How to detect AdBlockers using JavaScript [Simple Examples]
Last updated: Apr 4, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- How to detect AdBlockers using JavaScript
- How to detect AdBlockers and Privacy Badger in JavaScript using fetch()
- How to detect Ad Blockers and Privacy Badger with a script tag
# How to detect AdBlockers using JavaScript
To detect AdBlockers using JavaScript:
- Create a file called
ads-prebid-wp-banners.jscontaining the following line.
window.runningAdsAllowed = true;
The idea behind the name of the file is that Ad Blockers usually block the words "ads", "prebid", "wp-banners".
- In your script, you just have to check if the
window.runningAdsAllowedvariable is set.
Here is an example HTML file that has a script tag that does that.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <style> body { margin: 100px; } </style> <!-- 👇️ load the ads-prebid-wp-banners.js file here 👇️ --> <script src="./ads-prebid-wp-banners.js"></script> </head> <body> <h2>bobbyhadz.com | Home</h2> <h2 id="adblock-message"></h2> <script> // 👇️ if this runs, the user has an Ad Blocker active if (window.runningAdsAllowed === undefined) { console.log('Detected Ad content Blocker'); const h2 = document.getElementById('adblock-message'); h2.innerHTML = 'Disable your ad block to support us'; } </script> </body> </html>
Notice that we loaded the ads-prebid-wp-banners.js script in the head tag.
<head> <!-- 👇️ load the ads-prebid-wp-banners.js file here 👇️ --> <script src="./ads-prebid-wp-banners.js"></script> </head>
Then we can check if the window.runningAdsAllowed variable is set.
<script> // 👇️ if this runs, the user has an Ad Blocker active if (window.runningAdsAllowed === undefined) { console.log('Detected Ad content Blocker'); const h2 = document.getElementById('adblock-message'); h2.innerHTML = 'Disable your ad block to support us'; } </script>
If the variable is undefined, then the user has an Ad Content Blocker.
Otherwise, they don't.
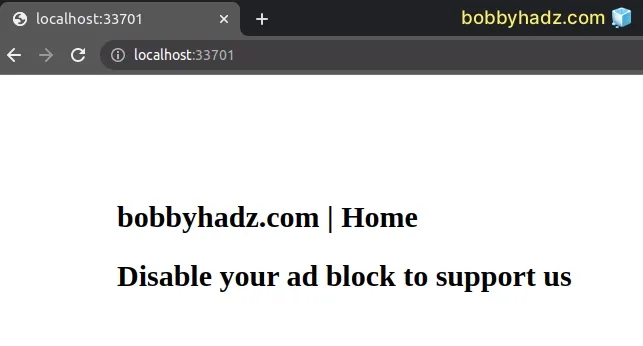
This is what the Home page looks like if the user has an Ad Blocker.
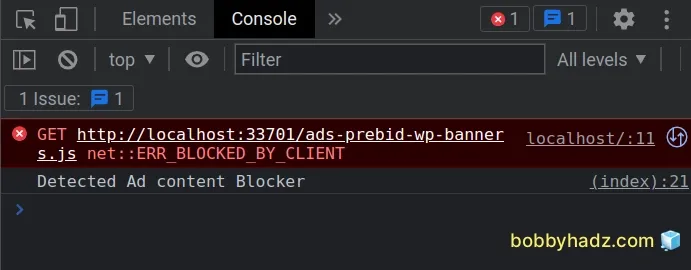
Open the developer tools on the page by pressing F12 and then click on the
Console tab.
You will see that the ads-prebid-wp-banners.js file is blocked by the Ad
Blocker.
Ad Blockers block the script based on its name, therefore the following line isn't run.
window.runningAdsAllowed = true;
If the line doesn't run, the window.runningAdsAllowed variable will be
undefined and the following condition is met.
if (window.runningAdsAllowed === undefined) { console.log('Detected Ad content Blocker'); const h2 = document.getElementById('adblock-message'); h2.innerHTML = 'Disable your ad block to support us'; }
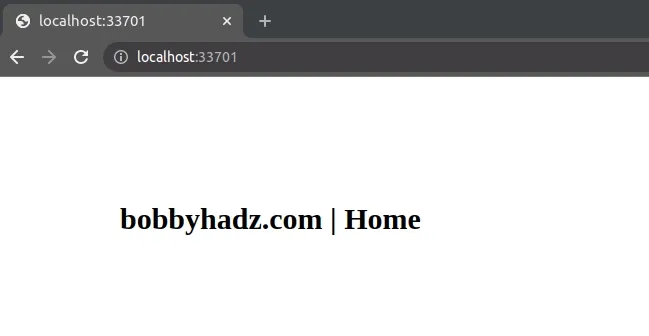
If the user accesses the page without an Ad Blocker active, no message is shown
as the ads-prebid-wp-banners.js script is loaded.
However, this approach doesn't detect the Privacy Badger extension.
If you also need to detect the extension, use the approach from the next subheading.
# How to detect AdBlockers and Privacy Badger in JavaScript using fetch()
You can also use the fetch() method to detect AdBlockers in JavaScript.
To be on the safe side, combine the solution from the previous subheading with the following solution.
