How to get the Value of an Input field in React
Last updated: Apr 7, 2024
Reading time·9 min

# Table of Contents
- Get the value of an Input field in React
- Get the value of an Input field using a Ref in React
- Get Input value when Enter key is pressed in React
- Get input values on Form submit in React
- Get input values on Form submit using a
ref - Get input values on Form submit using
event.target
# Get the value of an Input field in React
To get the value of an input field in React:
- Declare a state variable that tracks the value of the input field.
- Add an
onChangeprop to the input field. - Use
event.target.valueto get the input field's value and update the state variable.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const [message, setMessage] = useState(''); const handleChange = event => { setMessage(event.target.value); console.log('value is:', event.target.value); }; return ( <div> <input type="text" id="message" name="message" onChange={handleChange} value={message} /> <h2>Message: {message}</h2> </div> ); }; export default App;
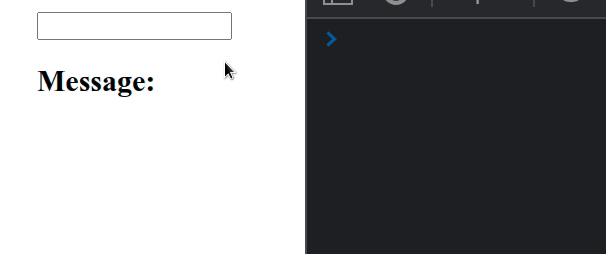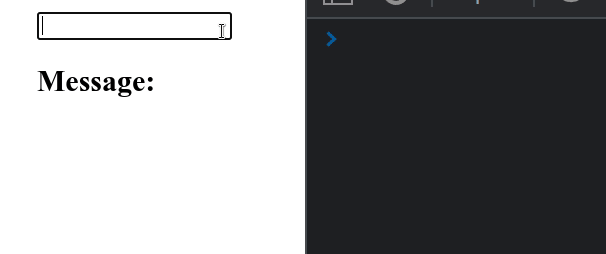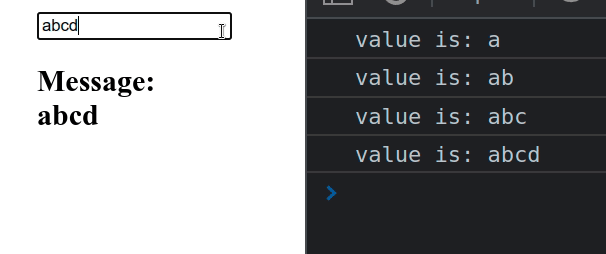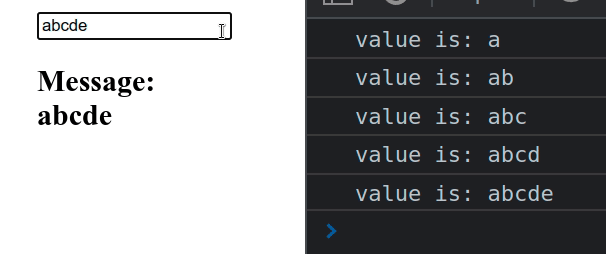
We used the useState hook to track the value of the input field.
onChange prop on the field, so every time its value changes, the handleChange function is invoked.We can access the value of the input element as event.target.value in the
handleChange function.
target property on the event object refers to the input element.You can use the message state variable to access the value of the input field
anywhere outside the handleChange function.
Alternatively, you can use an uncontrolled input field with a ref.
# Get the value of an Input field using a Ref in React
To get the value of an input field using a ref:
- Initialize a ref using the
useRefhook. - Set the
refprop on the input field. - Access the value of the input field as
ref.current.value.
import {useRef} from 'react'; const App = () => { const inputRef = useRef(null); function handleClick() { console.log(inputRef.current.value); } return ( <div> <input ref={inputRef} type="text" id="message" name="message" /> <button onClick={handleClick}>Log message</button> </div> ); }; export default App;
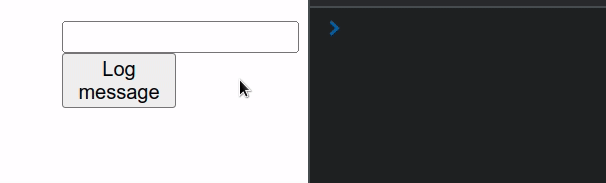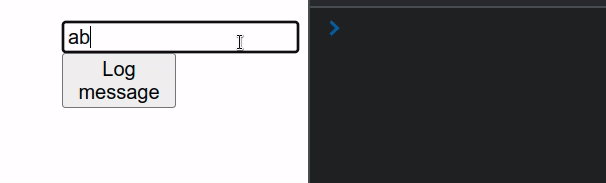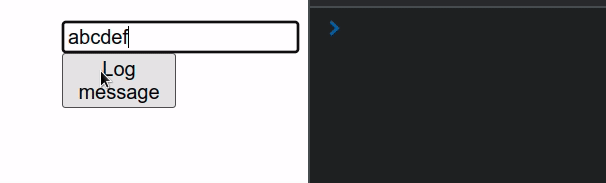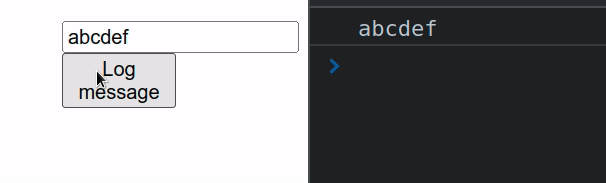
This example uses an uncontrolled input. Notice that the input field doesn't
have an onChange or value props set.
