Username and Password inputs with 3 attempts in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Username and password inputs with 3 attempts in Python
- Display asterisks when user inputs their password in Python
- Prompt for username and password in Python
# Username and password inputs with 3 attempts in Python
To take username and password input values with 3 attempts:
- Use a
whileloop to iterate a maximum of 3 times. - Use the
input()function to take values for the username and password from the user. - If the credentials are correct, break out of the loop.
attemps = 0 while attemps < 3: username = input('Enter your username: ') password = input('Enter your password: ') if username == 'user123' and password == 'password123': print('You have successfully logged in.') break else: print('Incorrect credentials. Check if you have Caps lock on and try again.') attemps += 1 continue
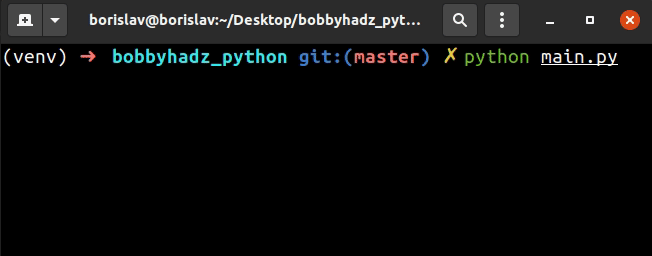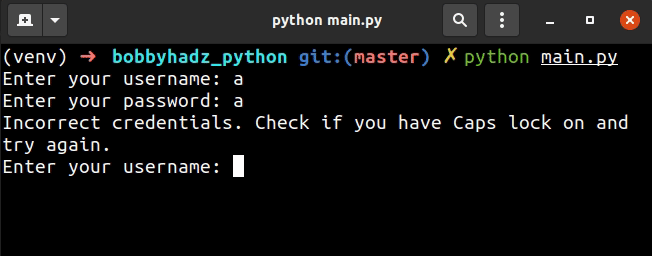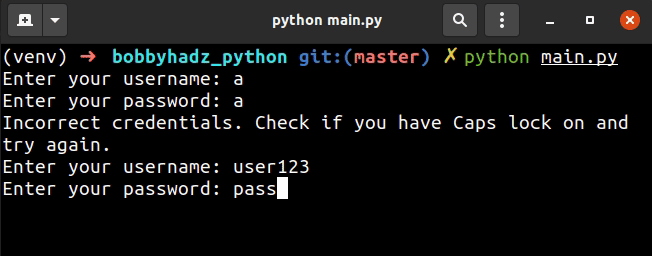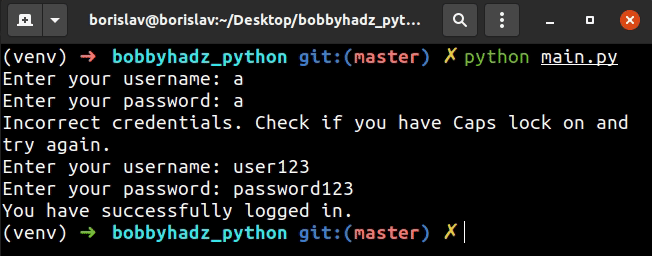
We used a while loop to iterate a maximum of 3 times.
# Hiding the Password while the user types
If you want to hide the password text while the user is typing, use the
getpass() method.
import getpass attemps = 0 while attemps < 3: username = input('Enter your username: ') password = getpass.getpass('Enter your password: ') if username == 'user123' and password == 'password123': print('You have successfully logged in.') break else: print('Incorrect credentials. Check if you have Caps lock on and try again.') attemps += 1 continue
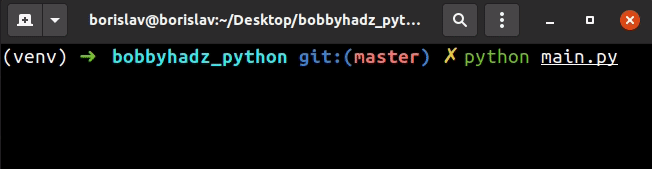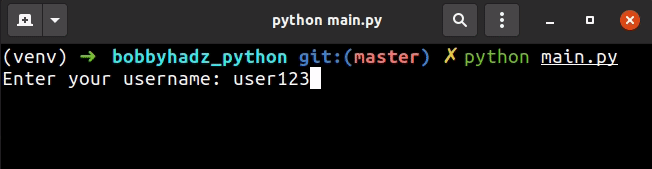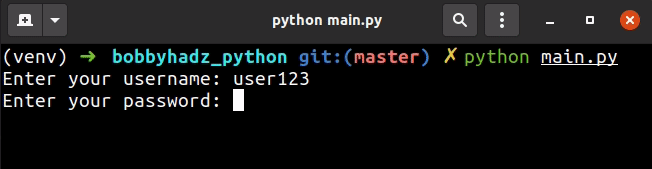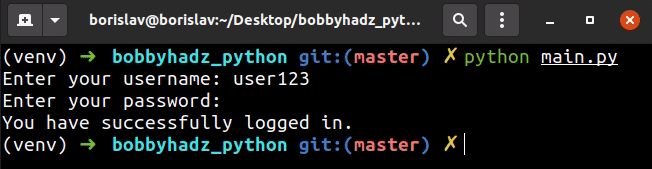
We used the
getpass()
method from the getpass module to prompt the user for a password without
echoing.
