Edit and replay XHR (HTTP) requests in Chrome & Firefox
Last updated: Apr 5, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Edit and replay XHR (HTTP) requests in Chrome
- Replay or edit a Chrome request by using "Copy as fetch"
- Edit and replay XHR (HTTP) requests in Firefox
# Edit and replay XHR (HTTP) requests in Chrome
To edit or replay an XHR (HTTP) request in Chrome:
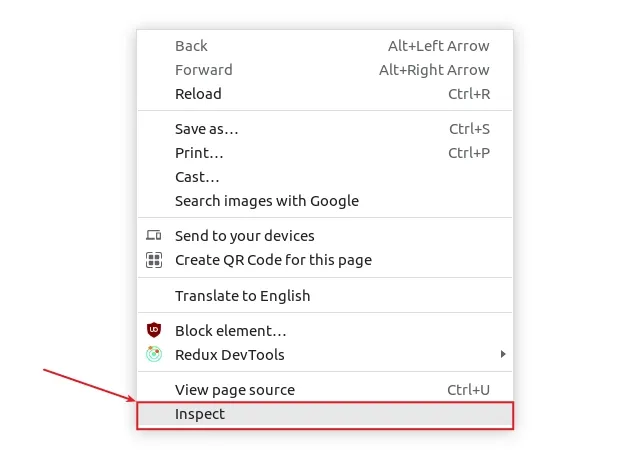
- Open your developer tools by right-clicking on the page and selecting
Inspect or by pressing
F12.
- Click on the Network tab.
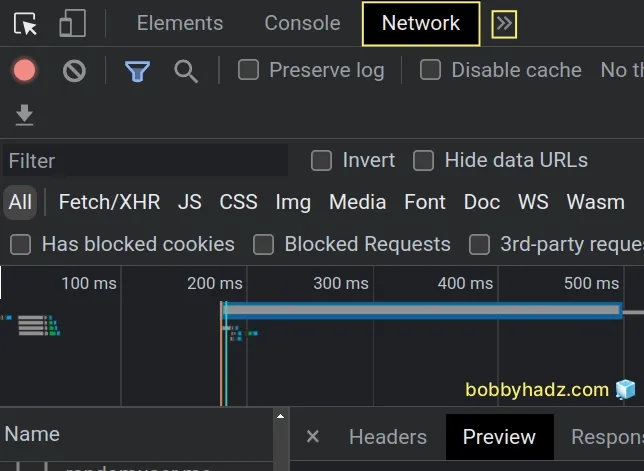
If you don't see the Network tab, click on the >> icon and select
Network from the dropdown menu.
You might have to refresh the page by pressing
F5if you don't see any HTTP requests.Find the request you'd like to replay or edit and left-click on it in the
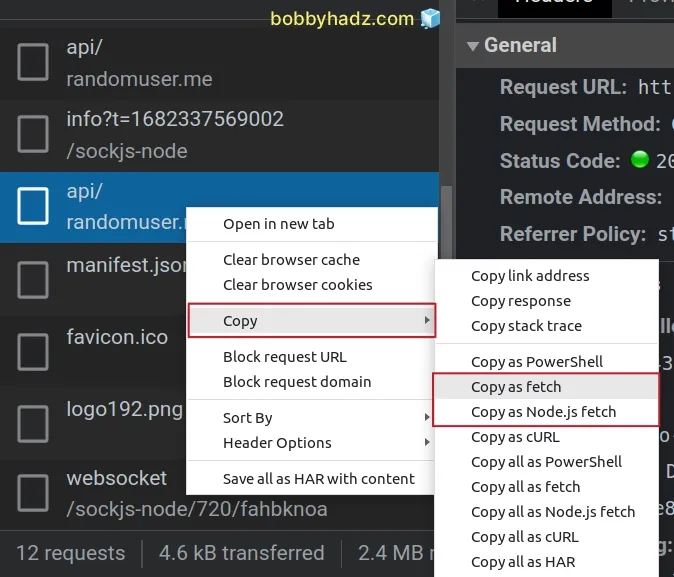
Namecolumn.Once the request is selected, right-click on it.
