How to take Integer user input in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
# Take integer user input in Python
To take an integer user input:
- Use the
input()function to take input from the user. - Use a
try/exceptstatement to make sure the input value is an integer. - Use the
int()class to convert the string to an integer.
# ✅ Take user input integer value user_input = int(input('Enter an integer: ')) print(user_input) # ------------------------------------------------ # ✅ Take user input integer value with validation try: user_input = int(input('Enter an integer: ')) print(user_input) except ValueError: print('Enter a valid integer')
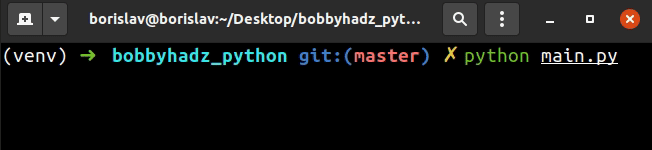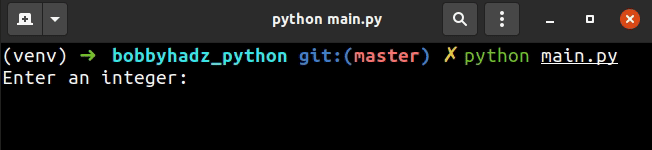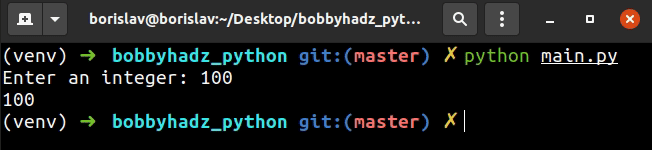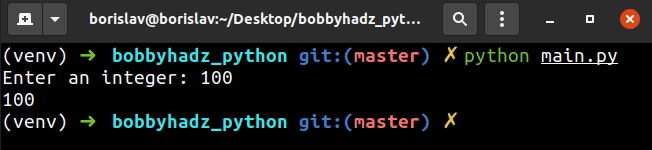
We used the input() function to take user input.
The input() function takes an optional prompt
argument and writes it to standard output without a trailing newline.
The function then reads the line from the input, converts it to a string and returns the result.
input function is guaranteed to return a string, even if the user entered an integer.This is why we used the int() class to convert the value to an integer.
user_input = int(input('Enter an integer: ')) print(user_input)
If the user enters an invalid integer, we'd get a ValueError.
You can handle the error using a try/except statement.
try: user_input = int(input('Enter an integer: ')) print(user_input) except ValueError: print('Enter a valid integer')
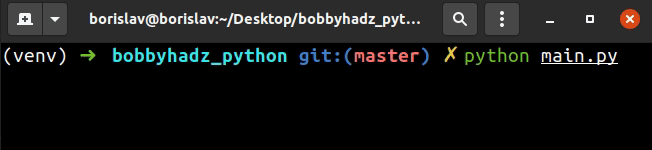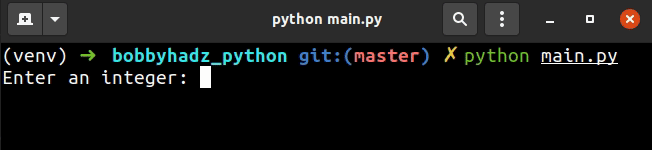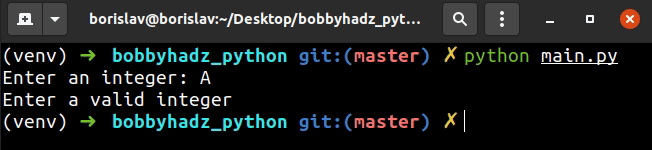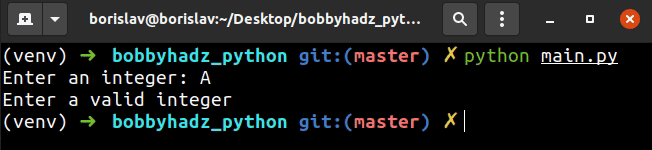
int() class throws a ValueError which gets handled in the except block.# Only allow Integer user input in Python
To only allow integer user input:
- Use a
while Trueloop to loop until the user enters an integer. - Use the
int()class to attempt to convert the value the user entered to an integer. - If the user entered an integer, use the
breakstatement to break out of the loop.
while True: try: num = int(input('Your favorite integer: ')) print(num) break except ValueError: print('Please enter an integer.')
