How to check if a File is Empty in Python
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if a file is empty in Python
- Check if a file is empty using os.path.getsize()
- Check if a file is empty using pathlib.path()
# Check if a file is empty in Python
To check if a file is empty:
- Use the
os.stat()method to get the status of the file. - Use the
st_sizeattribute to get the size of the file in bytes. - If the size of the file is
0bytes, then the file is empty.
import os # ✅ with relative path if os.stat('example.txt').st_size == 0: print('The file is empty') else: print('The file is not empty') # --------------------------------------------- # ✅ with absolute path if os.stat( '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/example.txt' ).st_size == 0: print('The file is empty') else: print('The file is not empty')
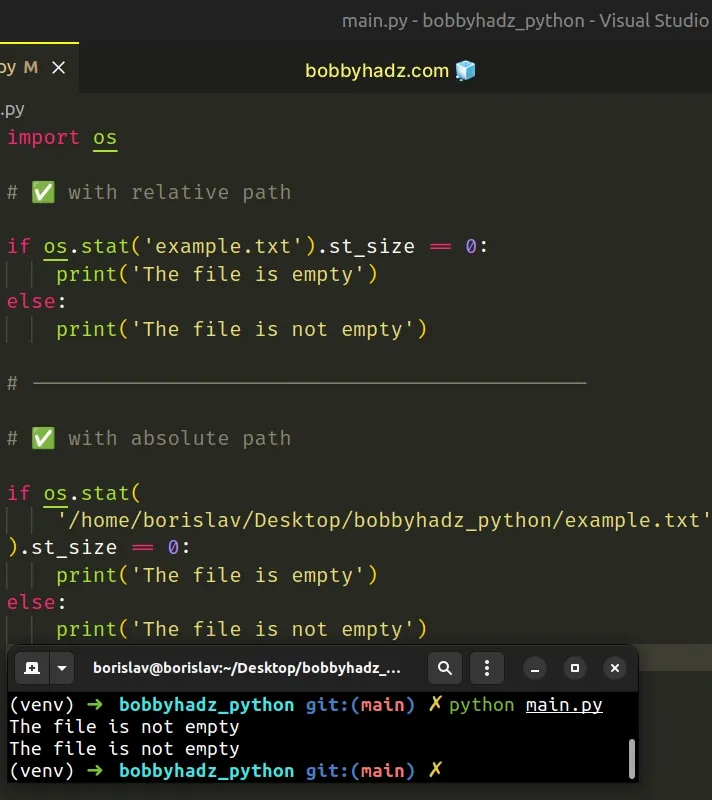
We used the os.stat() method to get the status of a file.
The method can be passed a relative path or an absolute path to the file.
The os.stat() method
returns a stat_result object representing the status of the given file.
The st_size attribute of the object returns the size of the file in bytes.
import os if os.stat('example.txt').st_size == 0: print('The file is empty') else: print('The file is not empty')
0 bytes, then the file is empty.# Checking if a file is NOT empty
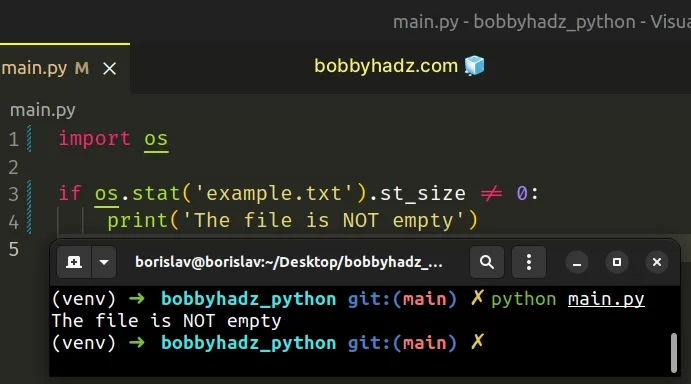
You can use the not equals != operator if you need to check if the file is not
empty.
import os if os.stat('example.txt').st_size != 0: print('The file is NOT empty')
The method will raise a FileNotFoundError exception if the specified file
doesn't exist.
# Handling a case where the file doesn't exist
You can use a try/except statement if you need to handle the error.
import os try: if os.stat('not-found.txt').st_size == 0: print('The file is empty') except FileNotFoundError: # 👇️ this runs print('The specified file does NOT exist')
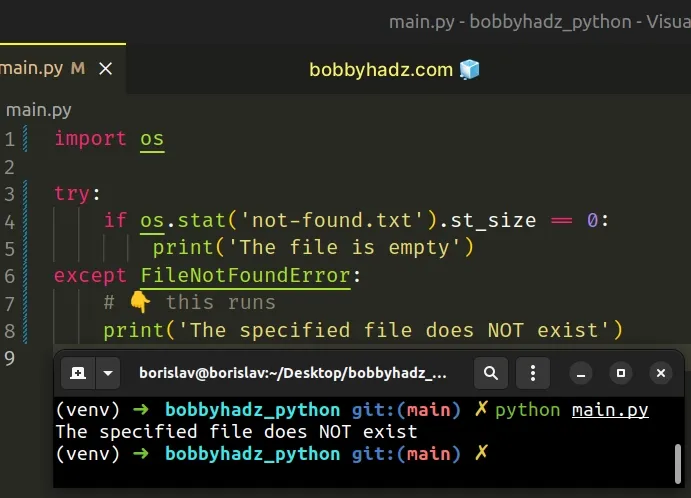
The specified file doesn't exist, so a FileNotFoundError exception is raised
and is then handled by the except block.
