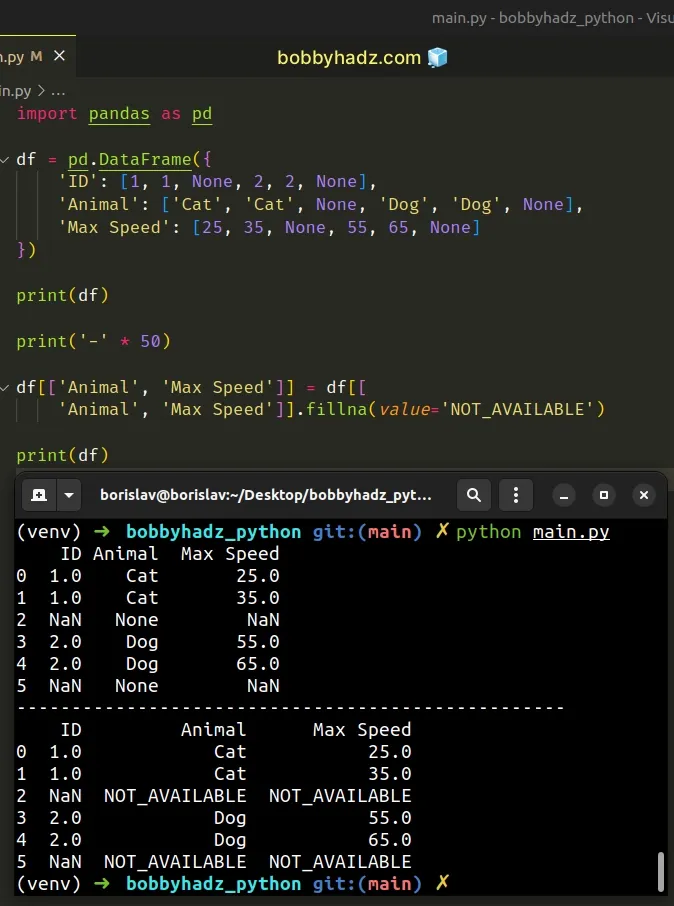
Notice that two sets of square brackets [[]] are used when selecting multiple
columns.
df[['Animal', 'Max Speed']] = df[[ 'Animal', 'Max Speed']].fillna(value='NOT_AVAILABLE')
Once we've selected the multiple columns, we can call the fillna() method with
the replacement.
The code sample used the "NOT_AVAILABLE" string for the replacement, but you
can use any other value.
The value doesn't necessarily have to be a string.
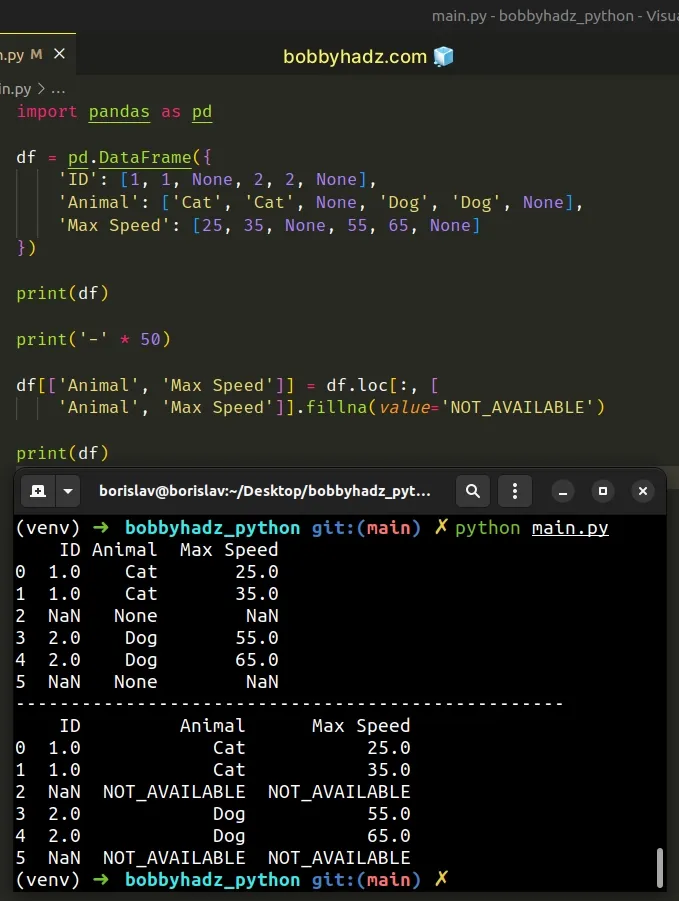
You can also use the DataFrame.loc label-based indexer, however, this isn't necessary.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': [1, 1, None, 2, 2, None], 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', None, 'Dog', 'Dog', None], 'Max Speed': [25, 35, None, 55, 65, None] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df[['Animal', 'Max Speed']] = df.loc[:, [ 'Animal', 'Max Speed']].fillna(value='NOT_AVAILABLE') print(df)
Running the code sample produces the same output.
