OSError: [WinError 193] %1 is not a valid Win32 application
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·2 min
# OSError: [WinError 193] %1 is not a valid Win32 application
The Python "OSError: [WinError 193] %1 is not a valid Win32 application" occurs when you try to run a script but forget to specify the executable file.
To solve the error, specify the executable file, e.g. python.exe.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
Suppose we have the following example.py file.
print('bobbyhadz.com') for i in range(3): print(f'bobbyhadz.com {i}')
And we want to run the Python script from another script named main.py.
import subprocess # ⛔️ OSError: [WinError 193] %1 is not a valid Win32 application subprocess.call(['example.py'])
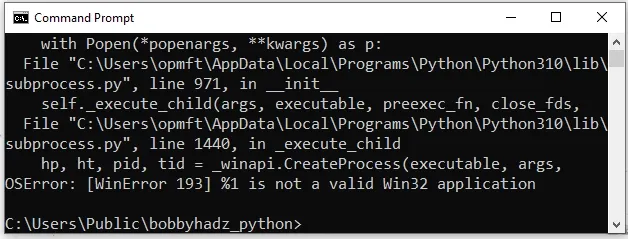
The error is raised because we forgot to specify the executable as the first list item.
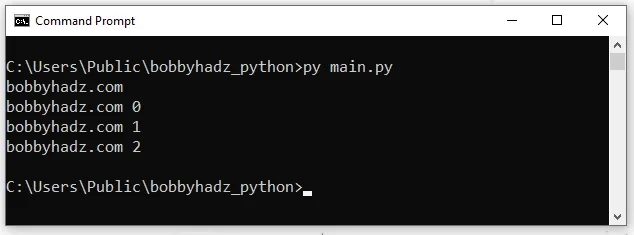
If you're trying to run a Python script from another Python script, you should
use python.exe as the executable.
import subprocess # ✅ Works subprocess.call(['python.exe', 'example.py'])
On Windows, you might also have to set py.exe as the executable.
import subprocess # ✅ Works subprocess.call(['py.exe', 'example.py'])
py is a Windows alias for python.
The examples use the subprocess.call() method, however, the same can be achieved using subprocess.Popen().
import subprocess # ✅ Works subprocess.Popen(['python.exe', 'example.py'])
If you don't have python in your PATH environment variable, try using
sys.executable instead.
import subprocess # ✅ Works subprocess.Popen([sys.executable, 'example.py'])
The sys.executable attribute is a string that returns the absolute path to the executable binary of the Python interpreter.
# Setting shell to True to solve the error
You can also try to set the shell argument to True in the call to
subprocess.call() to solve the error.
import subprocess subprocess.call(['example.py'], shell=True)
If the shell argument is set to True, the specified command is executed
through the shell.
True, subprocess spawns an intermediate shell process and runs the command.By default, the shell argument is set to False, so the command is run
directly.
# Running a shell script from a Python script on Windows
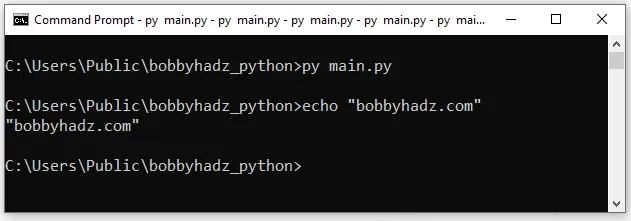
If you are trying to run a .cmd file from a Python script on Windows, use the
following code sample.
import subprocess subprocess.call(['example.cmd'], shell=True)
The code sample assumes that you have an example.cmd file located in the same
directory as your main.py file.
echo bobbyhadz.com
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to get the File path of a Class in Python
- Taking a file path from user input in Python
- NameError: name '__file__ is not defined in Python [Fixed]
- csv.Error: line contains NULL byte Python error [Solved]
- How to update a JSON file in Python [3 Ways]
- OSError: [Errno 8] Exec format error in Python [Solved]
- ValueError: invalid mode: 'rU' while trying to load binding.gyp