The getpass module is available in the standard library, so you don't have to
install anything.
getpass method is usually used to prompt the user for a password or other sensitive information.If both conditions in the if statement evaluate to True, the if block runs
where we break out of the while loop.
The break statement breaks out of the innermost enclosing for or while loop.
If one or both conditions evaluate to False, the else block runs.
else block, we increment the attempts variable by 1 and continue to the next iteration of the while loop.The continue statement continues with the next iteration of the loop.
If the user enters incorrect credentials 3 times, the attempts variable gets
set to 3 and the condition in the while loop is no longer met.
# Display asterisks when user inputs their password in Python
To display asterisks when a user inputs their password:
- Install the
pwinput()module. - Use the
pwinput()method to take input from the user and display asterisks. - The method takes a
maskargument that can be set to an asterisk.
import pwinput import getpass # ✅ Display * (asterisks) when user types their password password = pwinput.pwinput(prompt='Enter your password: ', mask='*') print(password) # ------------------------------------------------ # ✅ Don't display anything when user types their password password = getpass.getpass('Enter your password: ') print(password)
pwinput module by opening your shell in your project's root directory and running the pip install pwinput command.pip install pwinput # 👇️ or with pip3 pip3 install pwinput
Now you can use the pwinput method to show asterisks while the user enters
their password.
import pwinput password = pwinput.pwinput(prompt='Enter your password: ', mask='*') print(password)
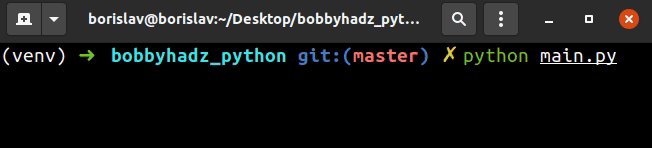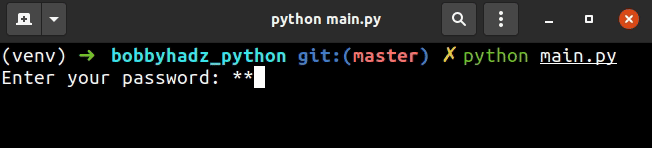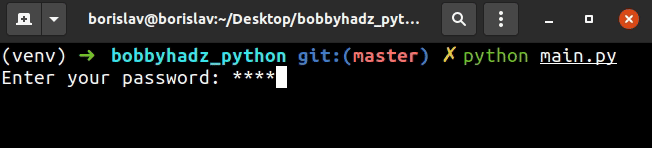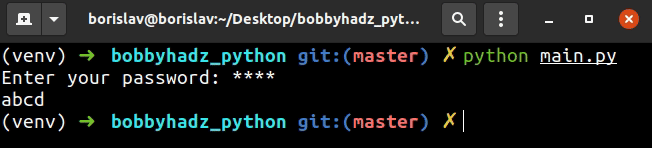
The prompt argument is the message that gets displayed and the mask argument
is what to mask the user input with.
getpass module.import getpass password = getpass.getpass('Enter your password: ') print(password)
The getpass()
method from the getpass module is used to hide the input while the user types
their password.
The getpass module is available in the standard library, so you don't have to
install anything.
getpass method is usually used to prompt the user for a password or other sensitive information.The argument the method takes is the message that is displayed to the user.