defaultValue prop. However, this is not necessary and you can omit the prop if you don't want to set an initial value.When using uncontrolled input fields, we access the input using a ref.
The useRef() hook can be passed an initial value as an argument. The hook
returns a mutable ref object whose .current property is initialized to the
passed argument.
current property on the ref object to get access to the input element on which we set the ref prop.When we pass a ref prop to an element, e.g. <input ref={myRef} />, React sets
the .current property of the ref object to the corresponding DOM node.
useRef hook creates a plain JavaScript object but gives you the same ref object on every render. In other words, it's a memoized object value with a .current property.It should be noted that when you change the value of the current property of
the ref, no re-renders are caused.
Every time the user clicks on the button in the example, the value of the uncontrolled input gets logged.
You shouldn't set the value prop on an uncontrolled input (an input field that
doesn't have an onChange handler) because that would make the input field
immutable and you wouldn't be able to type in it.
If you need to set the input field's value using a ref, check out the
following article.
# Get Input value when Enter key is pressed in React
To get an input's value when the Enter key is pressed in React:
- Set the
onKeyDownprop on the input field. - When a user presses a key, check if the key is
Enter. - Access the input field's value from the state variable.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const [message, setMessage] = useState(''); const handleKeyDown = event => { console.log(event.key); if (event.key === 'Enter') { event.preventDefault(); // 👇️ Access input value from state console.log(message); // 👇️ Access input value from event object // console.log(event.target.value) console.log('User pressed Enter ✅'); } }; return ( <div> <input type="text" id="message" name="message" value={message} onChange={event => setMessage(event.target.value)} onKeyDown={handleKeyDown} /> </div> ); }; export default App;
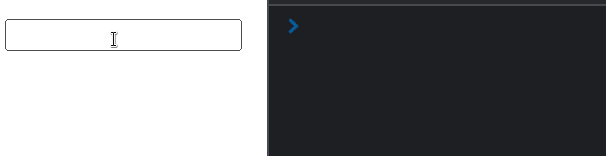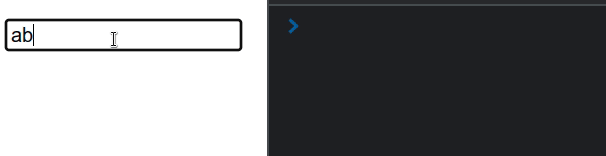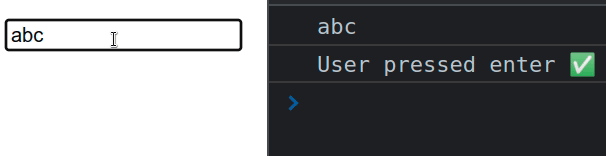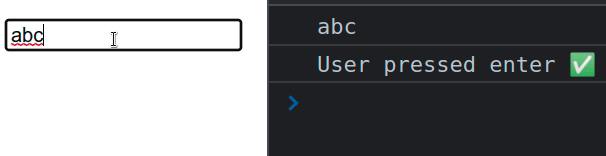
We used the useState hook to store the value of the input field.
onKeyDown prop is added to an input field, we only listen for keys the user pressed when the input field is focused.Every time the user presses a key, the handleKeyDown function runs. We use the
key
property on the event object to check if the user pressed Enter.
The condition if (event.key === 'Enter') {} covers all operating systems -
Windows, Mac, Linux, Android, etc.
If you don't want to track the state of the input field, you can get its value
on the target property of the event object.
const App = () => { const handleKeyDown = event => { if (event.key === 'Enter') { event.preventDefault(); console.log('User pressed Enter ✅'); // 👇️ Access input value console.log(event.target.value); } }; return ( <div> <input type="text" id="message" name="message" onKeyDown={handleKeyDown} /> </div> ); }; export default App;
Instead of storing the value of the input field, we get it using the event
object.