- Here is the HTML code for the example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <script src="./ads-prebid-wp-banners.js"></script> </head> <body> <h2>bobbyhadz.com | Home</h2> <h2 id="adblock-message"></h2> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
async function detectAdBlockUsingFetch() { let adBlockEnabled = false; const googleAdsURL = 'https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js'; try { await fetch(new Request(googleAdsURL)).catch(_ => { adBlockEnabled = true; }); } catch (err) { adBlockEnabled = true; } finally { console.log(`AdBlock enabled: ${adBlockEnabled}`); if (adBlockEnabled) { // The user has an Ad Block enabled const h2 = document.getElementById('adblock-message'); h2.innerHTML = 'Disable your ad block to support us'; } } } detectAdBlockUsingFetch(); // -------------------------------------------------- function detectAdBlockUsingGlobalVariable() { if (window.runningAdsAllowed === undefined) { console.log('Detected Ad content Blocker'); const h2 = document.getElementById('adblock-message'); h2.innerHTML = 'Disable your ad block to support us'; } } detectAdBlockUsingGlobalVariable();
We used the fetch() method to make an HTTP request to a Google script that the
Ad Blockers target.
If an error is raised, we use the .catch() method to handle the error and set
the adBlockEnabled variable to true.
await fetch(new Request(googleAdsURL)).catch(_ => { adBlockEnabled = true; });
If another error occurs, the catch() method is run where we also set the
adBlockEnabled variable to true.
catch (err) { adBlockEnabled = true; }
The finally block runs regardless if an error occurred or not.
finally { console.log(`AdBlock enabled: ${adBlockEnabled}`); if (adBlockEnabled) { // The user has an Ad Block enabled const h2 = document.getElementById('adblock-message'); h2.innerHTML = 'Disable your ad block to support us'; } }
We simply check for the value of the adBlockEnabled variable.
If the variable is set to true, then the user has an Ad Blocker enabled.
This approach also detects the Privacy Badger extension.
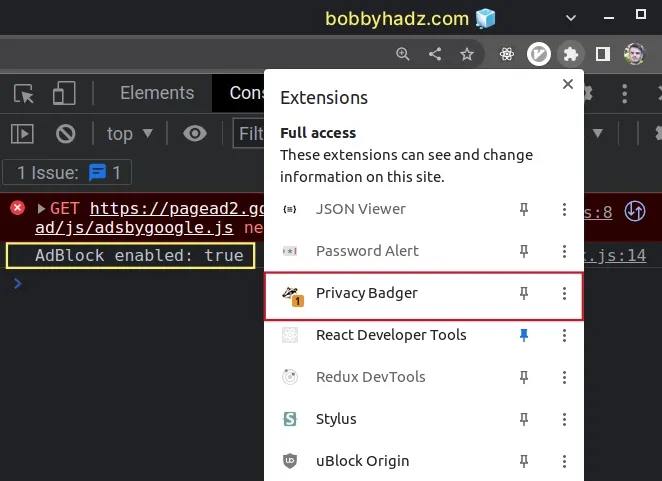
If the user doesn't have an Ad Blocker enabled or the Privacy Badger extension, no message is shown.
# How to detect Ad Blockers and Privacy Badger with a script tag
You can also manually add a script tag that loads the Google ads page that is
blocked by Ad Blockers.
Here is the updated HTML code.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <script async id="ads-by-google" src="//pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js" ></script> </head> <body> <h2>bobbyhadz.com | Home</h2> <h2 id="adblock-message"></h2> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the updated JavaScript code.
function detectAdBlockUsingGlobalVariable() { if (window.runningAdsAllowed === undefined) { console.log('Detected Ad content Blocker'); const h2 = document.getElementById('adblock-message'); h2.innerHTML = 'Disable your ad block to support us'; } } detectAdBlockUsingGlobalVariable(); // ------------------------------------------------------------- const scriptElement = document.getElementById('ads-by-google'); scriptElement.addEventListener('error', adBlockEnabledFunction); function adBlockEnabledFunction() { // The user has an Ad Block enabled console.log('adBlockEnabledFunction runs...'); const h2 = document.getElementById('adblock-message'); h2.innerHTML = 'Disable your ad block to support us'; }
We added the following script tag in the head section of the index.html
file.
<head> <script async id="ads-by-google" src="//pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js" ></script> </head>
The next step is to add an error event listener to the script tag.
The error event is triggered when the script fails to load (e.g. because it was blocked by an AdBlocker).
const scriptElement = document.getElementById('ads-by-google'); scriptElement.addEventListener('error', adBlockEnabledFunction); function adBlockEnabledFunction() { // The user has an Ad Block enabled console.log('adBlockEnabledFunction runs...'); const h2 = document.getElementById('adblock-message'); h2.innerHTML = 'Disable your ad block to support us'; }
If the script fails to load, the user has an Ad Blocker enabled or Google's servers are down (unlikely).
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Edit and replay XHR (HTTP) requests in Chrome & Firefox
- Failed to set up Chromium! Set "PUPPETEER_SKIP_DOWNLOAD"
- Unchecked runtime lastError The message port closed before a response was received
- Paused in debugger in Chrome issue [Solved]
- Unable to preventDefault inside passive event listener due to target being treated as passive
- Get Browser name (Chrome, Firefox, etc) and Version in JS
- Browserslist: caniuse-lite is outdated NPM issue [Solved]