ID Animal Max Speed 0 1.0 Cat 25.0 1 1.0 Cat 35.0 2 NaN None NaN 3 2.0 Dog 55.0 4 2.0 Dog 65.0 5 NaN None NaN -------------------------------------------------- ID Animal Max Speed 0 1.0 Cat 25.0 1 1.0 Cat 35.0 2 NaN NOT_AVAILABLE NOT_AVAILABLE 3 2.0 Dog 55.0 4 2.0 Dog 65.0 5 NaN NOT_AVAILABLE NOT_AVAILABLE
# Panda: Using fillna() with specific columns in a DataFrame using a dict
You can also pass a dictionary to the fillna() method to only call the method
on specific columns.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': [1, 1, None, 2, 2, None], 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', None, 'Dog', 'Dog', None], 'Max Speed': [25, 35, None, 55, 65, None] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df = df.fillna( {'Animal': 'Anonymous', 'Max Speed': 'NOT_AVAILABLE'} ) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
ID Animal Max Speed 0 1.0 Cat 25.0 1 1.0 Cat 35.0 2 NaN None NaN 3 2.0 Dog 55.0 4 2.0 Dog 65.0 5 NaN None NaN -------------------------------------------------- ID Animal Max Speed 0 1.0 Cat 25.0 1 1.0 Cat 35.0 2 NaN Anonymous NOT_AVAILABLE 3 2.0 Dog 55.0 4 2.0 Dog 65.0 5 NaN Anonymous NOT_AVAILABLE
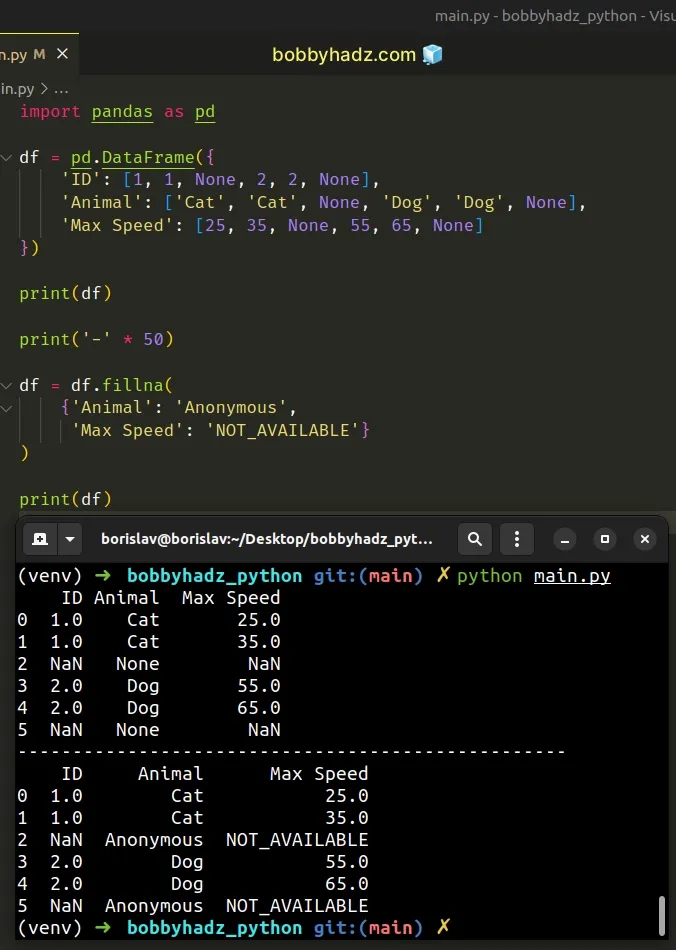
We used the column names as dictionary keys and the replacements as dictionary values.
df = df.fillna( {'Animal': 'Anonymous', 'Max Speed': 'NOT_AVAILABLE'} )
You can include as many key-value pairs in the dictionary as necessary.