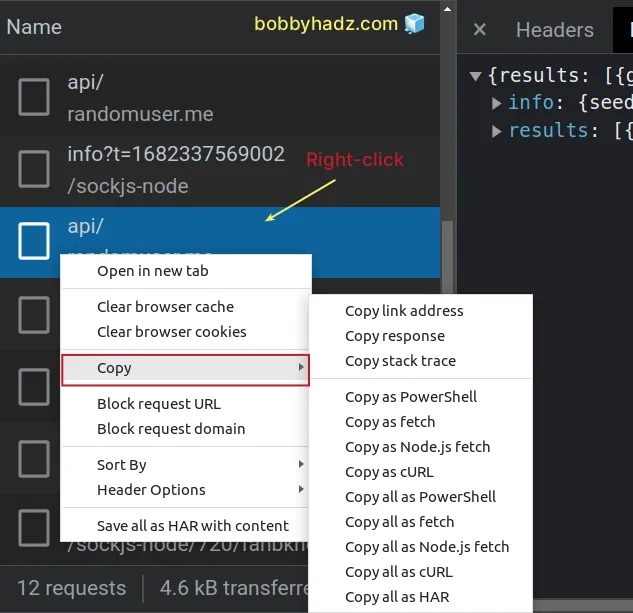
Make sure you have selected the request first by left-clicking on it before you right-click.
- Select how you'd like to copy the request. The most common option is to use
cURL.
You can select Copy as cURL.
Notice that there is also a Copy all as cURL option.
If you only want to copy a single request as cURL, make sure to select Copy as cURL instead.
- Paste the request in a code or text editor and edit it according to your needs.
curl 'https://randomuser.me/api/' \ -H 'authority: randomuser.me' \ -H 'accept: application/json' \ -H 'accept-language: en-US,en;q=0.9,de;q=0.8' \ -H 'dnt: 1' \ -H 'if-none-match: W/"491-gknRcHuot4JOqQ1E7XuQ3bjZ8xk"' \ -H 'origin: http://localhost:3001' \ -H 'referer: http://localhost:3001/' \ -H 'sec-ch-ua: "Chromium";v="112", "Google Chrome";v="112", "Not:A-Brand";v="99"' \ -H 'sec-ch-ua-mobile: ?0' \ -H 'sec-ch-ua-platform: "Linux"' \ -H 'sec-fetch-dest: empty' \ -H 'sec-fetch-mode: cors' \ -H 'sec-fetch-site: cross-site' \ -H 'sec-gpc: 1' \ -H 'user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/112.0.0.0 Safari/537.36' \ --compressed
- Run the request from your terminal.
cURL is installed on most macOS and Linux machines, however, it might not be installed on Windows.
If you are on Windows, check out the following article:
If you use the Postman app, you can select Copy as cURL and import the cURL request into Postman.
- Click on the "My Workspace" icon in the top left corner.
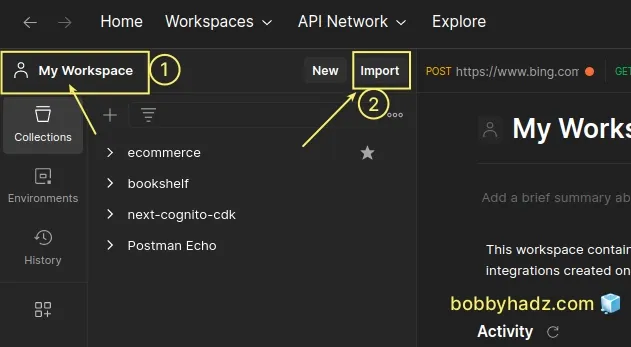
Click on the Import button.
Paste the cURL request you previously copied.
There is also a "Copy as PowerShell" option if you are on Windows.
# Replay or edit a Chrome request by using "Copy as fetch"
- If you need to replay the HTTP request in your code, right-click on the request and select:
- Copy as fetch (for browser-based applications).
- Copy as Node.js fetch (for server-based applications).
Here is an example of a copied fetch request.
fetch("https://randomuser.me/api/", { "headers": { "accept": "application/json", "accept-language": "en-US,en;q=0.9,de;q=0.8", "if-none-match": "W/\"494-U1fSzfRAnnckIQxsWvYjoMOfGk8\"", "sec-ch-ua": "\"Chromium\";v=\"112\", \"Google Chrome\";v=\"112\", \"Not:A-Brand\";v=\"99\"", "sec-ch-ua-mobile": "?0", "sec-ch-ua-platform": "\"Linux\"", "sec-fetch-dest": "empty", "sec-fetch-mode": "cors", "sec-fetch-site": "cross-site", "sec-gpc": "1" }, "referrer": "http://localhost:3001/", "referrerPolicy": "strict-origin-when-cross-origin", "body": null, "method": "GET", "mode": "cors", "credentials": "omit" });
Copying the request as Node.js fetch is quite similar as both approaches use the built-in fetch function.
You can either send the request from your code or the browser.
