How to unzip a .gz file using Python [5 simple Ways]
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- How to unzip a .gz file using Python
- Unzip a .gz file to read its contents
- Using the
shmodule to unzip a.gzfile in Python
# How to unzip a .gz file using Python
To unzip a .gz file using Python:
- Use the
gzip.open()method to open the gzip-compressed file in binary mode. - Use the
with open()statement to open a file you want to write the contents of the compressed file to. - Use the
shutil.copyfileobj()method to copy the data from the compressed file to the newly created file.
import gzip import shutil with gzip.open('example.json.gz', 'rb') as file_in: with open('example.json', 'wb') as file_out: shutil.copyfileobj(file_in, file_out) print('example.json file created')
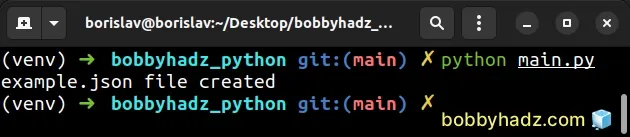
The code sample assumes that you have a file named example.json.gz in the same
directory as your Python script.
You can download a sample .gz file from
wiki.mozilla.org.
Make sure to rename the file to example.json.gz once you download it.
Running the code sample produces the following example.json file in the same
directory as my main.py script.
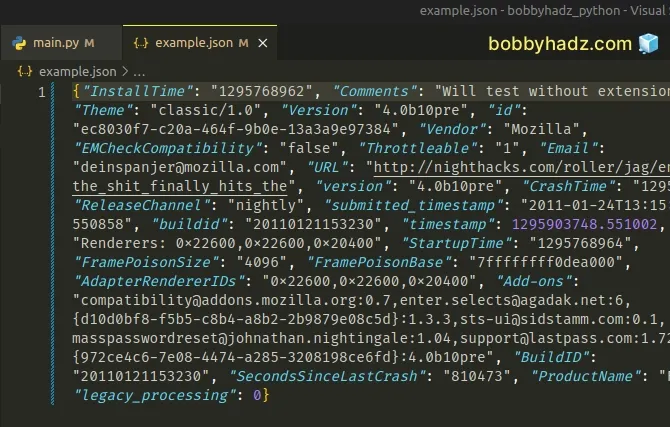
We used the with open() statement twice in the example.
The with open() statement takes care of automatically closing the file even if an error occurred.
The gzip.open() method opens a gzip-compressed file in binary or text mode and returns a text object.
import gzip import shutil with gzip.open('example.json.gz', 'rb') as file_in: # ...
The first argument the method takes is the filename and the second is the mode.
By default, the mode is set to rb. The rb mode stands for "read bytes".
The next step is to open the file to which we want to write the contents of the
file object that was returned from gzip.open().
import gzip import shutil with gzip.open('example.json.gz', 'rb') as file_in: with open('example.json', 'wb') as file_out: shutil.copyfileobj(file_in, file_out) print('example.json file created')
We passed 2 arguments to the shutil.copyfileobj() method:
- The source file.
- The output file.
The method copies the contents of the source file to the output file.
You can optionally pass a third argument to shutil.copyfileobj() - an integer
length that sets the buffer size.
By default, the data is read in chunks to avoid uncontrolled memory consumption.
If a negative length is supplied, the data is copied without looping over the source data in chunks.
# Unzip a .gz file to read its contents
If you only need to unzip the .gz file to read its contents, use the following
code sample instead.
import gzip with gzip.open('example.json.gz', 'rb') as file_in: file_contents = file_in.read() print(file_contents)
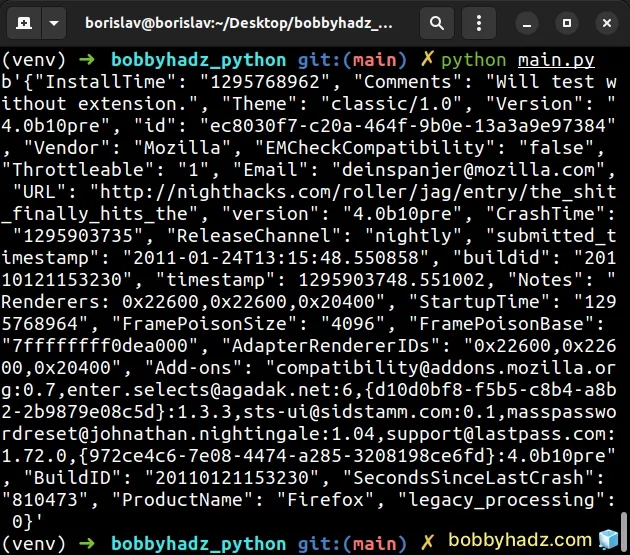
The code sample assumes that you have an example.json.gz file in the same
directory as your Python script.
