Python: Compare two CSV files and print the differences
Last updated: Apr 13, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Python: Compare two CSV files and print the differences
- Using the csv-diff package to compare two CSV files in Python
- Using the pandas package to compare two CSV files in Python
- Using the pandas package with DataFrame.merge()
# Python: Compare two CSV files and print the differences
To compare two CSV files and print the differences in Python:
- Use the
with open()statement to open the two CSV files. - Read the lines of each file and store the results in two variables.
- Iterate over the lines of the second file and check if each line is not contained in the first file.
Here are the contents of the first CSV file, named csv-file-1.csv.
Alice,Smith,500 Bob,Smith,600 Carl,Smith,400
And here are the contents of the second CSV file, named csv-file-2.csv.
Alice,Smith,500 Bob,Smith,600 Dan,Smith,2500
Here is the related Python script, named main.py.
with open( 'csv-file-1.csv', encoding='utf-8' ) as file_1, open( 'csv-file-2.csv', encoding='utf-8' ) as file_2: file_1_lines = file_1.readlines() file_2_lines = file_2.readlines() with open( 'differences.csv', 'w', encoding='utf-8' ) as differences_file: for line in file_2_lines: if line not in file_1_lines: print(line) differences_file.write(line)
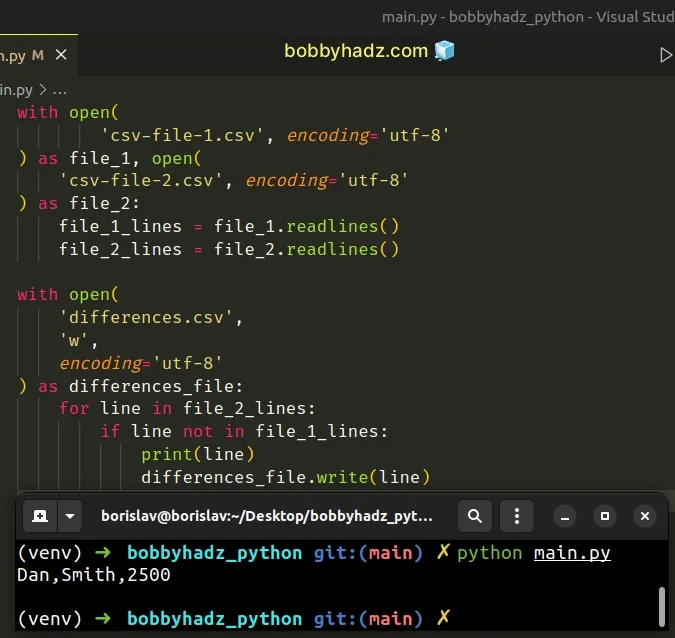
We used the with open() statement to open the two CSV files.
The with open() statement takes care of closing the files after we're done
(even if an exception has occurred).
The file.readlines() method reads the lines of the file into a Python list.
with open( 'csv-file-1.csv', encoding='utf-8' ) as file_1, open( 'csv-file-2.csv', encoding='utf-8' ) as file_2: file_1_lines = file_1.readlines() # 👇️ ['Alice,Smith,500\n', 'Bob,Smith,600\n', 'Carl,Smith,400'] print(file_1_lines) file_2_lines = file_2.readlines() # 👇️ ['Alice,Smith,500\n', 'Bob,Smith,600\n', 'Dan,Smith,2500\n'] print(file_2_lines)
Once we have the two lists of lines, we use the with open() statement to open
a differences.csv file in w (write) mode.
with open( 'differences.csv', 'w', encoding='utf-8' ) as differences_file: for line in file_2_lines: if line not in file_1_lines: print(line) differences_file.write(line)
The for loop iterates over the lines of
csv-file-2 and.
On each iteration, we use the not in operator to check if the current line is
NOT present in the lines of csv-file-1.
If the condition is met, we print the line and write it to the output CSV file.