# Check if a file is empty using os.path.getsize()
Alternatively, you can use the os.path.getsize() method.
If the os.path.getsize() method returns 0, then the file has a size of 0
bytes and is empty.
import os # 👇️ with relative path if os.path.getsize('example.txt') == 0: print('The file is empty') else: print('The file is NOT empty') # --------------------------------------------- # 👇️ with absolute path if os.path.getsize( '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/example.txt' ) == 0: print('The file is empty') else: print('The file is NOT empty')
The os.path.getsize() method takes a path and returns the size of the path in bytes.
If the file has a size of 0 bytes, then it's empty.
# Handling a case where the specified file doesn't exist
The method raises an OSError exception if the specified file doesn't exist or
is inaccessible.
Use a try/except statement if you need to handle the error.
import os try: if os.path.getsize('not-found.txt') == 0: print('The file is empty') except OSError: # 👇️ this runs print('The specified file does NOT exist')
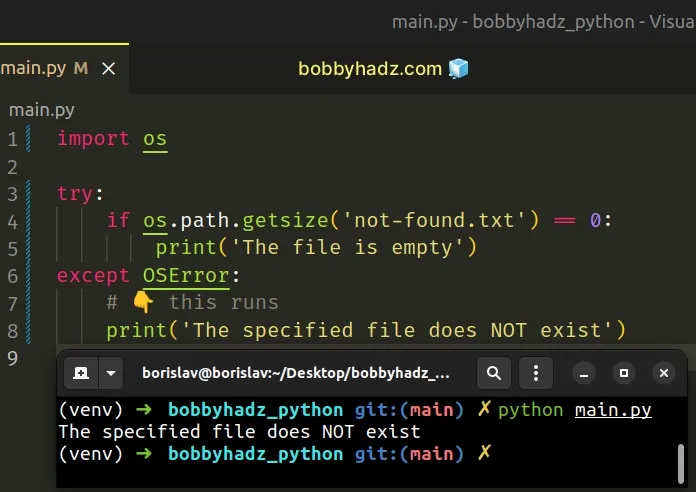
The given path doesn't exist, so an OSError exception is raised and is then
handled by the except block.
Alternatively, you can check if the file exists using the os.path.exists()
method.
import os my_path = '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/example.txt' if os.path.exists(my_path) and os.path.getsize(my_path) == 0: print('The file is empty') else: print('The file does NOT exist or is not empty')
os.path.exists() method returns True if the provided path exists and False otherwise.Alternatively, you can use the pathlib.Path class.
# Check if a file is empty using pathlib.path()
This is a four-step process:
- Instantiate the
pathlib.Path()class to create a Path object. - Use the
stat()method to get astat_resultobject. - Use the
st_sizeattribute to get the file's size. - If the file's size is
0bytes, then it's empty.
import pathlib my_path = pathlib.Path( '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/example.txt' ) if my_path.stat().st_size == 0: print('The file is empty') else: print('The file is NOT empty')
The pathlib.Path
class is used to create a PosixPath or a WindowsPath object depending on
your operating system.
The
Path.stat()
method returns a stat_result object just like the one from the os.stat()
method.
The object has a st_size attribute that returns the size of the file in bytes.
# Handling a case where the file doesn't exist
If the specified path doesn't exist, a FileNotFoundError exception is raised.
You can use a try/except block if you need to handle the error.
import pathlib my_path = pathlib.Path( '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/example.txt' ) try: if my_path.stat().st_size == 0: print('The file is empty') else: print('The file is NOT empty') except FileNotFoundError: print('The file does NOT exist')
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. They all get the file's size.
If the file has a size of 0 bytes, then it's empty, otherwise, it isn't empty.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Count number of unique Words in a String or File in Python
- Create a file name using Variables in Python
- How to get the File path of a Class in Python
- Taking a file path from user input in Python
- NameError: name '__file__ is not defined in Python [Fixed]
- How to unzip a .gz file using Python [5 simple Ways]
- OSError [Errno 22] invalid argument in Python [Solved]
- OSError: [Errno 8] Exec format error in Python [Solved]
- How to open an HTML file in the Browser using Python
- Python: Get the Type, File and Line Number of Exception
- Python: Check if a File path is symlink (symbolic link)
- Remove __pycache__ folders and .pyc files in Python Project
- SyntaxError: future feature annotations is not defined
- How to Copy Files and Rename them in Python [4 Ways]
- Run multiple Python files concurrently / one after the other
- Python: How to ignore #comment lines in a File

