Check if a Date is between Two Dates using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 6, 2024
Reading time·9 min

# Table of Contents
- Check if a Date is between Two Dates using JavaScript
- Check if a Date is within 30 days in JavaScript
- Check if a Date is within 24 hours in JavaScript
# Check if a Date is between Two Dates using JavaScript
To check if a date is between two dates:
- Use the
Date()constructor to convert the dates toDateobjects. - Check if the date is greater than the start date and less than the end date.
- If both conditions are met, the date is between the two dates.
const date = new Date('2022-09-24'); const start = new Date('2022-03-18'); const end = new Date('2022-11-22'); if (date > start && date < end) { console.log('✅ date is between the 2 dates'); } else { console.log('⛔️ date is not in the range'); }
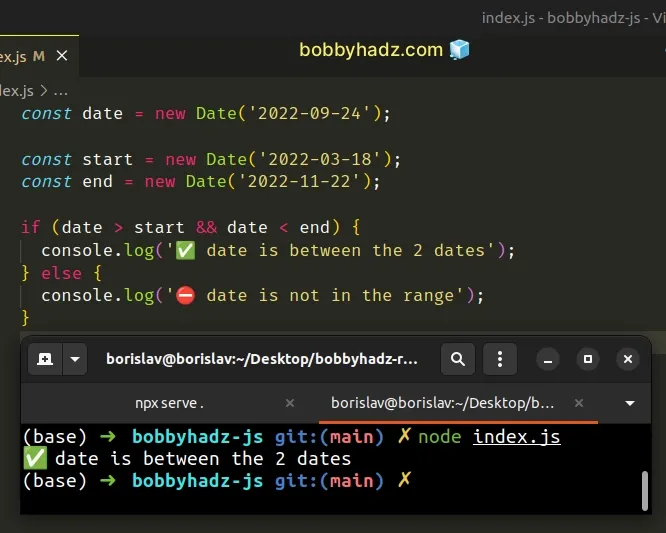
We passed the date strings to the
Date() constructor to create
Date objects.
Date() constructor doesn't return a valid date, then you have to format your date strings differently, e.g. yyyy-mm-dd (more on that below).We are able to compare the dates because under the hood each date stores a timestamp - the number of milliseconds elapsed between the 1st of January 1970 and the given date.
const date = new Date('2022-09-24'); // 👇️ 1663977600000 console.log(date.getTime());
getTime() method on each date.We used the
logical AND (&&)
operator, which checks if both conditions are met before running our if block.
# Dealing with invalid date strings
If you have difficulties creating a valid Date object from your date
strings, you can pass 2 types of parameters to the Date() constructor:
- a valid ISO 8601 string, formatted as
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.sssZ, or justYYYY-MM-DD, if you only have a date without time. - multiple, comma-separated parameters that represent the
year,month(0 = January to 11 = December),day of the month,hours,minutesandseconds.
Here is an example that splits a string and passes the parameters to the
Date() constructor to create a Date object.
// 👇️ Formatted as MM/DD/YYYY const dateStr = '07/21/2022'; const [month, day, year] = dateStr.split('/'); // 👇️ Create valid Date object const date = new Date(+year, month - 1, +day); console.log(date); // 👉️ Thu Jul 21 2022
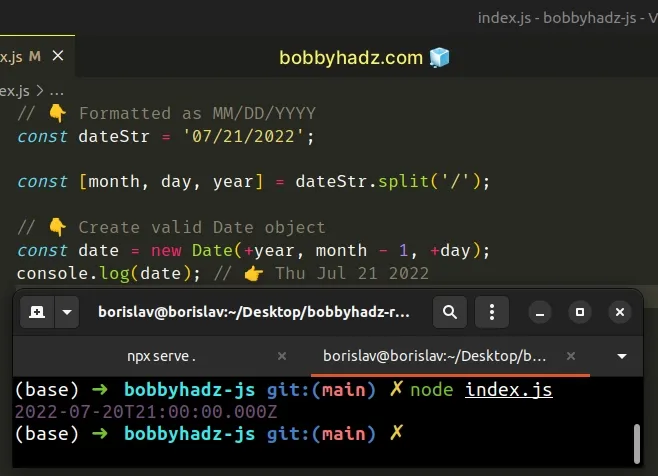
The date string is formatted as mm/dd/yyyy, but the approach applies to any
other format.
Notice that we
subtracted 1 from the month when
passing it to the Date() constructor.
Date constructor expects a zero-based value, where January = 0, February = 1, March = 2, etc.We String.split the string on each forward slash to get an array of substrings.
const str = '07/21/2022'; // 👇️ ['07', '21', '2022'] console.log(str.split('/'))
Date() constructor.Once you have created Date objects from the date strings, you can just compare
the dates as you would compare numbers because Date objects get converted to a
timestamp before the comparison takes place.