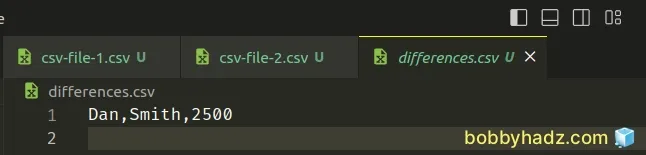
You can open the differences.csv file (located in the same directory) to see
lines in csv-file-2 that are not present in csv-file-1.
# Using the csv-diff package to compare two CSV files in Python
You can also use the csv-diff package to compare two CSV files in Python.
First, install the module by running the following command.
pip install csv-diff # or with pip3 pip3 install csv-diff
Here are the contents of the first CSV file, named csv-file-1.csv.
first,last,salary Alice,Smith,500 Bob,Smith,600 Carl,Smith,400
And here are the contents of the second CSV file, named csv-file-2.csv.
first,last,salary Alice,Smith,500 Bob,Smith,600 Dan,Smith,2500
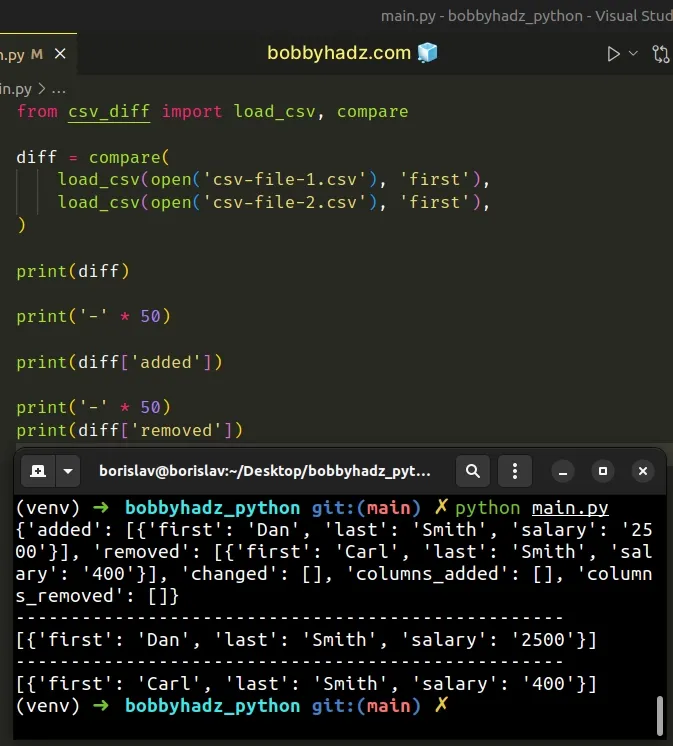
Here is the related Python script, named main.py.
from csv_diff import load_csv, compare diff = compare( load_csv(open('csv-file-1.csv'), 'first'), load_csv(open('csv-file-2.csv'), 'first'), ) # {'added': [{'first': 'Dan', 'last': 'Smith', 'salary': '2500'}], 'removed': [{'first': 'Carl', 'last': 'Smith', 'salary': '400'}], 'changed': [], 'columns_added': [], 'columns_removed': []} print(diff) print('-' * 50) # [{'first': 'Dan', 'last': 'Smith', 'salary': '2500'}] print(diff['added']) print('-' * 50) # [{'first': 'Carl', 'last': 'Smith', 'salary': '400'}] print(diff['removed'])
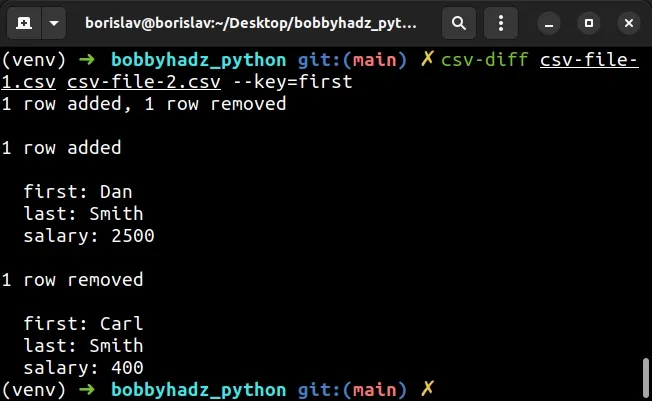
You can also use the module via the command line.