The target property on the event refers to the input element.
You can view the possible keys the user might press by visiting this MDN page.
This approach is useful when we need to run some logic when the user has
finished typing and don't want to use a form with an onSubmit event handler.
If you need to handle the onKeyDown event on a Div element, click on the link and follow the instructions.
If you need to detect when the Enter key is pressed, click on the
following article.
I've also written an article on how to submit a form using the Enter key.
# Get input values on Form submit in React
To get input values on form submit in React:
- Store the values of the input fields in state variables.
- Set the
onSubmitprop on the form element. - Access the values of the input fields in your
handleSubmitfunction.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const [firstName, setFirstName] = useState(''); const [lastName, setLastName] = useState(''); const [message, setMessage] = useState(''); const handleSubmit = event => { console.log('handleSubmit ran'); event.preventDefault(); // 👈️ prevent page refresh // 👇️ Access input values here console.log('firstName 👉️', firstName); console.log('lastName 👉️', lastName); setMessage(`Hey, ${firstName} ${lastName}`); // 👇️ Clear all input values in the form setFirstName(''); setLastName(''); }; return ( <div> <form onSubmit={handleSubmit}> <input id="first_name" name="first_name" type="text" placeholder="First Name" onChange={event => setFirstName(event.target.value)} value={firstName} /> <br /> <input id="last_name" name="last_name" type="text" placeholder="Last Name" value={lastName} onChange={event => setLastName(event.target.value)} /> <br /> <button type="submit">Submit form</button> <h2>{message}</h2> </form> </div> ); }; export default App;
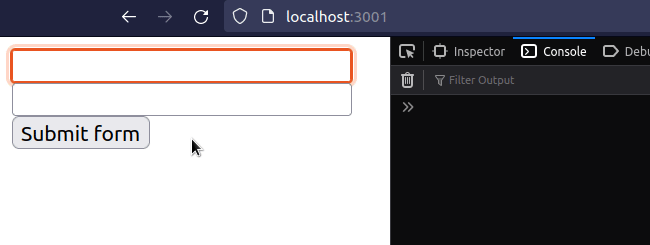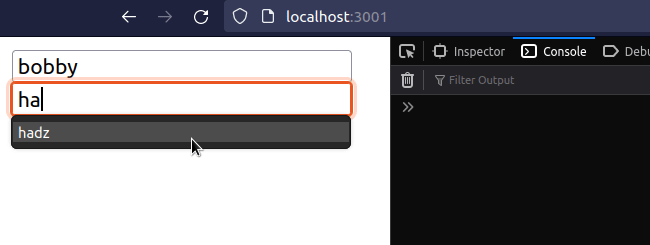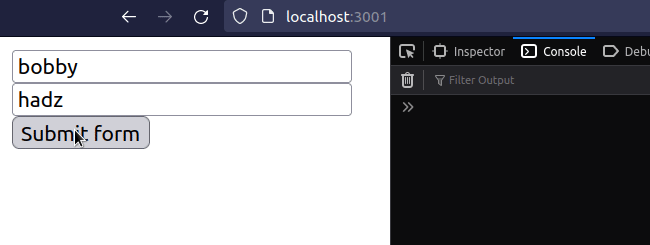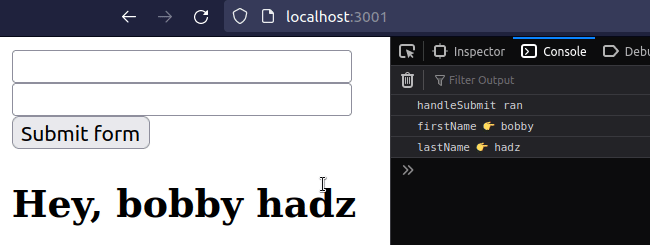
We used the useState hook to track the values of the input fields.
const [firstName, setFirstName] = useState(''); const [lastName, setLastName] = useState('');
onChange prop on the fields, so when their values change, we update the corresponding state variables.<input id="first_name" name="first_name" type="text" onChange={event => setFirstName(event.target.value)} value={firstName} />
The button element in the form has a type of submit, so every time it is
clicked, the submit event is fired on the form.
<button type="submit">Submit form</button>
We used the event.preventDefault() method in the handleSubmit function to
prevent the page from refreshing
when the form is submitted.
const handleSubmit = event => { console.log('handleSubmit ran'); event.preventDefault(); // 👈️ Prevent page refresh // 👇️ Access input values here console.log('firstName 👉️', firstName); console.log('lastName 👉️', lastName); setMessage(`Hey, ${firstName} ${lastName}`); // 👇️ Clear all input values in the form setFirstName(''); setLastName(''); };
To get the input values on form submit, we simply access the state variables.
