How to load an HTML page in a div using JavaScript
Last updated: Apr 4, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- How to load an HTML page in a div using JavaScript
- How to load an HTML page in a div using fetch in JavaScript
- Load HTML page in a div using jQuery
# How to load an HTML page in a div using JavaScript
To load an HTML page in a div using JavaScript:
- Select the
divelement. - Use the
innerHTMLproperty to set the element's content. - Use the
<object>tag to load an HTML page in thediv.
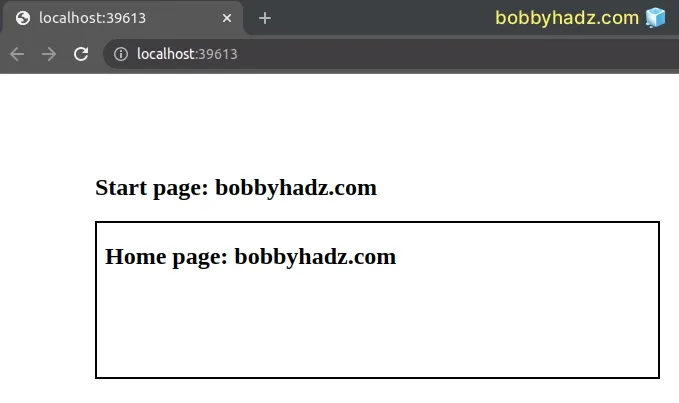
Here is the HTML for the index.html file.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <style> body { margin: 100px; } #box { border: 2px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>Start page: bobbyhadz.com</h2> <!-- 👇️ will load page content in this div --> <div id="box"></div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the HTML for the home.html file that is located in the same
directory.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>Home Page - bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <h2>Home page: bobbyhadz.com</h2> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
const box = document.getElementById('box'); box.innerHTML = '<object width="100%" type="text/html" data="home.html"</object>';
We used the document.getElementById()
method to select the div element by its id attribute.
The next step is to use the innerHTML attribute to set the element's inner HTML content.
The object tag represents an external resource.
Make sure to set the type attribute of the object tag to text/html.
data attribute should be set to the path to the HTML file that you want to load in the div.const box = document.getElementById('box'); box.innerHTML = '<object width="100%" type="text/html" data="home.html"</object>';
The example assumes you have the following folder structure.
my-project/ └── index.html └── home.html └── index.js
Alternatively, you can use the
document.createElement() method to
create the object element.
const box = document.getElementById('box'); const objectTag = document.createElement('object'); objectTag.style.width = '100%'; objectTag.type = 'text/html'; objectTag.data = 'home.html'; box.appendChild(objectTag);
We used the document.createElement method to create the object element and
used dot notation to set its properties.
The last step is to use the appendChild() method to add the element to the page.
# How to load an HTML page in a div using fetch in JavaScript
You can also load an HTML page in a div element using fetch().
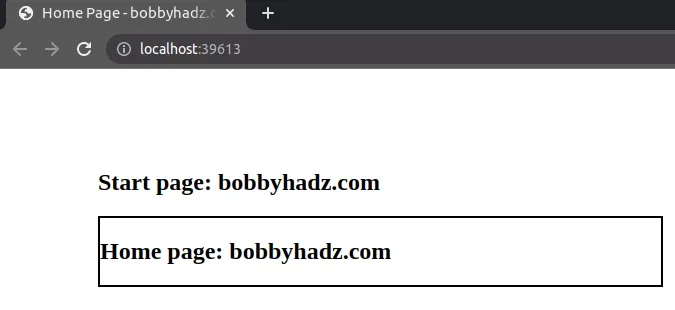
Here is the code for the index.html file.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <style> body { margin: 100px; } #box { border: 2px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>Start page: bobbyhadz.com</h2> <!-- 👇️ will load page content in this div --> <div id="box"></div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the code for the home.html file that is located in the same
directory.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>Home Page - bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <h2>Home page: bobbyhadz.com</h2> </body> </html>
Finally, here is the code for the index.js file.
