Python OSError: [Errno 98] Address already in use [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Python OSError: [Errno 98] Address already in use
- Use the
SO_REUSEADDRflag before binding the socket - Using a different host and port
- Set the allow_reuse_address attribute to True
- Setting debug to False in a Flask application
# Python OSError: [Errno 98] Address already in use [Solved]
The article addresses the following 2 related errors:
- OSError: [Errno 98] Address already in use
- socket.error: [Errno 98] Address already in use
The Python error "OSError: [Errno 98] Address already in use" occurs when you have another process running on the specified port.
You can resolve the error by using the SO_REUSEADDR attribute or by
identifying and stopping the process before you start your server.
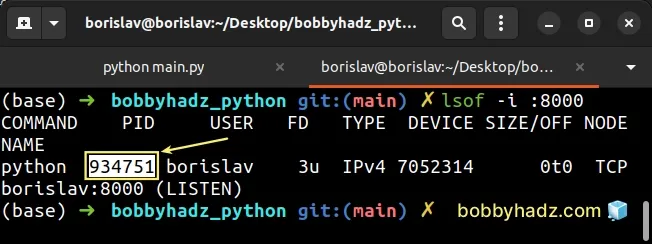
If you are on macOS or Linux, you can use the lsof command to get the process
ID of the process that is running on the specified port.
lsof -i :8000
Make sure to replace 8000 with your specific port number.
If you get a permissions error, rerun the command with sudo.
sudo lsof -i :8000
The PID column contains the ID of the process that is running on the specified
port.
You can stop the process by issuing the kill command.
sudo kill -9 <YOUR_PID>
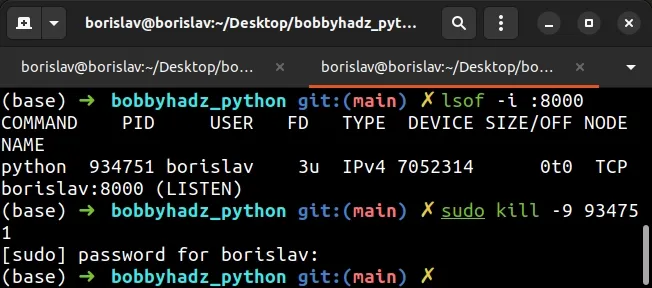
Make sure to replace the <YOUR_PID> placeholder with the process ID you got
from issuing the lsof command.
If you use bash or zsh, you can also try running the following command to
stop the python process.
# for bash and zsh kill -9 $(ps -A | grep python | awk '{print $1}')
# Use the SO_REUSEADDR flag before binding the socket
You can also use the socket.SO_REUSEADDR flag before binding the socket to
solve the error.
import socket sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
Make sure to call the sock.setsockopt() method with the socket.SO_REUSEADDR
flag before binding the socket.
import socket def start_server(): host = socket.gethostname() port = 8000 sock = socket.socket() # 👇️ Call the method before calling bind() sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) sock.bind((host, port)) sock.listen(2) conn, _address = sock.accept() while True: data = conn.recv(1024).decode() if not data: break print("user: " + str(data)) data = input(' > ') conn.send(data.encode()) conn.close() if __name__ == '__main__': start_server()
The socket.setsockopt() method sets the value of the given socket option.
The first argument we passed to the method is the message level and the second
is the socket.SO_REUSEADDR attribute.
Starting your Python socket server several times with a small delay causes the "OSError: [Errno 98] Address already in use" error.
The cause of the error is that the previous execution has left the socket in a
TIME_WAIT state, so it cannot be immediately reused.
You can prevent this behavior by setting the socket.SO_REUSEADDR flag.
sock = socket.socket() # 👇️ Call the method before calling bind() sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) sock.bind((host, port))
When the socket.SO_REUSEADDR flag is set, the Python kernel reuses local
sockets in TIME_WAIT state without waiting for their timeout to expire.
socket.SO_REUSEADDR option to reuse the sockets which were previously bound to the same address and are still in a TIME_WAIT state.It is very important to call the setsockopt() method before you call bind(),
otherwise, the method call won't have an effect.
# Using a different host and port
If the error persists, try to specify a different host and port when calling the
bind() method.
host = socket.gethostname() port = 5000 sock = socket.socket() sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) sock.bind((host, port))
Assuming the specified port is available, you should be able to connect.
# Set the allow_reuse_address attribute to True
If you get the error when using the
SimpleHTTPRequestHandler,
set the allow_reuse_address attribute to True.
import http.server import socketserver PORT = 8000 Handler = http.server.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler with socketserver.TCPServer(("", PORT), Handler) as httpd: httpd.allow_reuse_address = True print("serving at port", PORT) httpd.serve_forever()
This will enable you to reuse the address, so starting and stopping your server should not cause an "Address already in use" error.
When the allow_reuse_address attribute is set to true, the
socket.SO_REUSEADDR flag is set under the hood.
# This code runs when `allow_reuse_address` is `True` if self.allow_reuse_address: self.socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# Setting debug to False in a Flask application
If you got the error in a Flask application, try to set the debug argument to
False when calling app.run().
app.run(debug=False)
I've written a detailed guide on how to run Flask in production mode.
You can also try to set the use_reloader argument to False if you don't need
to change your code and auto-reload the server.
app.run(debug=True, use_reloader=False)
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to change the Port and Host in a Flask application
- OSError [Errno 22] invalid argument in Python [Solved]
- FileExistsError: [Errno 17] File exists in Python [Solved]
- Using try without except (ignoring exceptions) in Python
- ValueError: invalid mode: 'rU' while trying to load binding.gyp
- OMP: Error #15 Initializing libiomp5md.dll, but found mk2iomp5md.dll already initialized

