Wait for a Promise to Resolve before Returning in JS
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Wait for a Promise to Resolve before Returning in JavaScript
- Wait for N seconds before resolving a Promise
- Using a
try/catchstatement to handle Rejected promises - Using then() to wait for a Promise to resolve before returning
# Wait for a Promise to Resolve before Returning in JavaScript
You can use the async/await syntax or call the .then() method on a promise
to wait for it to resolve.
Inside functions marked with the async keyword, you can use await to wait
for the promises to resolve before continuing to the next line of the
function.
async function getNum() { const promise = new Promise(resolve => resolve(42)); const num = await promise; console.log(num); // 👉️ 42 return num; } getNum() .then(num => { console.log(num); // 👉️ 42 }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
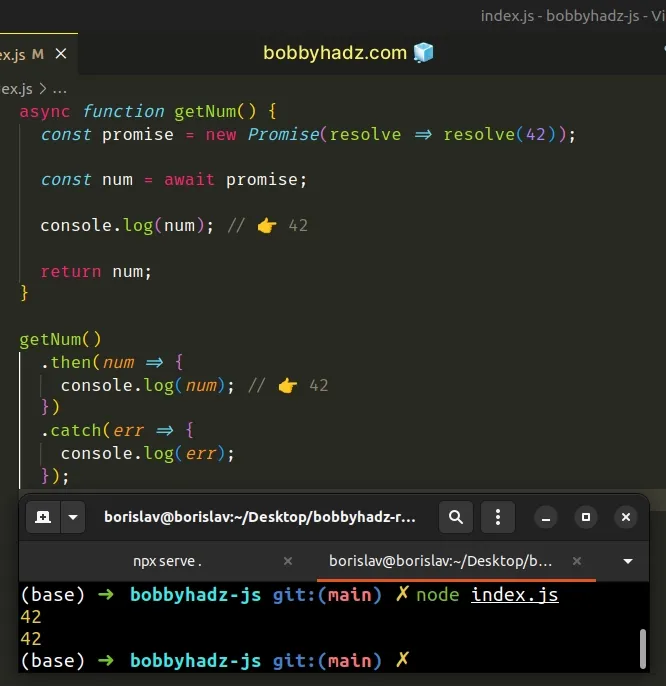
We can use the await keyword to handle promises in functions marked as
async.
The async/await syntax doesn't block the execution of all your JavaScript
code. Rather, it runs the code in the function sequentially.
await keyword is used in a function, the next line of the function is not run before the promise has been resolved or rejected.A Promise can have 3 states in JavaScript:
pending- initial state, neither fulfilled nor rejected.fulfilled- the operation was successful and the promise is resolved.rejected- operation failed.
Even though the async function seemingly returns a number, it actually returns
a promise.
All async functions wrap their return value in a Promise.
This is why we had to use the Promise.then() method to read the resolved value
of the Promise.
# Wait for N seconds before resolving a Promise
You can use the setTimeout() function to wait for N seconds before resolving a
Promise.
function getNum() { const resolveValue = 42; return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve(resolveValue); }, 3000); }); } getNum() .then(num => { console.log(num); // 👉️ 42 }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
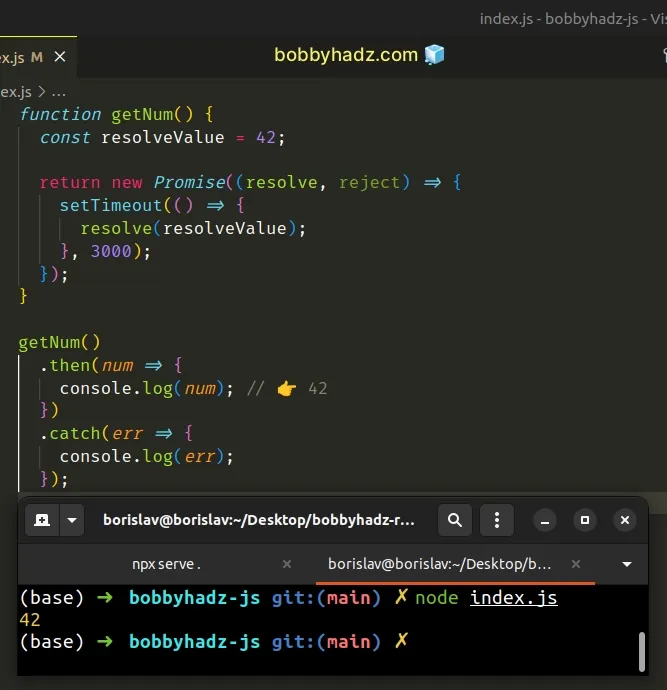
The function returns a new Promise that resolves with the value 42 after 3
seconds.
Notice that the function is not marked as async but it still returns a
Promise.
The same approach can be used outside a function.
const p1 = new Promise(resolve => { const resolveValue = 42; setTimeout(() => { resolve(resolveValue); }, 3000); }); p1.then(num => { console.log(num); // 👉️ 42 }).catch(err => { console.log(err); });
The promise in the example resolves after 3 seconds with the value 42.