function loadPage() { const box = document.getElementById('box'); fetch('home.html') .then(response => response.text()) .then(html => { box.innerHTML = html; }) .catch(error => { console.log(error); }); } loadPage();
fetch() method, e.g.fetch('https://example.com/home.html').If you run into issues, try to set the Accept header to text/html when
making the GET request.
function loadPage() { const box = document.getElementById('box'); fetch('home.html', { // 👇️ set Accept header to `text/html` headers: { Accept: 'text/html', }, }) .then(response => response.text()) .then(html => { box.innerHTML = html; }) .catch(error => { console.log(error); }); } loadPage();
We used the fetch() method to fetch the home.html file.
The example assumes you have the following folder structure.
my-project/ └── index.html └── home.html └── index.js
Once the response is converted to text, we can set the innerHTML property on
the box element to the HTML string.
The example above loads the HTML page in a div immediately as the page loads.
Here is an example that loads the HTML page in a div when a button is clicked.
Here is the updated code for the index.html file.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <style> body { margin: 100px; } #box { border: 2px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>Start page: bobbyhadz.com</h2> <button id="btn">Load page</button> <br /> <br /> <!-- 👇️ will load page content in this div --> <div id="box"></div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
The code for the home.html file remains the same.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>Home Page - bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <h2>Home page: bobbyhadz.com</h2> </body> </html>
Here is the code for the index.js file.
const button = document.getElementById('btn'); button.addEventListener('click', () => { loadPage(); }); function loadPage() { const box = document.getElementById('box'); fetch('home.html') .then(response => response.text()) .then(html => { box.innerHTML = html; }) .catch(error => { console.log(error); }); }
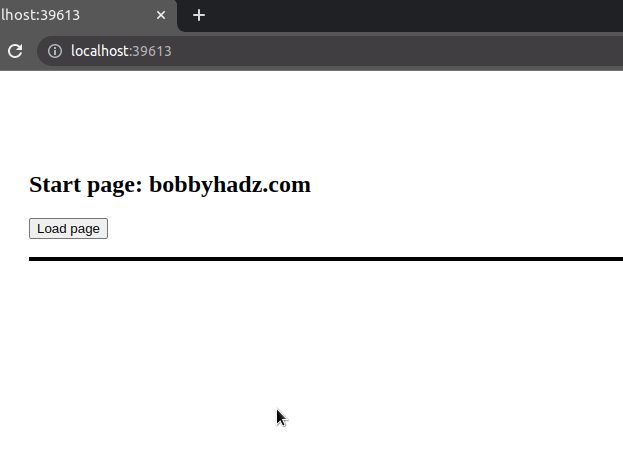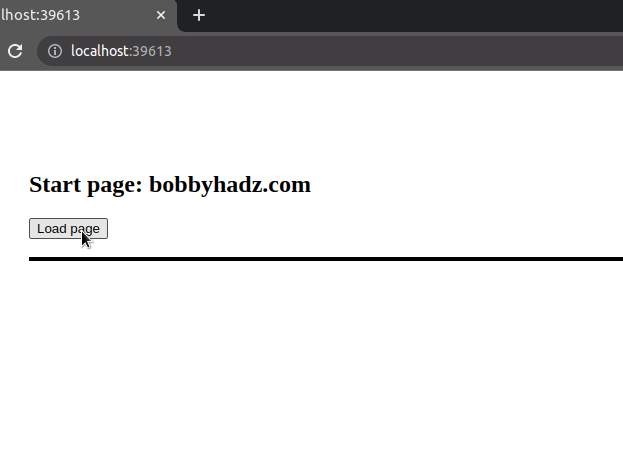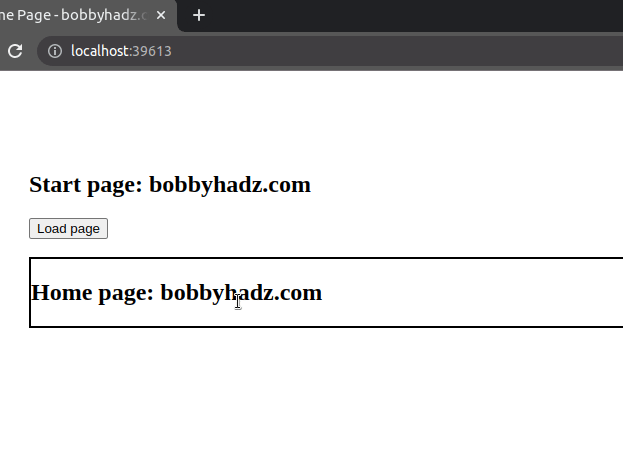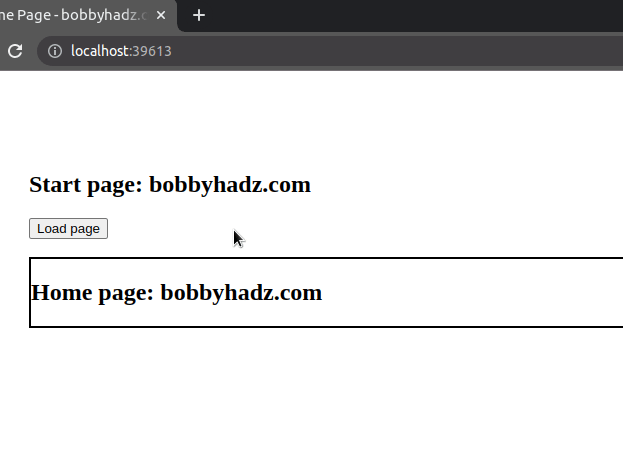
We
added a click event listener to the button.
Every time the button is clicked, its event handler function is invoked.
In the event handler function, we simply call the loadPage() function which
fetches the HTML page and renders it.
If you want to run some code after the page has been loaded in the div, return
the fetch call from the function.
const button = document.getElementById('btn'); button.addEventListener('click', () => { loadPage().then(() => { console.log('Page loaded in the div tag'); }); }); function loadPage() { const box = document.getElementById('box'); return fetch('home.html') .then(response => response.text()) .then(html => { box.innerHTML = html; }) .catch(error => { console.log(error); }); }