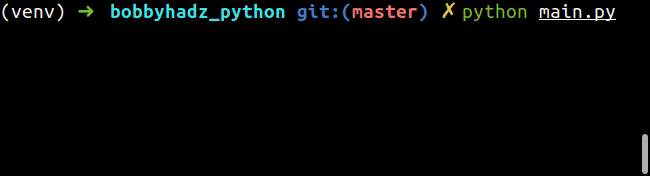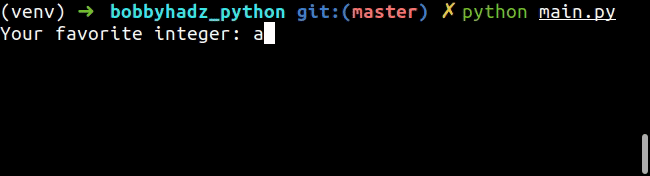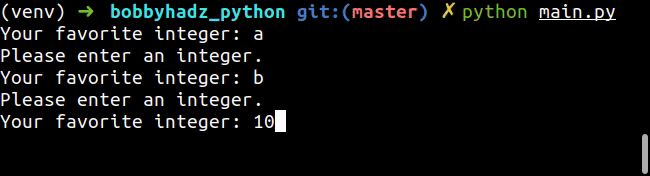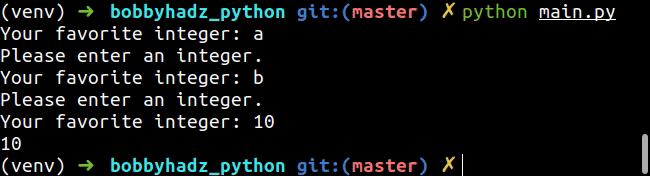
We used a while True loop to iterate until the user enters an integer value.
The input() function takes an optional prompt argument and writes it to
standard output without a trailing newline.
The function then reads the line from the input, converts it to a string and returns the result.
input() function always returns a string, even if the user enters an integer.We used the int() class to try to convert the value the user entered to an
integer.
while True: try: num = int(input('Your favorite integer: ')) print(num) break except ValueError: print('Please enter an integer.')
If the attempt to convert the value fails, a ValueError is raised and the
except block runs.
The except block prints the "Please enter an integer" message and the loop
re-runs.
break out of the while loop.The break statement breaks out of the
innermost enclosing for or while loop.
# Only allow integer user input in a given range
If you need to make sure the user enters an integer in a given range, use an
if statement.
while True: try: num = int(input('Integer between 1 and 100: ')) print(num) if num < 1 or num > 100: raise ValueError break except ValueError: print('Please enter an integer between 1 and 100.')
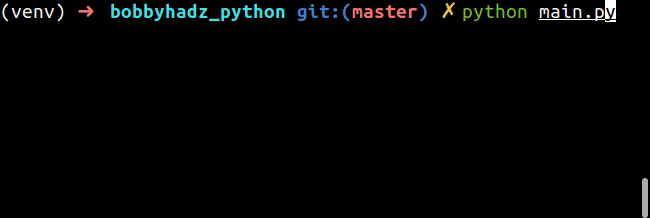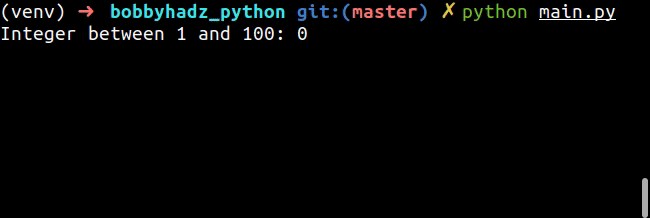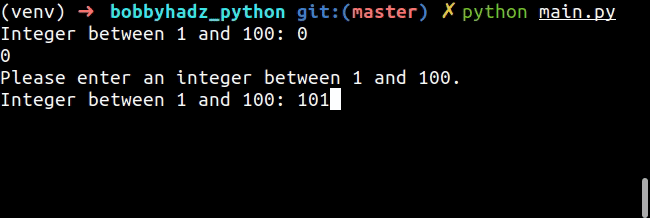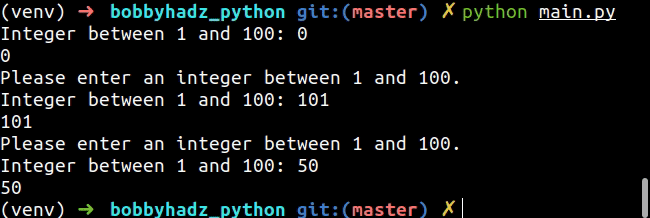
The code snippet only allows a user to enter an integer between 1 and 100.
If the value is not an integer, is less than 1 or is greater than 100, a
ValueError is raised and the loop re-runs.
Once the user enters an integer in the specified range, no ValueError is
raised and we break out of the while loop.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Taking user input boolean (True/False) values in Python
- How to Create a Date from user Input in Python
- Taking a file path from user input in Python
- How to take Float user input in Python
- Multiple lines user Input in Python
- Only accept a single character from user Input in Python
- Creating a Tuple or a Set from user Input in Python
- How to Validate user input in Python
- Yes/No question with user input in Python
- How to save user input to a File in Python
- Using user input to Select an Option from a List in Python
- EOFError: EOF when reading a line in Python [Solved]