If no message is provided, it defaults to "Password: ".
import getpass password = getpass.getpass() print(password)
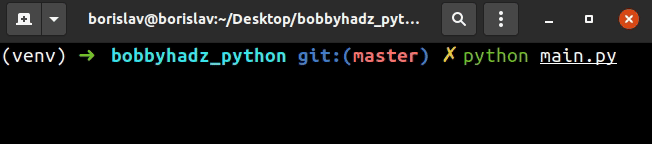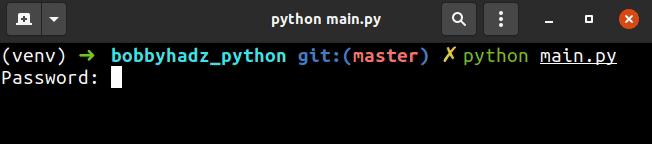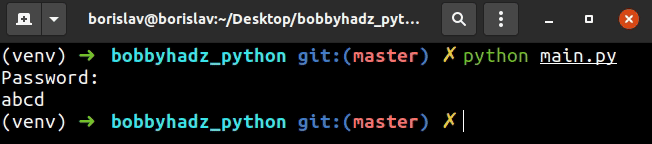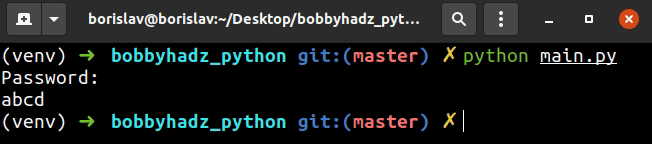
We didn't pass a message to the getpass() method so it displayed the default
"Password: " message.
You can use the getpass() method to take any other sensitive information from
the user without displaying the text, it doesn't have to be a password.
# Prompt for username and password in Python
To prompt the user for username and password:
- Use the
input()function to take non-sensitive input values, such as the username. - Use the
getpass()method to take sensitive values, such as the password.
import getpass # ✅ Prompt for username and password username = input('Enter your username: ') print(username) password = input('Enter your password: ') print(password) # ---------------------------------------------------- # ✅ Prompt for username and password with hidden inputs username = getpass.getpass('Enter your username: ') print(username) password = getpass.getpass('Enter your password: ') print(password)
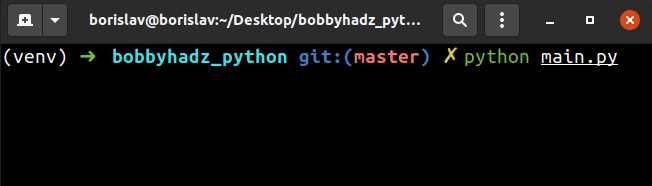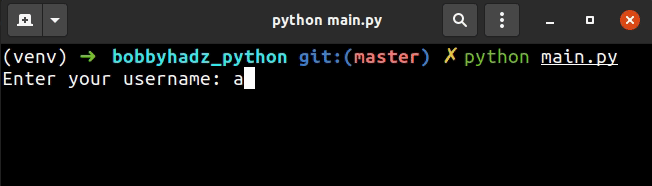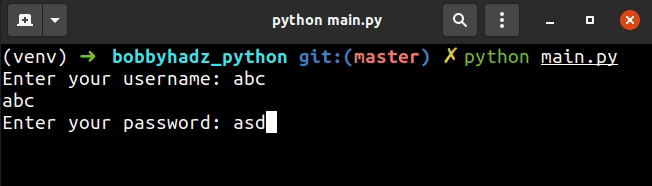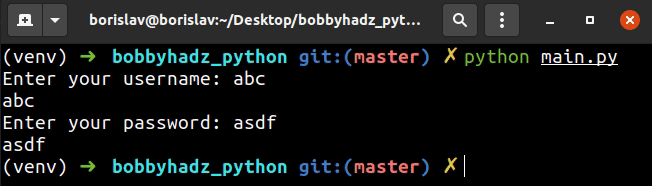
The first example uses the input() function to take the user's username and
password.
The input() function shows the text as the user is typing.
The input function takes an optional prompt
argument and writes it to standard output without a trailing newline.