// 👇️ Formatted as MM/DD/YYYY const dateStr = '07/21/2022'; const [month1, day1, year1] = dateStr.split('/'); const date = new Date(+year1, month1 - 1, +day1); const startStr = '03/24/2022'; const [month2, day2, year2] = startStr.split('/'); const startDate = new Date(+year2, month2 - 1, +day2); const endStr = '11/28/2022'; const [month3, day3, year3] = endStr.split('/'); const endDate = new Date(+year3, month3 - 1, +day3); if (date > startDate && date < endDate) { console.log('✅ date is between start and end dates'); } else { console.log('⛔️ date is NOT between start and end dates'); }
We repeated the process for each of the dates and split each by the forward slashes to get the month, day and year values.
1 from the value of the month, because the Date() constructor expects a zero-based value for the month (January = 0, February = 1, March = 2).The if block from the example runs because the date is between the start and
end dates.
# Check if a Date is within 30 days in JavaScript
To check if a date is within 30 days:
- Subtract the timestamp of the current date from the timestamp of the date.
- Pass the result to the
Math.abs()function. - Convert the result to days.
- Check if the days between the dates are less than
30.
const then = new Date('2022-01-21'); const now = new Date(); const msBetweenDates = Math.abs(then.getTime() - now.getTime()); // 👇️ convert ms to days hour min sec ms const daysBetweenDates = msBetweenDates / (24 * 60 * 60 * 1000); if (daysBetweenDates < 30) { console.log('date is within 30 days'); } else { console.log('date is NOT within 30 days'); }
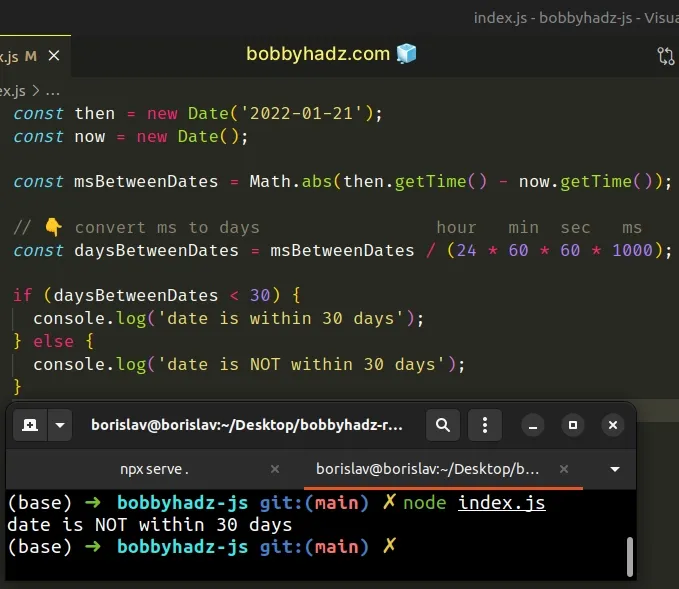
The getTime() method returns the number of milliseconds elapsed between the 1st of January 1970 and the given date.
We have to subtract the timestamp of the first date from the timestamp of the second date.
We used the Math.abs() function to convert a possibly negative to a positive number.
The only parameter the function takes is the number we want to get the absolute value of.
The Math.abs() function returns the provided number if it's positive or zero
and the negation of the number if it's negative.
console.log(Math.abs(-3)); // 👉️ 3 console.log(Math.abs(-3.5)); // 👉️ 3.5 console.log(Math.abs(-0)); // 👉️ 0
The msBetweenDates variable stores the number of milliseconds between the two
dates.
The next step is to convert the milliseconds to days.
Once we have the number of days between the two days, all we have to do is check
if the days are less than 30 to see if the date is within 30 days.
Note that this could mean that the date is within 30 days in the future or
30 days in the past.
# Check if a Date is more than 30 days from today's date in JS
To check if a date is more than 30 days from today's date:
- Get a timestamp representing a date 30 days in the past or future.
- Compare the result to the timestamp for the specific date.
// ✅ Check if the date is more than 30 days AGO function isMoreThan30DaysAgo(date) { // days hours min sec ms const thirtyDaysInMs = 30 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000; const timestampThirtyDaysAgo = new Date().getTime() - thirtyDaysInMs; if (timestampThirtyDaysAgo > date) { console.log('date is more than 30 days into the past'); return true; } else { console.log('date is NOT more than 30 days into the past'); return false; } } // 👇️ true console.log(isMoreThan30DaysAgo(new Date('2021-09-24'))); // 👇️ false console.log(isMoreThan30DaysAgo(new Date('2021-12-26'))); // ----------------------------------------------------- // ✅ Check if the date is more than 30 days IN THE FUTURE function isMoreThan30DaysInFuture(date) { // days hours min sec ms const thirtyDaysInMs = 30 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000; const timestampThirtyDaysInFuture = new Date().getTime() + thirtyDaysInMs; if (date > timestampThirtyDaysInFuture) { console.log('date is more than 30 days into the future'); return true; } else { console.log('date is NOT more than 30 days into the future'); return false; } } // 👇️ true console.log(isMoreThan30DaysInFuture(new Date('2029-04-25'))); // 👇️ false console.log(isMoreThan30DaysInFuture(new Date('2022-02-23')));
We calculated the number of milliseconds there are in 30 days.