You can set the state variables to empty strings if you want to clear the values of the fields after the form has been submitted.
Alternatively, you can use uncontrolled input fields.
# Get input values on Form submit using a ref
This is a three-step process:
- Set the
refprop on each input field - Set the
onSubmitprop on the form element. - Access the input values on the ref objects, e.g.
ref.current.value.
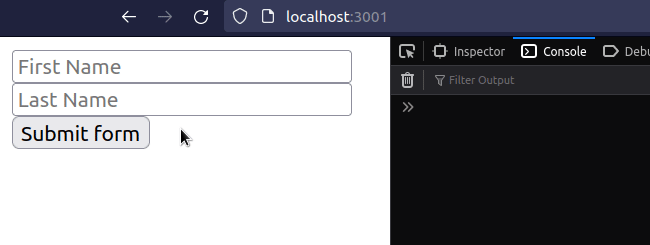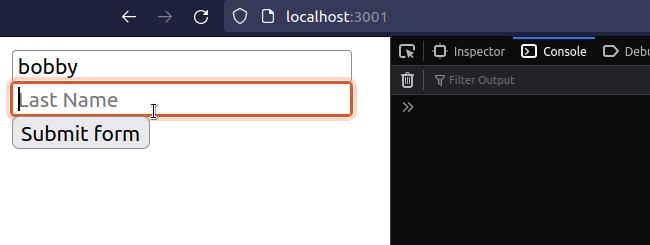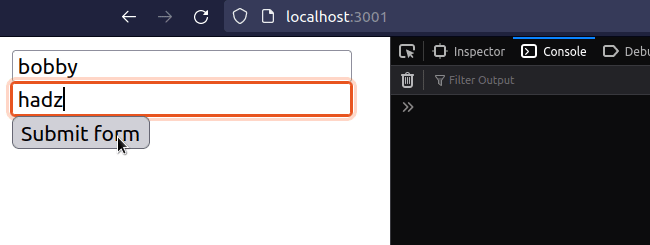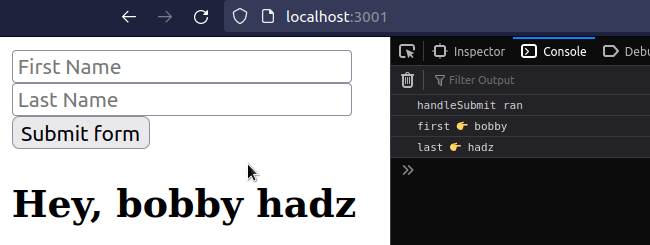
import {useRef, useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const firstRef = useRef(null); const lastRef = useRef(null); const [message, setMessage] = useState(''); const handleSubmit = event => { console.log('handleSubmit ran'); event.preventDefault(); // 👈️ Prevent page refresh // 👇️ Access input values here console.log('first 👉️', firstRef.current.value); console.log('last 👉️', lastRef.current.value); setMessage( `Hey, ${firstRef.current.value} ${lastRef.current.value}`, ); // 👇️ Clear all input values in the form event.target.reset(); }; return ( <div> <form onSubmit={handleSubmit}> <input ref={firstRef} id="first_name" name="first_name" type="text" placeholder="First Name" /> <br /> <input ref={lastRef} id="last_name" name="last_name" type="text" placeholder="Last Name" /> <br /> <button type="submit">Submit form</button> <h2>{message}</h2> </form> </div> ); }; export default App;
The example above uses uncontrolled input fields. Notice that the input fields
do not have an onChange prop or value set.
<input ref={firstRef} id="first_name" name="first_name" type="text" placeholder="First Name" />
defaultValue prop. However, this is not necessary and you can omit the prop if you don't want to set an initial value.When using uncontrolled input fields, we access the input using a ref.
The useRef() hook can be passed an initial value as an argument. The hook
returns a mutable ref object whose .current property is initialized to the
passed argument.
current property on the ref object to get access to the input element on which we set the ref prop.const handleSubmit = event => { console.log('handleSubmit ran'); event.preventDefault(); // 👈️ Prevent page refresh // 👇️ Access input values here console.log('first 👉️', firstRef.current.value); console.log('last 👉️', lastRef.current.value); setMessage( `Hey, ${firstRef.current.value} ${lastRef.current.value}`, ); // 👇️ Clear all input values in the form event.target.reset(); };
When we pass a ref prop to an element, e.g. <input ref={myRef} />, React sets
the .current property of the ref object to the corresponding DOM node.
useRef hook creates a plain JavaScript object but gives you the same ref object on every render. In other words, it's pretty much a memoized object value with a .current property.It should be noted that when you change the value of the current property of
the ref, no re-renders are caused.