The function then reads the line from the input, converts it to a string and returns the result.
input() function is guaranteed to return a string even if the user enters a number.The second example uses the getpass method to take the user's username and
password without showing the text as the user is typing.
import getpass username = getpass.getpass('Enter your username: ') print(username) password = getpass.getpass('Enter your password: ') print(password)
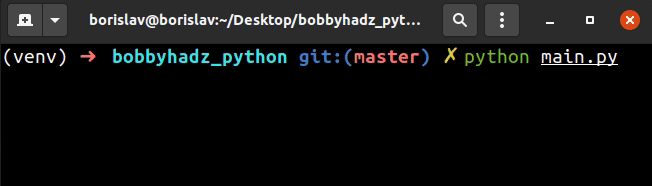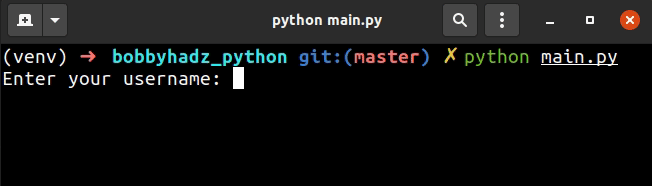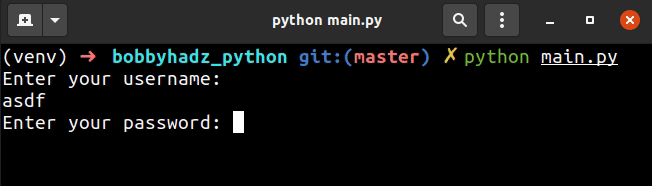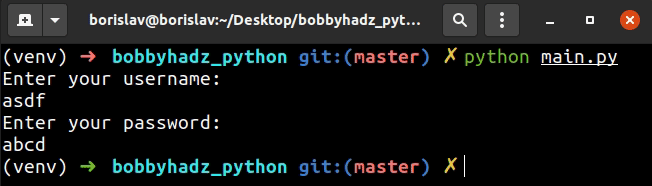
We used the
getpass()
method from the getpass module to prompt the user for input without echoing.
The getpass module is available in the standard library, so you don't have to
install anything.
getpass method is usually used to prompt the user for a password or other sensitive information.The argument the method takes is the message that is displayed to the user.
You can also combine the solutions and use the input() function to take the
username and the getpass() method to take the password.
import getpass username = input('Enter your username: ') print(username) password = getpass.getpass('Enter your password: ') print(password)
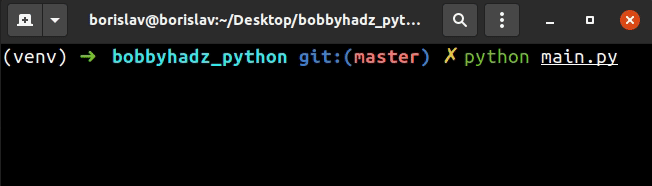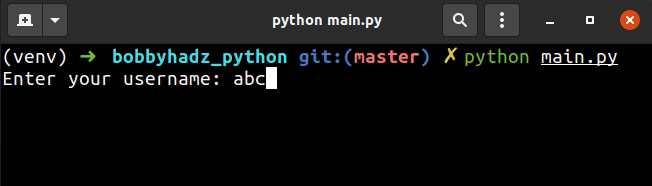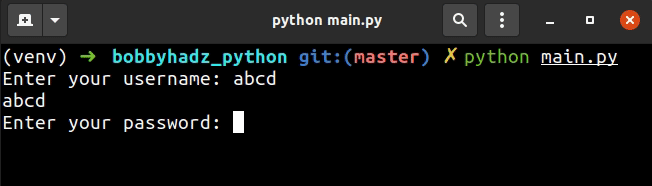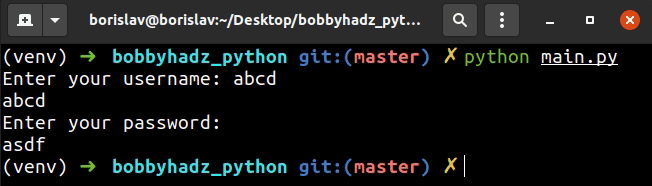
The input() function prompts for the username and shows the text while the
user is typing.
The getpass() method prompts for the user's password and hides the text.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to Add user input to a Dictionary in Python
- How to take a List from user input in Python
- How to check if User Input is Empty in Python
- Using a For or While Loop to take user input in Python
- Taking user input boolean (True/False) values in Python
- How to Create a Date from user Input in Python
- Taking a file path from user input in Python
- How to take Float user input in Python
- Multiple lines user Input in Python
- Only accept a single character from user Input in Python
- Creating a Tuple or a Set from user Input in Python
- How to Validate user input in Python
- Yes/No question with user input in Python

