NumPy RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
Last updated: Apr 12, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Table of Contents
- NumPy RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
- Use the
numpy.seterr()method to resolve the issue - Make sure you don't have
infvalues in either of the arrays
# NumPy RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
The NumPy "RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide" issue occurs
when you try to divide by zero, INF or divide by a missing value, such as
NaN.
To resolve the issue, use the numpy.seterr() method to specify that invalid
division operations should be ignored.
Here is an example of when the warning is shown.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([0, 2, 4, 6, 8]) arr2 = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) result = np.divide(arr1, arr2) # /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/main.py:17: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide # np.divide(x, y) print(result)
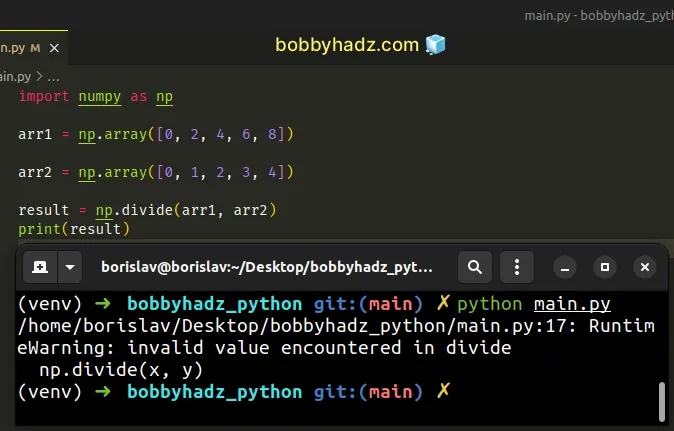
The first element-wise division tries to divide 0 by 0.
You'd get the same warning if only the divisor is set to 0.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 4, 6, 8]) arr2 = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) result = np.divide(arr1, arr2) # /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/main.py:7: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in divide # result = np.divide(arr1, arr2) # [inf 2. 2. 2. 2.] print(result)
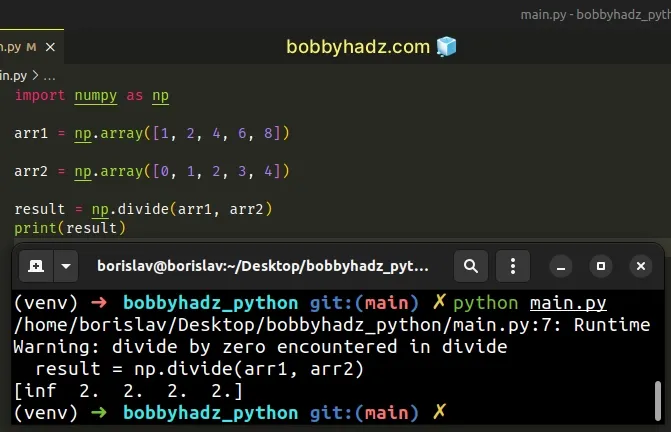
# Use the numpy.seterr() method to resolve the issue
One way to resolve the issue is to use the numpy.seterr() method to specify how floating-point errors and division by zero should be handled.
import numpy as np np.seterr(divide='ignore', invalid='ignore') arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 4, 6, 8]) arr2 = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) result = np.divide(arr1, arr2) print(result)
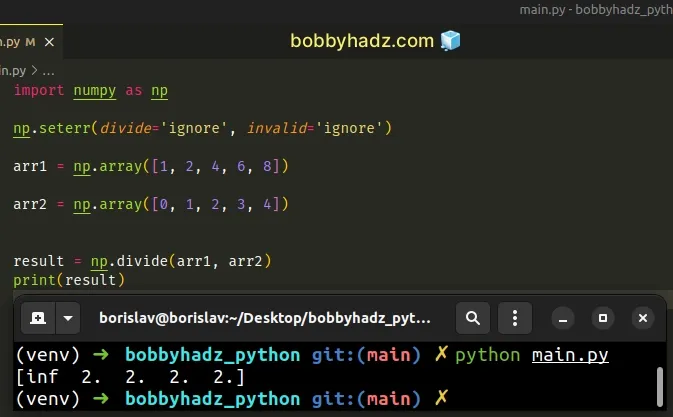
Make sure to use the numpy.seterr() method at the top of your module, before
calling numpy.divide().