Every time the user submits the form in the example, the values of the uncontrolled inputs get logged.
You shouldn't set the value prop on an uncontrolled input (an input field that
doesn't have an onChange handler) because that would make the input field
immutable and you wouldn't be able to type in it.
You can use the reset() method if you want to
clear the values of the uncontrolled inputs
after the form has been submitted.
The reset() method restores a form element's default values.
event.target.reset();
Regardless of how many uncontrolled input fields your form has, a single call to
the reset() method clears all of them.
# Get input values on Form submit using event.target
An alternative way to get the values of the input fields when the form is
submitted, is to access the form elements using their name prop.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const [message, setMessage] = useState(''); const handleSubmit = event => { console.log('handleSubmit ran'); event.preventDefault(); // 👇️ Access input values using name prop const firstName = event.target.first_name.value; const lastName = event.target.last_name.value; console.log('first 👉️', firstName); console.log('second 👉️', lastName); setMessage(`Hey, ${firstName} ${lastName}`); // 👇️ Clear all input values in the form event.target.reset(); }; return ( <div> <form onSubmit={handleSubmit}> <input id="first_name" name="first_name" type="text" /> <br /> <input id="last_name" name="last_name" type="text" /> <br /> <button type="submit">Submit form</button> <h2>{message}</h2> </form> </div> ); }; export default App;
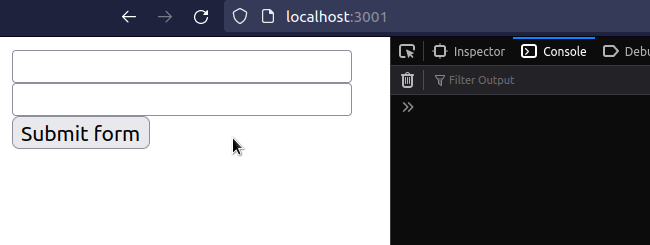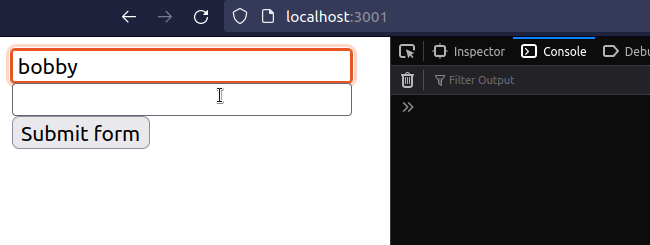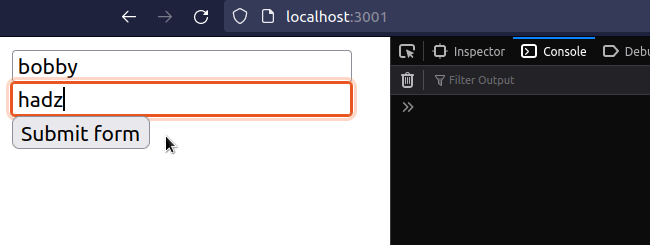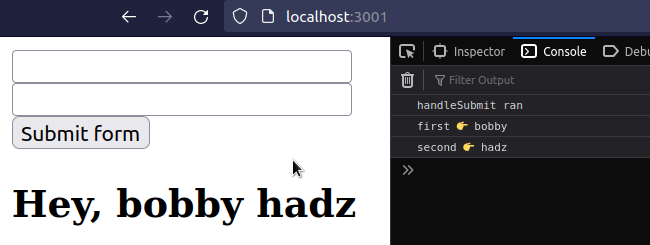
We used the name prop to access the values of the input fields when the form
is submitted.
The target property on the event object refers to the form element.
The most commonly used approach is to store input values in state variables. The ability to access state variables from anywhere allows for highly customizable forms.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to turn off autocomplete on an Input in React
- Validate an Email in an Input field in React
- How to Check if an Input is Empty in React
- How to clear an Input field's value in React.js
- Get the value of an Input on Button click in React
- Set a character limit on an Input field in React.js
- Restrict an Input field to only Letters in React
- Set a placeholder on an Input field in React
- Create a Numbers only Input field in React.js
- Create numeric input with Min and Max validation in React
- Open a file input box on button click in React
- Setting a default value for an Input element in React
- Set Input value using a Ref in React
- Unable to type in Input field issue in React [Solved]