To issue the HTTP request from your browser:
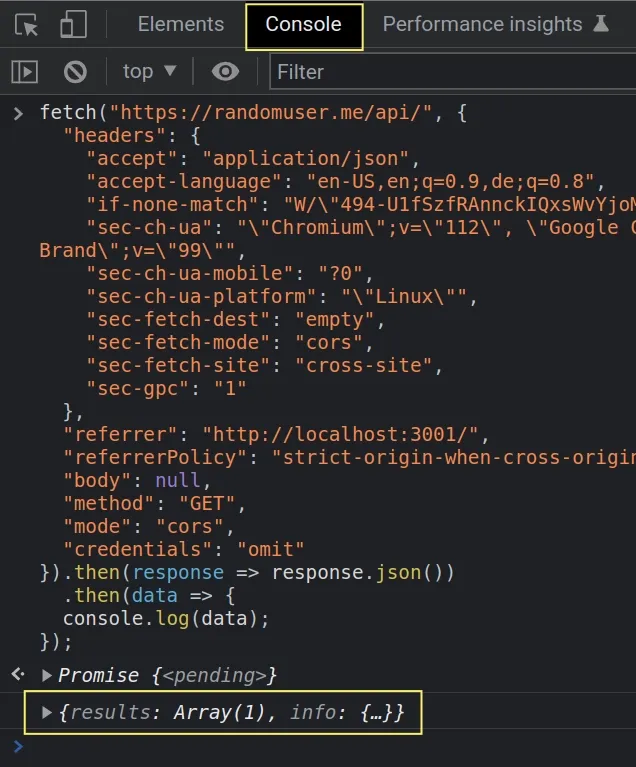
- Click on the Console tab.
- Paste the request in the console and hit
Enter. - Note that you will likely want to add code that waits for the promise to resolve.
Here is an example.
fetch("https://randomuser.me/api/", { "headers": { "accept": "application/json", "accept-language": "en-US,en;q=0.9,de;q=0.8", "if-none-match": "W/\"494-U1fSzfRAnnckIQxsWvYjoMOfGk8\"", "sec-ch-ua": "\"Chromium\";v=\"112\", \"Google Chrome\";v=\"112\", \"Not:A-Brand\";v=\"99\"", "sec-ch-ua-mobile": "?0", "sec-ch-ua-platform": "\"Linux\"", "sec-fetch-dest": "empty", "sec-fetch-mode": "cors", "sec-fetch-site": "cross-site", "sec-gpc": "1" }, "referrer": "http://localhost:3001/", "referrerPolicy": "strict-origin-when-cross-origin", "body": null, "method": "GET", "mode": "cors", "credentials": "omit" }).then(response => response.json()) .then(data => { console.log(data); });
The last 3 lines of the code sample wait for the promise to resolve so we can
console.log the data and not the pending Promise.
.then(response => response.json()) .then(data => { console.log(data); });
I've written a detailed article on how to wait for a promise to resolve.
# Edit and replay XHR (HTTP) requests in Firefox
To edit and replay XHR (HTTP) requests in Firefox:
Open your developer tools by right-clicking on the page and selecting Inspect or by pressing
F12.Click on the Network tab in your developer tools.
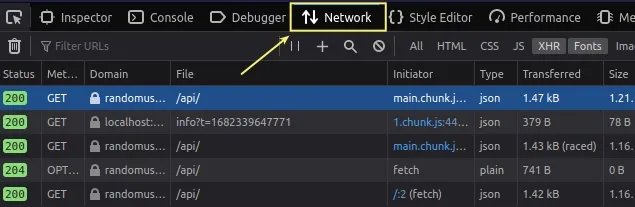
- Right-click on the request you want to edit or replay.
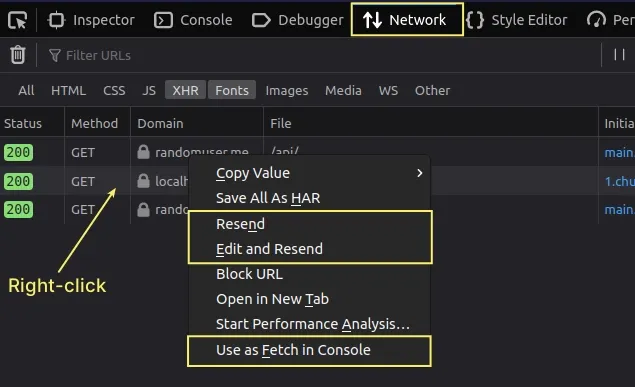
- If you need to replay the request, select Resend.