The key parameter is the name of the column by which you want to compare.
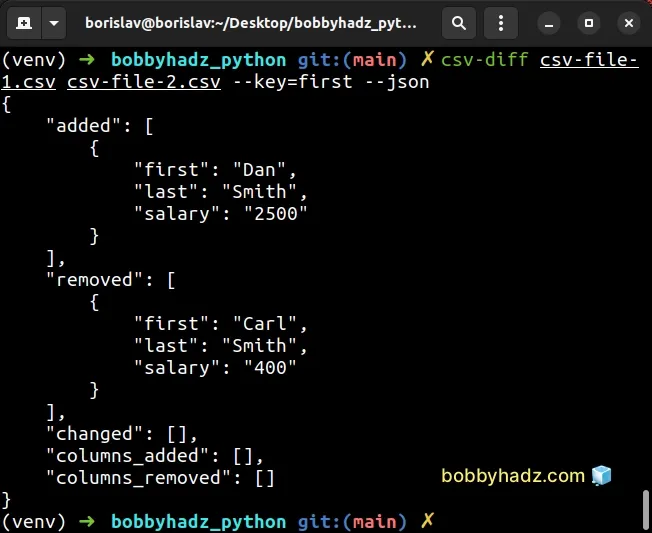
csv-diff csv-file-1.csv csv-file-2.csv --key=first
You can also use the --json option if you want to get the output as JSON.
csv-diff csv-file-1.csv csv-file-2.csv --key=first --json
# Using the pandas package to compare two CSV files in Python
You can also use the pandas package to compare two CSV files in Python.
First, make sure you
have the pandas module installed.
pip install pandas # or with pip3 pip3 install pandas
Here are the contents of the first CSV file, named csv-file-1.csv.
first,last,salary Alice,Smith,500 Bob,Smith,600 Carl,Smith,400
And here are the contents of the second CSV file, named csv-file-2.csv.
first,last,salary Alice,Smith,500 Bob,Smith,600 Dan,Smith,2500
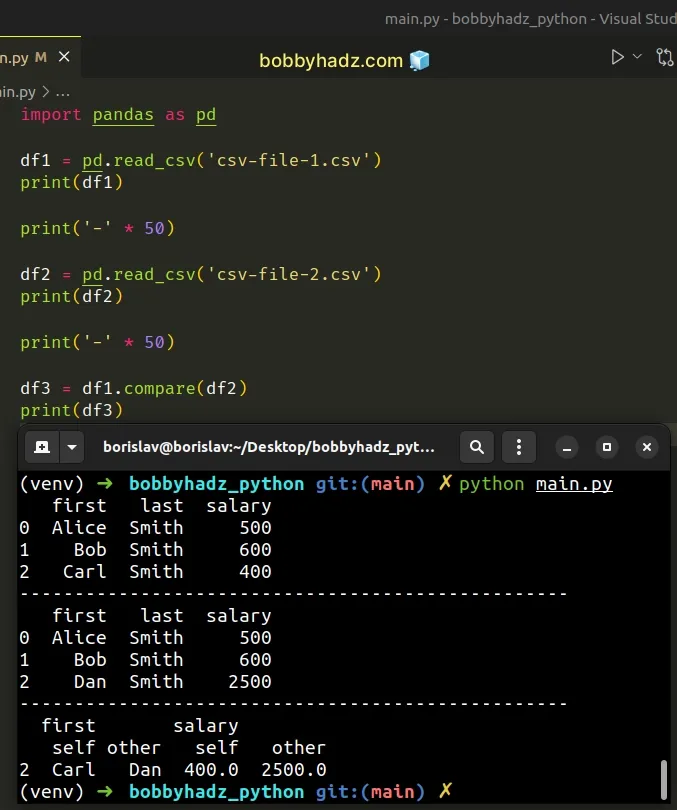
Here is the related Python script, named main.py.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.read_csv('csv-file-1.csv') print(df1) print('-' * 50) df2 = pd.read_csv('csv-file-2.csv') print(df2) print('-' * 50) df3 = df1.compare(df2) print(df3)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
first last salary 0 Alice Smith 500 1 Bob Smith 600 2 Carl Smith 400 -------------------------------------------------- first last salary 0 Alice Smith 500 1 Bob Smith 600 2 Dan Smith 2500 -------------------------------------------------- first salary self other self other 2 Carl Dan 400.0 2500.0
If your CSV files don't start with the column names, you can supply them when calling pandas.read_csv.
