Handling onKeyDown event on Div elements in React
Last updated: Apr 7, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
# Handling onKeyDown event on Div elements in React
To handle the onKeyDown event on div elements in React:
- Set the
onKeyDownprop on the div element. - Set the element's tab index to
0, e.g.tabIndex={0}. - Access the pressed key on the event object, e.g.
event.keyin your handler function.
const App = () => { const handleKeyDown = event => { console.log('User pressed: ', event.key); }; return ( <div> <div tabIndex={0} onKeyDown={handleKeyDown}> <h2>hello world</h2> </div> </div> ); }; export default App;
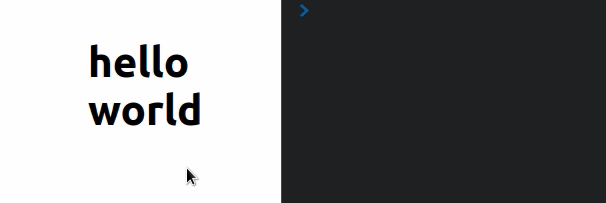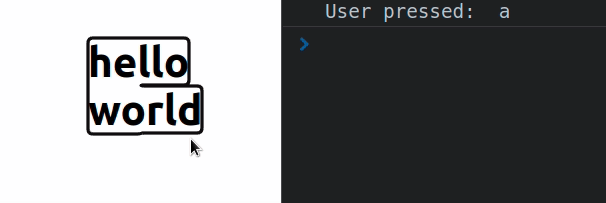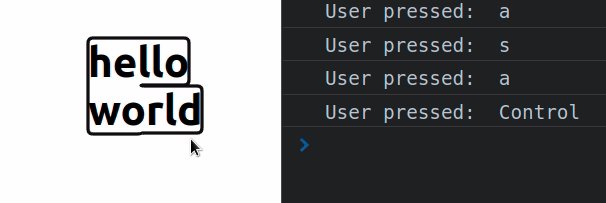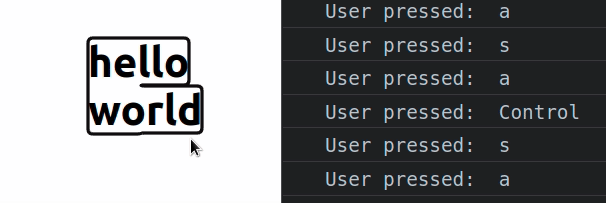
Div elements are not focusable by default, so in order to handle the onKeyDown
event on a div, we have to set the
tabIndex
prop on the element.
tabIndex attribute indicates that its element can be focused and where it participates in sequential keyboard navigation (using the Tab key).When an element's tabIndex is set to 0, the element is focusable in
sequential keyboard navigation, after any positive tabIndex values.
For example, if other elements on the page have a tab index of 1, 2, 3, etc, an
element with a tabIndex of 0 would get focused after the elements with
positive tabIndex.
# Setting tabIndex to -1
You could also set the element's tabIndex to -1, which means that the
element is not reachable via sequential keyboard navigation (using the Tab
key), but can be focused using JavaScript or by clicking on it with the mouse.
const App = () => { const handleKeyDown = event => { console.log('User pressed: ', event.key); }; return ( <div> <div tabIndex={-1} onKeyDown={handleKeyDown}> <h2>hello world</h2> </div> </div> ); }; export default App;
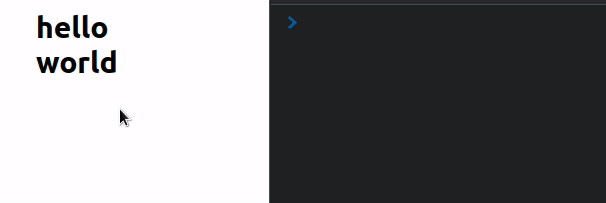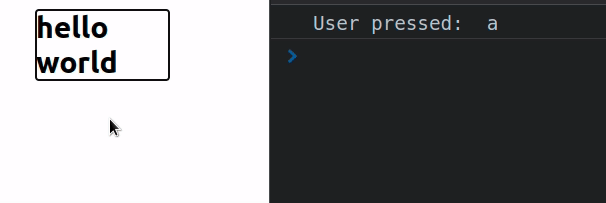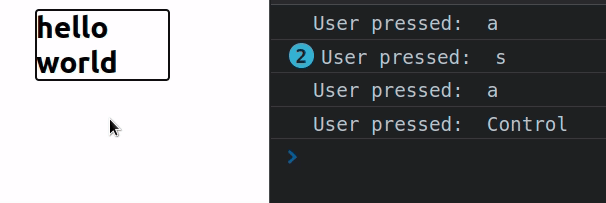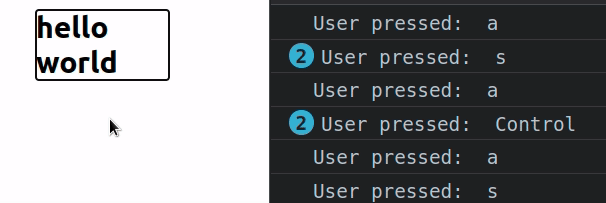
With the div's tabIndex set to -1, it can't be focused using the Tab key
but it can still be focused with a mouse click (or using JavaScript).
The key
property on the KeyboardEvent object returns the value of the key that was
pressed by the user.
keydown event is triggered anytime the user presses a key on their keyboard.You can view the possible keys the user might press by visiting this MDN page.