# Using a try/catch statement to handle Rejected promises
You can use a try/catch statement to handle a scenario where the promise is
rejected.
async function getNum() { try { const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => reject(new Error('test error')), ); await promise; return "This doesn't run" } catch (err) { // 👇️ this runs throw err; } } getNum() .then(num => { console.log(num); }) .catch(err => { // 👇️ this runs console.log(err.message); // ⛔️ "test error" });
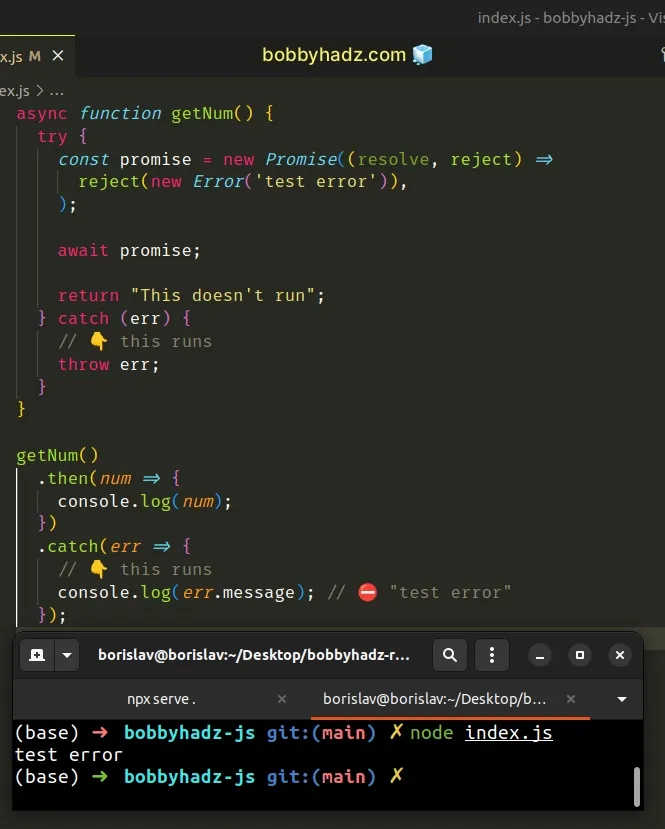
If an error or a promise rejection occurs in the try block, the error gets
passed to the catch block where we can handle it.
Alternatively, you could use the Promise.catch() method to catch an error as shown in the code sample above.
Calling the Promise.catch() method is the same as chaining another .then()
call and passing a function as the second argument to the method.
async function getNum() { try { const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => reject(new Error('test error')), ); await promise; return "This doesn't run"; } catch (err) { // 👇️ this runs throw err; } } getNum() .then(num => { console.log(num); return num; }) .then(undefined, err => { console.log(err.message); // 👉️ "test error" });
It's good to know that the second parameter of the .then() method is a
function that is called if the Promise is rejected.
However, this syntax is very rarely used.
# Using then() to wait for a Promise to resolve before returning
You could achieve the same result by using the Promise.then() method instead
of async/await.
However, the Promise.then() syntax is a bit more verbose and harder to read.
function getNum() { const p1 = new Promise(resolve => { resolve(42); }); return p1.then(value => { // 👇️ can run code here before returning console.log(value); // 👇️ return from the function here return 'example function return value'; }); } getNum() .then(value => { console.log(value); // 👉️ example function return value return value; }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
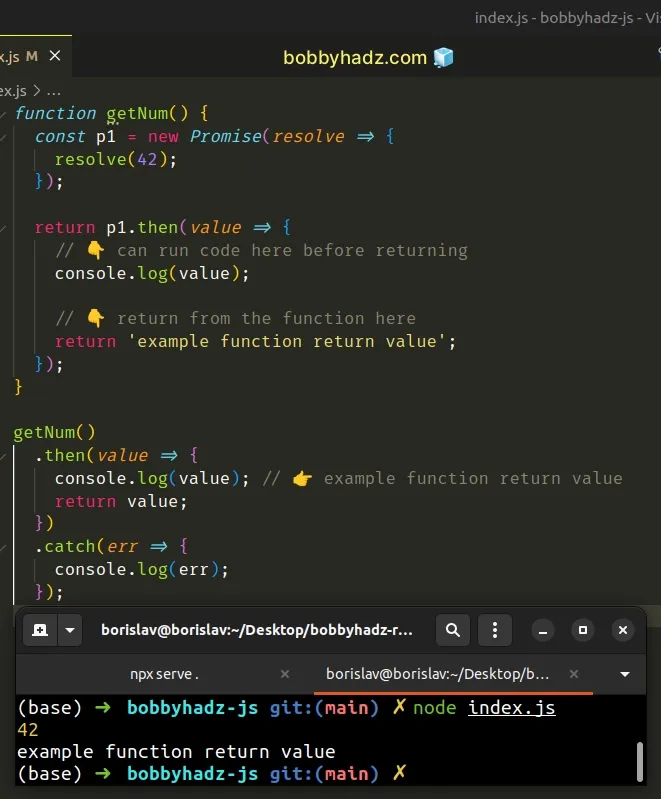
A very important detail in the code sample is that we return the call to
promise.then() from the function.
If you don't return the promise.then() call, you will get an error as the
function wouldn't return a Promise.
async return a Promise, however, in other functions, you have to explicitly return the Promise.You can wait for the promise to resolve inside the .then() call.
The return value of the .then() method is always wrapped in a promise, so you
can chain multiple calls to the .then() method.
const p1 = Promise.resolve(42); p1.then(value => { console.log(value); // 👉️ 42 return value + 1; }).then(value => { console.log(value); // 👉️ 43 return value + 2; });
The value you return from the .then() method gets wrapped in a promise and
passed as a parameter in the next call to the .then() method.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to access the Value of a Promise in JavaScript
- Check if a Value is a Promise using JavaScript
- How to Check if a Function is Async in JavaScript
- How to use await outside of an async function in JavaScript
- How to Wait for a DOM element to Exist in JavaScript
- Edit and replay XHR (HTTP) requests in Chrome & Firefox
- Resolve a Promise after a Delay in JavaScript
- navigator.clipboard is undefined in JavaScript issue [Fixed]