The getTime() method returns the number of milliseconds since the Unix Epoch.
Date object that represents the current date gets us the number of milliseconds elapsed between the 1st of January 1970 and the current date.If we subtract the number of milliseconds there are in 30 days, we get a
timestamp that represents a date and time exactly 30 days ago.
Similarly, if we add the number of milliseconds there are in 30 days to the
current timestamp, we get a date that is 30 days in the future.
If you need to check if a given date is more than 30 days into the past:
- get a timestamp of the date
30days ago. - check if the timestamp of
30days ago is greater than the date's timestamp. - if it is, the date is more than
30days into the past.
If you need to check if a given date is more than 30 days into the future:
- get a timestamp of the date
30days into the future. - check if the passed-in date is greater than the timestamp of the date
30days into the future. - if it is, the date is more than
30days into the future.
# Check if a Date is within 24 hours in JavaScript
To check if a date is within 24 hours:
- Subtract the timestamp of the current date from the timestamp of the date.
- Pass the result to the
Math.abs()function. - Convert the result to hours.
- Check if the hours between the dates are less than
24.
const then = new Date('2022-01-24T09:30:20'); const now = new Date(); const msBetweenDates = Math.abs(then.getTime() - now.getTime()); // 👇️ convert ms to hours min sec ms const hoursBetweenDates = msBetweenDates / (60 * 60 * 1000); console.log(hoursBetweenDates); if (hoursBetweenDates < 24) { console.log('date is within 24 hours'); } else { console.log('date is NOT within 24 hours'); }
The getTime() method returns the number of milliseconds elapsed between the 1st of January 1970 and the given date.
We have to subtract the timestamp of the first date from the timestamp of the second date.
We used the Math.abs() method to convert a possibly negative to a positive number.
The only parameter the function takes is the number we want to get the absolute value of.
The Math.abs function returns the provided number if it's positive or zero and
the negation of the number if it's negative.
console.log(Math.abs(-6)); // 👉️ 6 console.log(Math.abs(-6.5)); // 👉️ 6.5 console.log(Math.abs(-0)); // 👉️ 0
The msBetweenDates variable stores the number of milliseconds between the two
dates.
The next step is to convert the milliseconds to hours.
24 to see if the date is within 24 hours.Note that this could mean that the date is within 24 hours in the future or
24 hours in the past.
# Check if a Date is less than 24 Hours ago using JavaScript
To check if a date is less than 24 hours ago:
- Convert 24 hours to milliseconds.
- Get a timestamp that represents the time 24 hours ago.
- Check if the date's timestamp is greater than the timestamp 24 hours ago.
function isLessThan24HourAgo(date) { // 👇️ hour min sec milliseconds const twentyFourHrInMs = 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000; const twentyFourHoursAgo = Date.now() - twentyFourHrInMs; return date > twentyFourHoursAgo; } console.log(isLessThan24HourAgo(new Date())); // 👉️ true console.log(isLessThan24HourAgo(new Date('2022-01-25'))); // 👉️ false
We created a reusable function that takes a Date object as a parameter and
checks if the date is less than 24 hours ago.
true for dates in the future. If you only want to check if the Date is less than 24 hours ago and is NOT in the future, scroll down to the next code snippet.The first step is to calculate how many milliseconds there are in 24 hours.
The Date.now() method returns the number of milliseconds elapsed since midnight of the 1st of January 1970.
By subtracting 24 hours in milliseconds from the timestamp, we get the moment
in time 24 hours ago.
We are able to compare the date to a timestamp because under the hood each date stores a timestamp - the number of milliseconds elapsed between the 1st of January 1970 and the given date.
const date = new Date('2022-07-24'); // 👇️ 1658620800000 console.log(date.getTime());
getTime() method on each date.# Check if a date is less than 24 hours ago and is not in the future
If you need to check if a date is less than 24 hours ago and is not in the future, add a condition that checks that the date is less than or equal to the current timestamp.
function isLessThan24HourAgo(date) { // 👇️ hour min sec milliseconds const twentyFourHrInMs = 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000; const twentyFourHoursAgo = Date.now() - twentyFourHrInMs; return date > twentyFourHoursAgo && date <= Date.now(); } console.log(isLessThan24HourAgo(new Date())); // 👉️ true console.log(isLessThan24HourAgo(new Date('2045-09-24'))); // 👉️ false
The second condition would not be met for any dates in the future.
The logical AND (&&) operator will only return true if both conditions are
met, otherwise false is returned.
I've also written an article on how to change time format to 24 hours.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