# Focusing the element immediately after the page loads
If you want to focus the element on which the onKeyDown prop is set
immediately after the page loads, set a ref on the element and call the
focus() method in the useEffect hook.
import {useEffect, useRef} from 'react'; const App = () => { const handleKeyDown = event => { console.log('User pressed: ', event.key); }; const ref = useRef(null); useEffect(() => { ref.current.focus(); }, []); return ( <div> <div ref={ref} tabIndex={-1} onKeyDown={handleKeyDown}> <h2>hello world</h2> </div> </div> ); }; export default App;
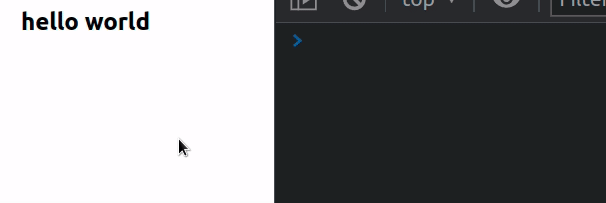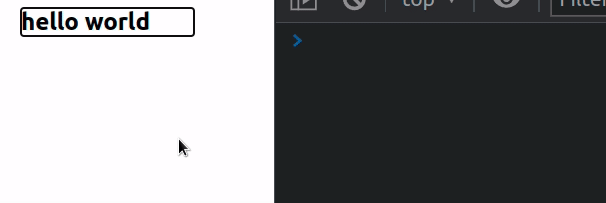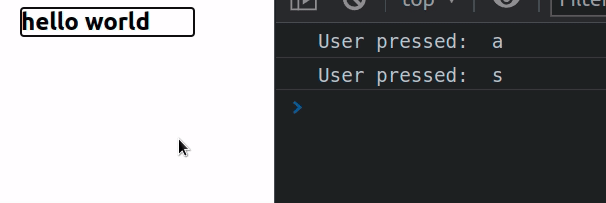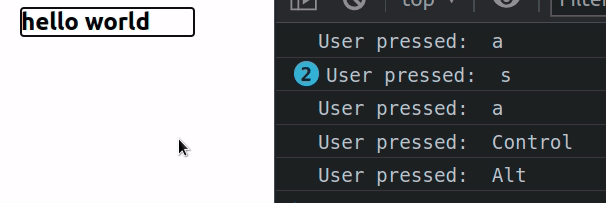
We used the useRef hook to create a ref object that gives us access to the div element.
The useRef() hook can be passed an initial value as an argument. The hook
returns a mutable ref object whose .current property is initialized to the
passed argument.
current property on the ref object to get access to the div element on which we set the ref prop.useEffect(() => { ref.current.focus(); }, []);
When we pass a ref prop to an element, e.g. <div ref={myRef} />, React sets
the .current property of the ref object to the corresponding DOM node.
We used the
focus()
method to focus the div in the useEffect hook.
The current property on the ref gives us access to the div element, so
calling ref.current.focus() sets the focus on the div.
# Handle the onKeyDown event in React
To handle the onKeyDown event:
- Set the
onKeyDownprop on the element. - Use the
keyproperty on theeventobject to get the key the user pressed. - For example,
if (event.key === 'Enter') {}.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const [message, setMessage] = useState(''); const handleKeyDown = event => { console.log(event.key); if (event.key === 'Enter') { console.log('✅ Enter key pressed'); } // 👇️ Access the input's value from the state // console.log(message); // 👇️ Access the input's value from the event object // console.log(event.target.value) }; return ( <div> <input type="text" id="message" name="message" value={message} onKeyDown={handleKeyDown} onChange={event => setMessage(event.target.value)} /> </div> ); }; export default App;
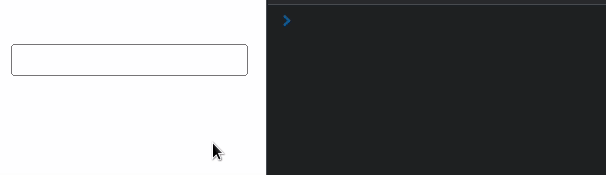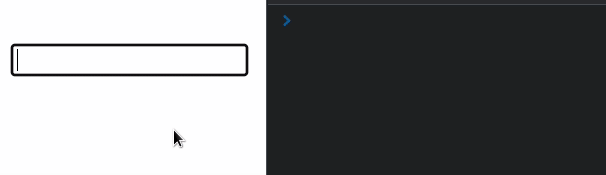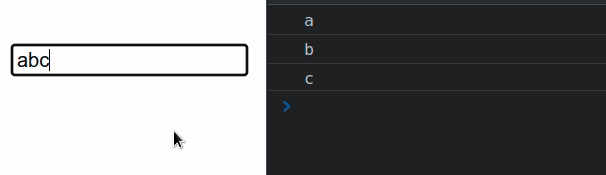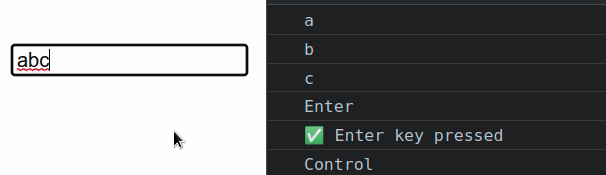
onKeyDown event listener on a div element, scroll down to the next code snippet.We set the onKeyDown prop on the input element, so every time the user
presses a button when the input has focus, the handleKeyDown function is
invoked.
The key
property on the event object returns the value of the key pressed by the user.
Every time the user presses a key, the handleKeyDown function runs and we
check if the user pressed Enter.
The condition if (event.key === 'Enter') {} covers all operating systems -
Windows, Mac, Linux, Android, etc.