Here are the updated contents of the first CSV file, named csv-file-1.csv.
Alice,Smith,500 Bob,Smith,600 Carl,Smith,400
And here are the updated contents of the second CSV file, named
csv-file-2.csv.
Alice,Smith,500 Bob,Smith,600 Dan,Smith,2500
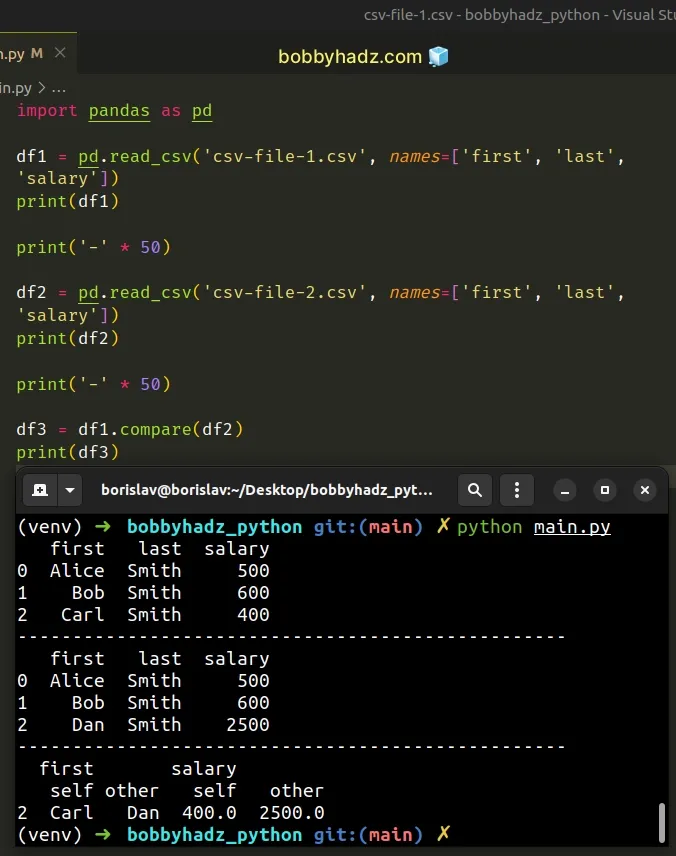
Here is the related Python code.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.read_csv('csv-file-1.csv', names=['first', 'last', 'salary']) print(df1) print('-' * 50) df2 = pd.read_csv('csv-file-2.csv', names=['first', 'last', 'salary']) print(df2) print('-' * 50) df3 = df1.compare(df2) print(df3)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
first last salary 0 Alice Smith 500 1 Bob Smith 600 2 Carl Smith 400 -------------------------------------------------- first last salary 0 Alice Smith 500 1 Bob Smith 600 2 Dan Smith 2500 -------------------------------------------------- first salary self other self other 2 Carl Dan 400.0 2500.0
The code sample uses the pandas.read_csv() method to read the CSV files into
DataFrame objects and the
DataFrame.compare()
method to compare the two DataFrames.
The DataFrame.compare() method returns a DataFrame that shows the
differences stacked side by side.
The resulting DataFrame has a MultiIndex with self and other stacked
alternately at the inner level.
# Using the pandas package with DataFrame.merge()
You can also use the pandas package with
DataFrame.merge()
to compare two CSV files.
Here are the contents of the first CSV file, named csv-file-1.csv.