- If you need to edit the request, select Edit and Resend.
If you click on Edit and Resend you are able to edit request headers, the body (if making a POST/PATCH/PUT request) and the URL parameters.
Once you're done, click on the Send button to issue the edited request.
You can click on the arrow that points to the left to hide the network action menu.
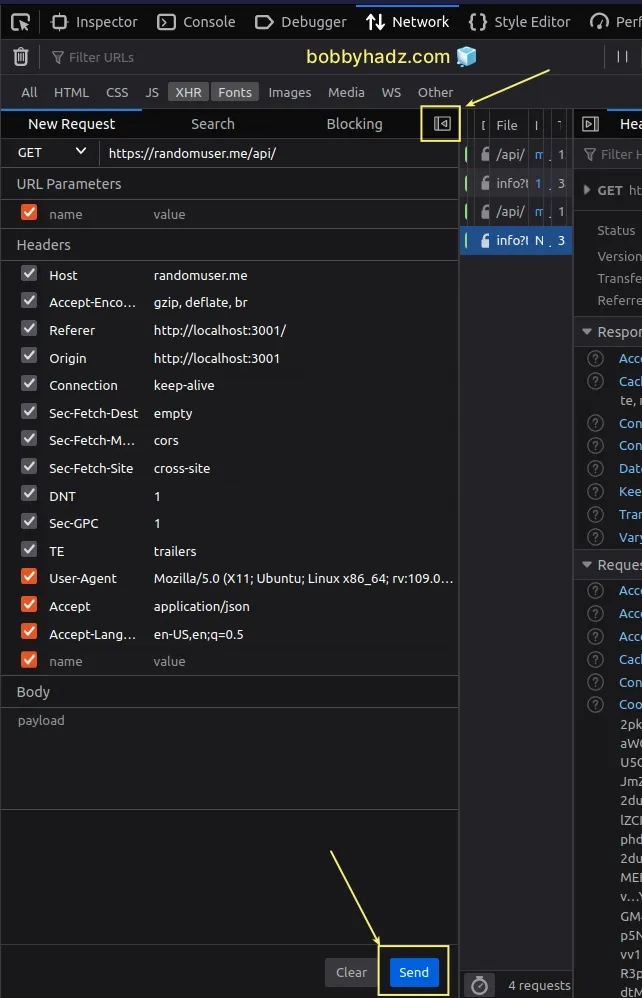
Alternatively, you can copy the request as
fetch.Right-click on the request in the Network tab and click Use as fetch in Console.
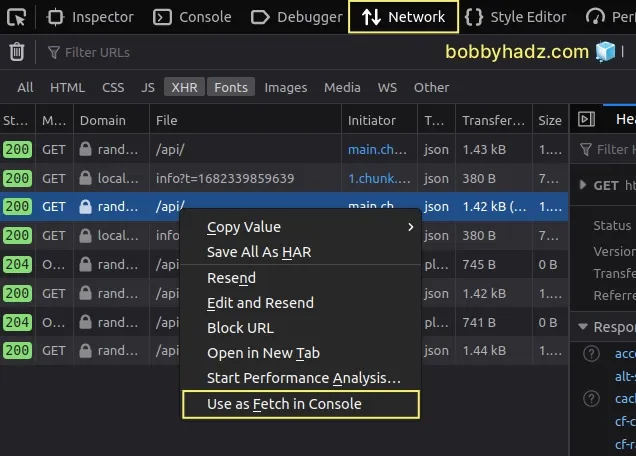
Once you click on Use as fetch in Console, the Console tab gets focused
and the fetch request gets automatically pasted.
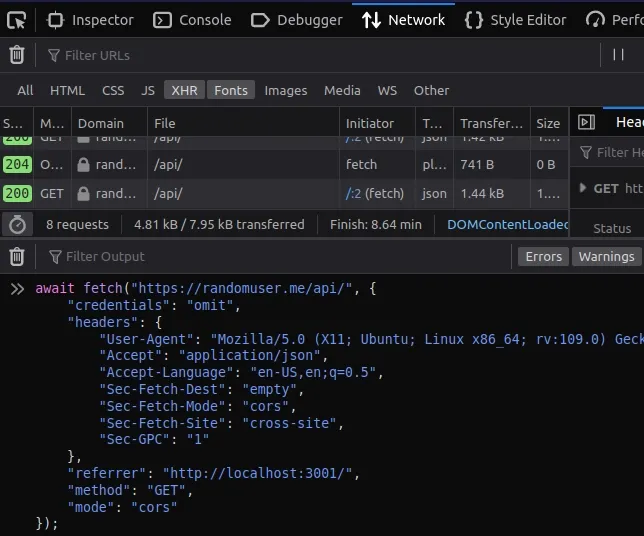
Your fetch request will look similar to the following.