You can download a sample .gz file from
wiki.mozilla.org.
Make sure to rename the file to example.json.gz once you download it.
We first use the gzip.open() method to open the gzip-compressed file in binary
mode.
The next step is to use the file.read() method to read the file's contents.
You can also read the file line by line.
import gzip with gzip.open('example.json.gz', 'rb') as file_in: for line in file_in: print(line.decode().strip())
Notice that we used the bytes.decode method to convert each line from bytes to string.
If you have a .gz file that stores a .csv file, you can use the
pandas library to read the file's contents.
import gzip import pandas as pd with gzip.open('example.csv.gz') as file_in: df = pd.read_csv(file_in) print(df.head())
The code sample assumes that you have an example.csv.gz file that stores a
.csv file.
The pandas.read_csv()
method reads a comma-separated-values (CSV) file into a DataFrame.
Make sure you have the pandas module installed.
pip install pandas # or with pip3 pip3 install pandas
You can also read a gzip-compressed .json file using
pandas.read_json.
import pandas as pd df = pd.read_json( 'example.json.gz', lines=True, compression='gzip' ) print(df.tail())
The pandas.read_json method converts a JSON string to a pandas object.
The compression keyword argument can be set to gzip for on-the-fly
decompression of on-disk data.
# Using the sh module to unzip a .gz file in Python
You can also use the sh module to unzip a .gz
file in Python.
First, make sure you have the module installed by running the following command.
pip install sh pip3 install sh
The gunzip() method will unzip the .gz file into an example.json file and
will delete the .gz file.
from sh import gunzip gunzip('example.json.gz')
The code sample assumes that you have a file named example.json.gz in the same
directory as your Python script.
You can download a sample .gz file from
wiki.mozilla.org.
Make sure to rename the file to example.json.gz once you download it.
After running the python main.py command, the following example.json file is
produced.
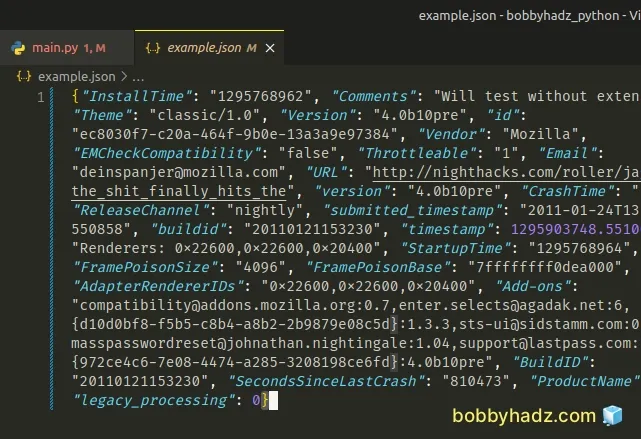
I've also written an article on how to create a Zip archive of a Directory in Python.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to save user input to a File in Python
- How to check if a File is Empty in Python
- Count number of unique Words in a String or File in Python
- Create a file name using Variables in Python
- How to get the File path of a Class in Python
- Taking a file path from user input in Python
- NameError: name '__file__ is not defined in Python [Fixed]
- csv.Error: line contains NULL byte Python error [Solved]
- How to update a JSON file in Python [3 Ways]
- OSError: [Errno 8] Exec format error in Python [Solved]
- OSError: [WinError 193] %1 is not a valid Win32 application
- Python: Get the Type, File and Line Number of Exception
- Python: Check if a File path is symlink (symbolic link)