Alice,Smith,500 Bob,Smith,600 Carl,Smith,400
And here are the contents of the second CSV file, named csv-file-2.csv.
first,last,salary Alice,Smith,500 Bob,Smith,600 Dan,Smith,2500
Here is the related Python script, named main.py.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.read_csv('csv-file-1.csv') print(df1) print('-' * 50) df2 = pd.read_csv('csv-file-2.csv') print(df2) print('-' * 50) df3 = df1.merge(df2, indicator=True, how='outer') print(df3)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
first last salary 0 Alice Smith 500 1 Bob Smith 600 2 Carl Smith 400 -------------------------------------------------- first last salary 0 Alice Smith 500 1 Bob Smith 600 2 Dan Smith 2500 -------------------------------------------------- first last salary _merge 0 Alice Smith 500 both 1 Bob Smith 600 both 2 Carl Smith 400 left_only 3 Dan Smith 2500 right_only
The DataFrame.merge() method merges the DataFrame objects with a
database-style join.
The second to last row in the resulting DataFrame is only contained in df1
(left_only).
The last row is only contained in df2 (right_only).
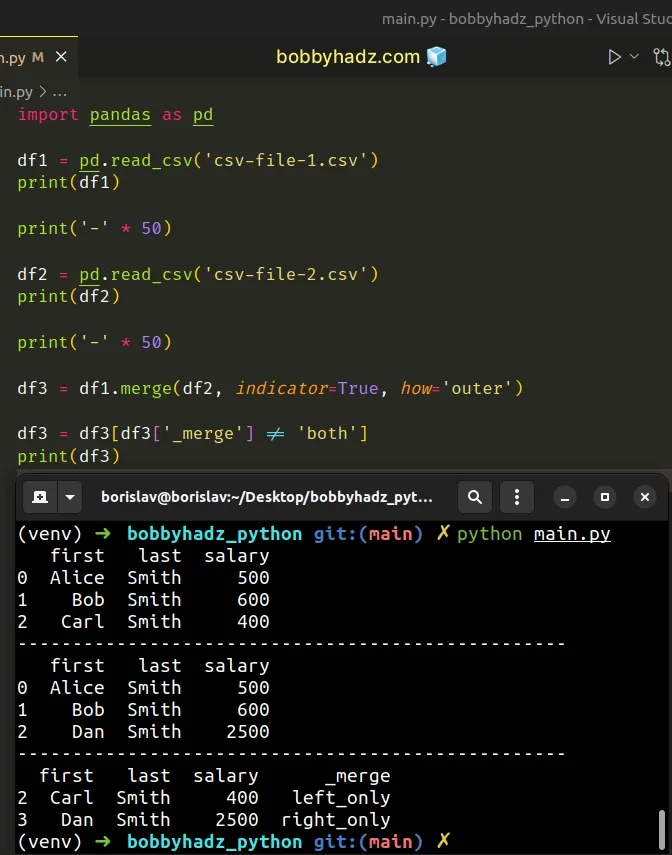
You can only get the left_only and right_only rows with a filter.
import pandas as pd df1 = pd.read_csv('csv-file-1.csv') print(df1) print('-' * 50) df2 = pd.read_csv('csv-file-2.csv') print(df2) print('-' * 50) df3 = df1.merge(df2, indicator=True, how='outer') df3 = df3[df3['_merge'] != 'both'] print(df3)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
first last salary 0 Alice Smith 500 1 Bob Smith 600 2 Carl Smith 400 -------------------------------------------------- first last salary 0 Alice Smith 500 1 Bob Smith 600 2 Dan Smith 2500 -------------------------------------------------- first last salary _merge 2 Carl Smith 400 left_only 3 Dan Smith 2500 right_only
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Pandas: Element-wise logical NOT and logical OR operators
- Update a Pandas DataFrame while iterating over its rows
- Matplotlib: No artists with labels found to put in legend
- ValueError: If using all scalar values, you must pass index
- Pandas: How to Convert a Pivot Table to a DataFrame
- Pandas: Count the unique combinations of two Columns
- Remove __pycache__ folders and .pyc files in Python Project
- SyntaxError: future feature annotations is not defined
- Run multiple Python files concurrently / one after the other