await fetch("https://randomuser.me/api/", { "credentials": "omit", "headers": { "User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:109.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/112.0", "Accept": "application/json", "Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.5", "Sec-Fetch-Dest": "empty", "Sec-Fetch-Mode": "cors", "Sec-Fetch-Site": "cross-site", "Sec-GPC": "1" }, "referrer": "http://localhost:3001/", "method": "GET", "mode": "cors" });
However, if you run the code as is, you would just log the Response object and
not the data.
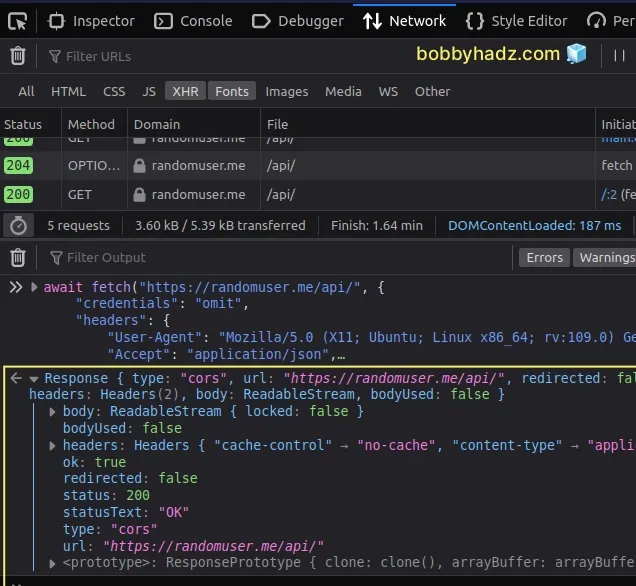
If you want to console.log the data, call the
response.json
method.
await fetch("https://randomuser.me/api/", { "credentials": "omit", "headers": { "User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:109.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/112.0", "Accept": "application/json", "Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.5", "Sec-Fetch-Dest": "empty", "Sec-Fetch-Mode": "cors", "Sec-Fetch-Site": "cross-site", "Sec-GPC": "1" }, "referrer": "http://localhost:3001/", "method": "GET", "mode": "cors" }).then(response => response.json()) .then(data => { console.log(data); })
I added the following 3 lines to resolve the Promise.
.then(response => response.json()) .then(data => { console.log(data); })
If I run the code sample, I can see that the data is logged to the console.
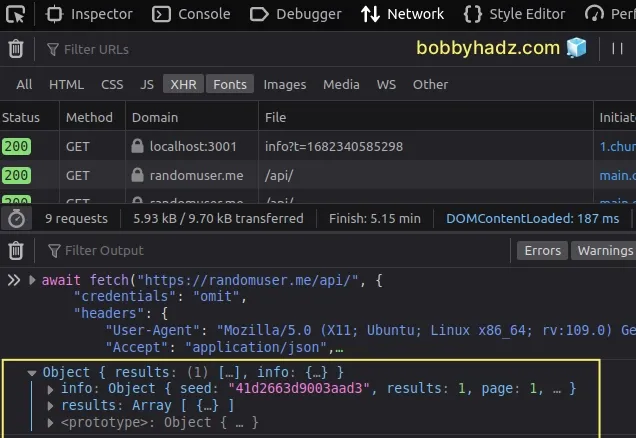
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to access the Value of a Promise in JavaScript
- Check if a Value is a Promise using JavaScript
- How to Check if a Function is Async in JavaScript
- How to use await outside of an async function in JavaScript
- How to Wait for a DOM element to Exist in JavaScript
- Unable to verify the first certificate in Node.js & Postman
- How to clear all Cookies or a specific Cookie in Postman
- Chrome: How to Copy an Object or Array from the Console tab
- Failed to set up Chromium! Set "PUPPETEER_SKIP_DOWNLOAD"
- Unchecked runtime lastError The message port closed before a response was received
- Paused in Debugger in Chrome issue [Solved]
- Unable to preventDefault inside passive event listener due to target being treated as passive
- Get Browser name (Chrome, Firefox, etc) and Version in JS
- DOMException: Blocked a frame with origin from accessing a cross-origin frame
- Provisional headers are shown Chrome warning [Solved]
- How to detect AdBlockers using JavaScript [Simple Examples]