The code sample above updates the DataFrame by reassigning the variable.
Alternatively, you can mutate the DataFrame directly by setting the inplace
argument to True.
import pandas as pd df = pd.DataFrame({ 'ID': [1, 1, None, 2, 2, None], 'Animal': ['Cat', 'Cat', None, 'Dog', 'Dog', None], 'Max Speed': [25, 35, None, 55, 65, None] }) print(df) print('-' * 50) df.fillna( {'Animal': 'Anonymous', 'Max Speed': 'NOT_AVAILABLE'}, inplace=True ) print(df)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
ID Animal Max Speed 0 1.0 Cat 25.0 1 1.0 Cat 35.0 2 NaN None NaN 3 2.0 Dog 55.0 4 2.0 Dog 65.0 5 NaN None NaN -------------------------------------------------- ID Animal Max Speed 0 1.0 Cat 25.0 1 1.0 Cat 35.0 2 NaN Anonymous NOT_AVAILABLE 3 2.0 Dog 55.0 4 2.0 Dog 65.0 5 NaN Anonymous NOT_AVAILABLE
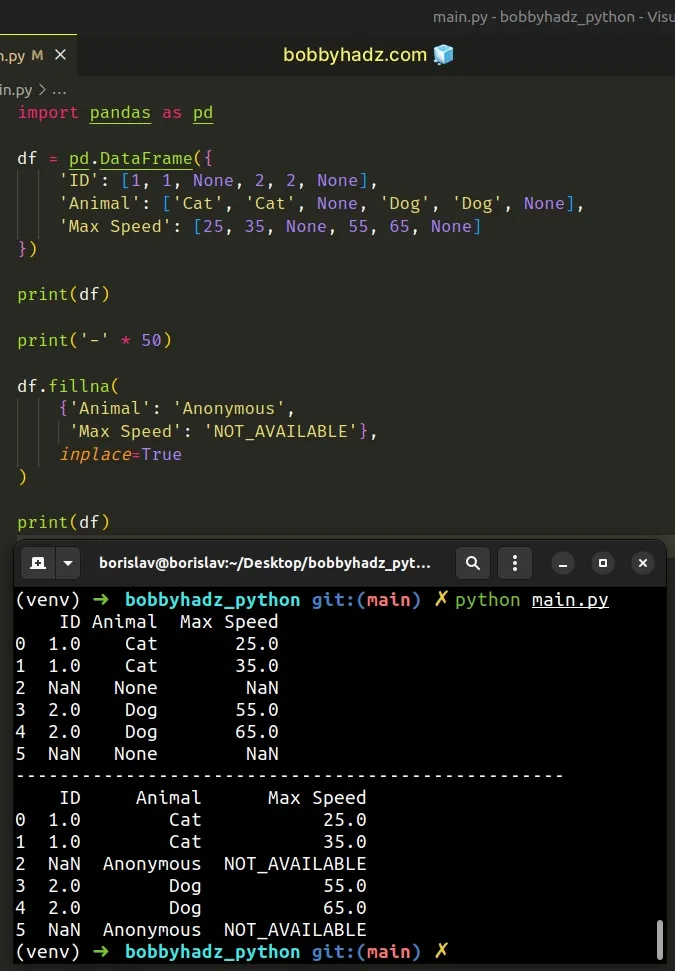
When the inplace argument is set to True, the fillna() method mutates the
DataFrame in place and returns None.
df.fillna( {'Animal': 'Anonymous', 'Max Speed': 'NOT_AVAILABLE'}, inplace=True )
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Pandas: How to Filter a DataFrame by value counts
- Pandas: Get the Rows that are NOT in another DataFrame
- How to Transpose a Pandas DataFrame without index
- Pandas: GroupBy columns with NaN (missing) values
- Pandas: Split a Column of Lists into Multiple Columns
- ValueError: Failed to convert a NumPy array to a Tensor (Unsupported object type float)
- Cannot convert non-finite values (NA or inf) to integer
- Pandas: How to efficiently Read a Large CSV File
- RuntimeError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate X MiB

