Python: Check if a File path is symlink (symbolic link)
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
- Python: Check if a File path is symlink (symbolic link)
- Python: Check if a File path is symlink (symbolic link) using os.path.islink()
# Python: Check if a File path is symlink (symbolic link)
To check if a file path is a symlink (symbolic link) in Python:
- Import the
Pathclass from thepathlibmodule. - Instantiate the class to create a
PurePathobject. - Use the
path.is_symlink()method to check if the file path is a symbolic link.
from pathlib import Path path = Path(r'/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/src') print(path.is_symlink()) # 👉️ True if path.is_symlink(): print('The given path points to a symbolic link') else: print('The path does NOT point to a symbolic link')
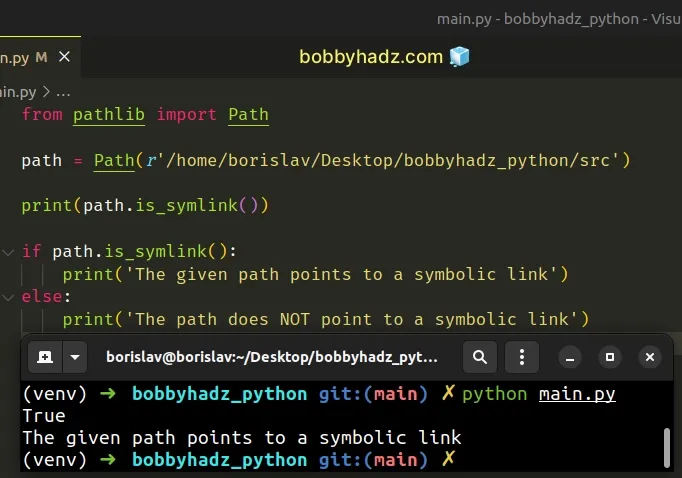
The pathlib.Path class takes one or more path segments as parameters and creates a PosixPath or a WindowsPath, depending on the operating system.
from pathlib import Path path = Path(r'/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/src') print(path.is_symlink()) # 👉️ True
Once you instantiate the Path object, you can use Path-specific methods, such
as
Path.is_symlink.
The Path.is_symlink() method returns True if the path points to a symbolic
link and False otherwise.
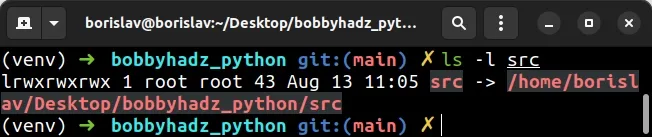
False if the path doesn't exist.On Linux, I can use the ls -l command to check that the path exists and is a
symbolic link.
ls -l /path/to/file
The is_symlink() method returns True as long as the specified object is a
symlink, even if the target of the link does not exist.
As previously noted, if the path doesn't exist or is not a symbolic link,
False is returned.
from pathlib import Path # 👇️ False path = Path(r'/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/another') print(path.is_symlink()) if path.is_symlink(): print('The given path points to a symbolic link') else: # 👇️ This runs print('The path does NOT point to a symbolic link')
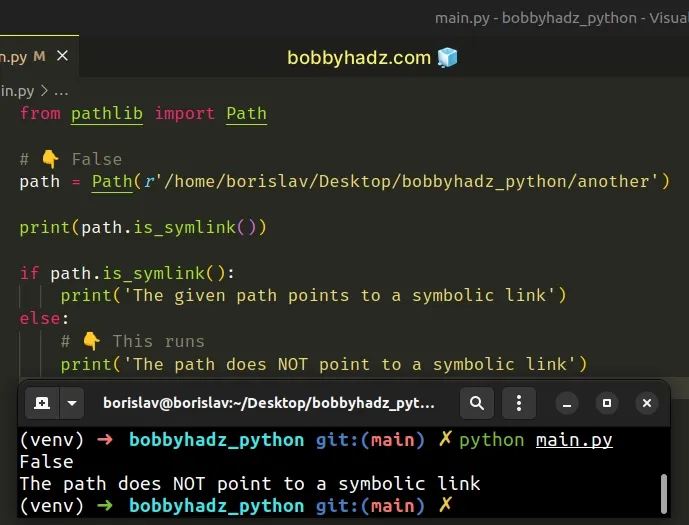
Note that you have to be running at least Python v3.4 to be able to use the pathlib module.
# Python: Check if a File path is symlink (symbolic link) using os.path.islink()
You can also use the os.path.islink() method to check if a file path is a symlink (symbolic link).
import os.path a_path = r'/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/src' print(os.path.islink(a_path)) if os.path.islink(a_path): print('The given path points to a symbolic link') else: # 👇️ This runs print('The path does NOT point to a symbolic link')
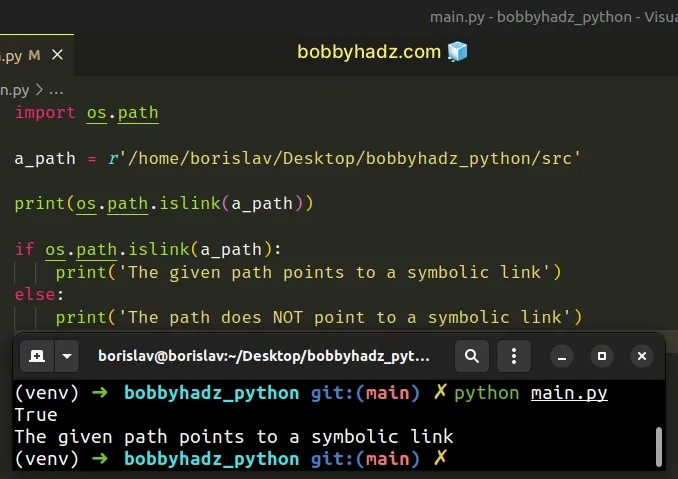
The os.path.islink() method takes a path as a parameter and returns True if
the supplied path refers to an existing directory entry that is a symbolic link.
If symbolic links are not supported by the Python runtime, the method returns
False.
os.path.islink().For example, ./my-directory/ might return a False even if the path is a
symbolic link.
Instead, use a path of ./my-directory.
path.is_symlink() method (from the previous subheading) because the Pathlib module is more operating system agnostic.The os.path.islink() method sometimes causes issues when checking for symbolic
links on Windows.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