The numpy.seterr() method doesn't only affect how floating-point errors are
handled.
int16) are also handled like floating-point, so they are also affected by the numpy.seterr() method.We set the divide keyword argument to "ignore" when calling the method.
import numpy as np np.seterr(divide='ignore', invalid='ignore')
When the divide argument is set to "ignore", division by zero errors are
ignored.
invalid argument is set to "ignore", invalid floating-point operations are also ignored.If you only want to suppress warnings for a block of code, use the with
statement with numpy.errstate()
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 4, 6, 8]) arr2 = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) with np.errstate(divide='ignore', invalid='ignore'): result = np.divide(arr1, arr2) print(result)
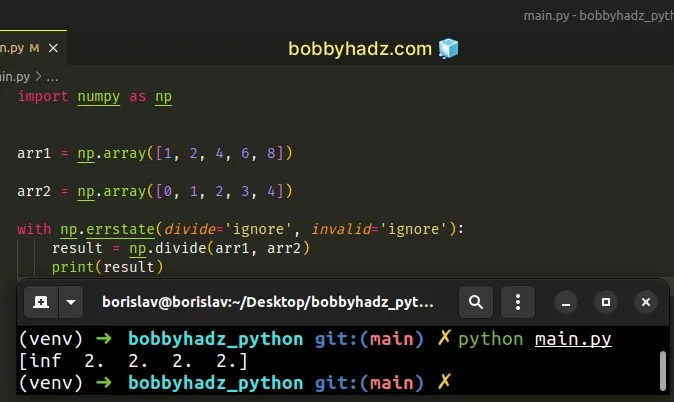
The numpy.errstate context manager is used for handling floating-point errors.
The settings are only applied to the indented block in the with statement.
Once you exit the with statement, you revert to the default settings.
# Make sure you don't have inf values in either of the arrays
Another common cause of the warning is having inf values in one or both of the
arrays.
Here is an example.
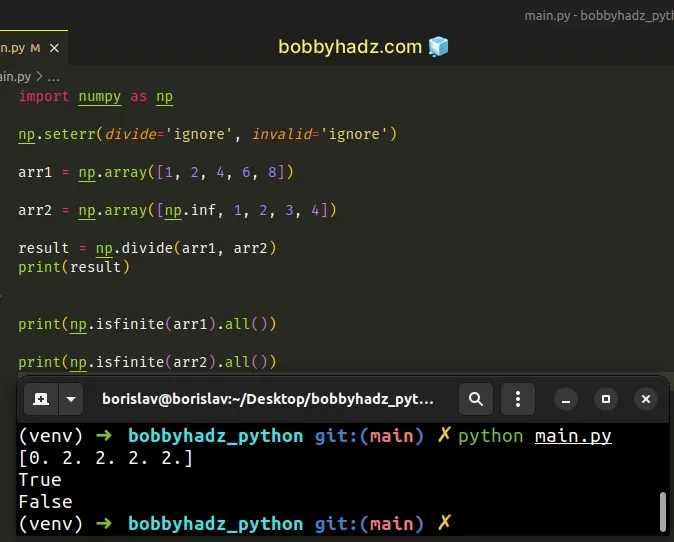
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 4, 6, 8]) arr2 = np.array([np.inf, 1, 2, 3, 4]) result = np.divide(arr1, arr2) print(np.isfinite(arr1).all()) # 👉️ True print(np.isfinite(arr2).all()) # 👉️ False
You can use the numpy.isfinite(arr).all() method to check if all values in the
arrays are finite.
The numpy.isfinite() method tests for finiteness (not infinite and not Not a Number).
You can use the numpy.seterr() method if you want to ignore the warning.
import numpy as np np.seterr(divide='ignore', invalid='ignore') arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 4, 6, 8]) arr2 = np.array([np.inf, 1, 2, 3, 4]) result = np.divide(arr1, arr2) print(np.isfinite(arr1).all()) print(np.isfinite(arr2).all())
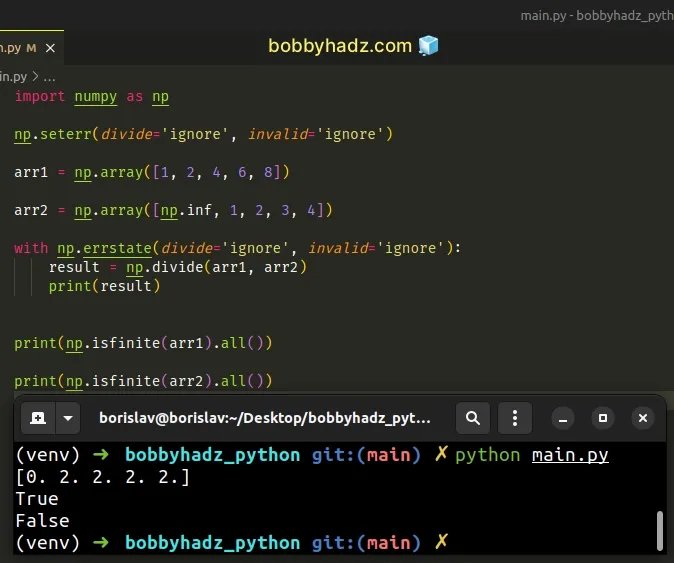
If you only want to disable the warning for a block of code, use the
numpy.errstate() method.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 4, 6, 8]) arr2 = np.array([np.inf, 1, 2, 3, 4]) with np.errstate(divide='ignore', invalid='ignore'): result = np.divide(arr1, arr2) print(result) print(np.isfinite(arr1).all()) print(np.isfinite(arr2).all())
Ignoring the warning is OK most of the time as there are many cases where division by zero is not an issue because it is handled in a later operation.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