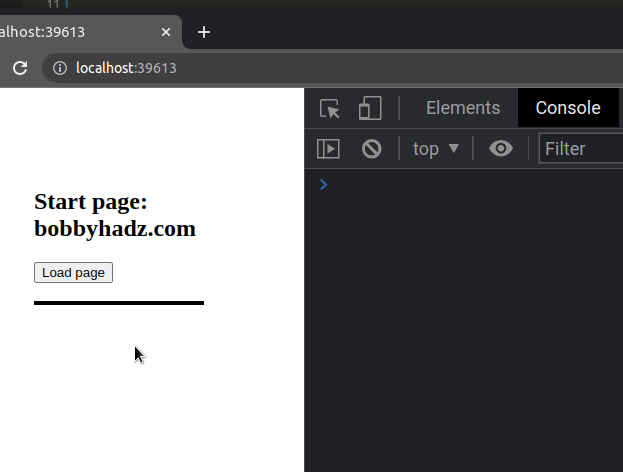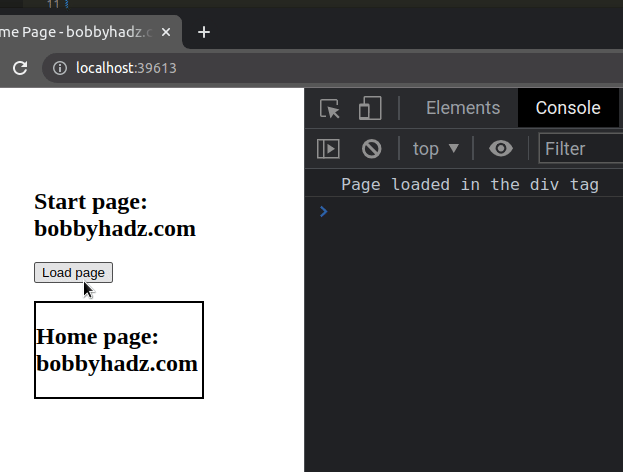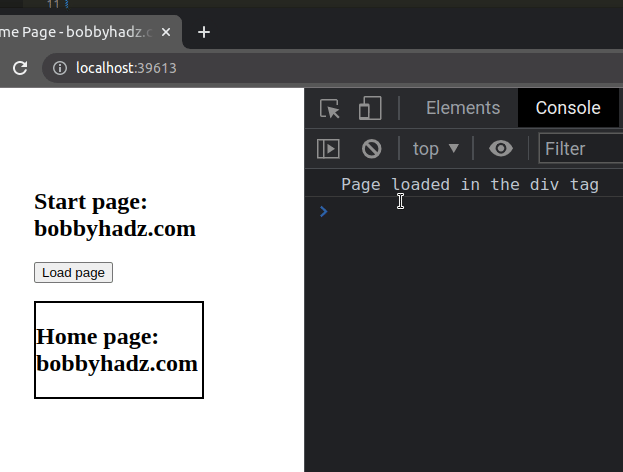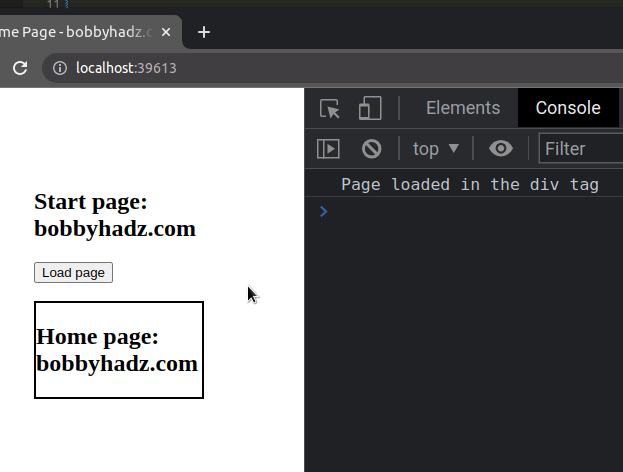
We returned the fetch() call from the loadPage() function and used the
.then() method in the event handler to run code after the page has been loaded
in the div.
Here is an example that loads an HTML page in a div on button click using async/await.
const button = document.getElementById('btn'); button.addEventListener('click', () => { loadPage(); }); async function loadPage() { const box = document.getElementById('box'); try { const response = await fetch('home.html'); const html = await response.text(); box.innerHTML = html; } catch (error) { console.log(error); } }
If you want to run some code after the page is loaded into the div element,
mark the event handler function as async.
const button = document.getElementById('btn'); button.addEventListener('click', async () => { await loadPage(); console.log('HTML page loaded into div'); }); async function loadPage() { const box = document.getElementById('box'); try { const response = await fetch('home.html'); const html = await response.text(); box.innerHTML = html; } catch (error) { console.log(error); } }
# Load HTML page in a div using jQuery
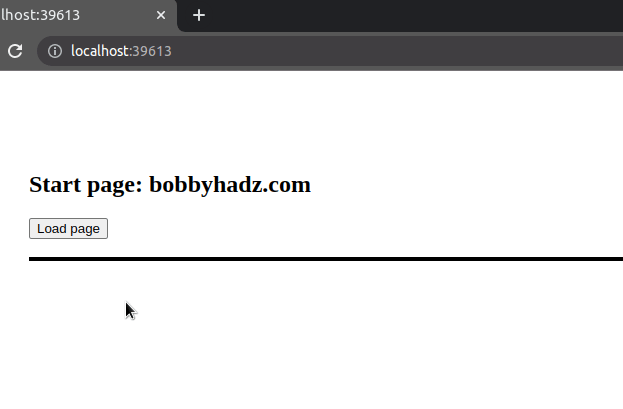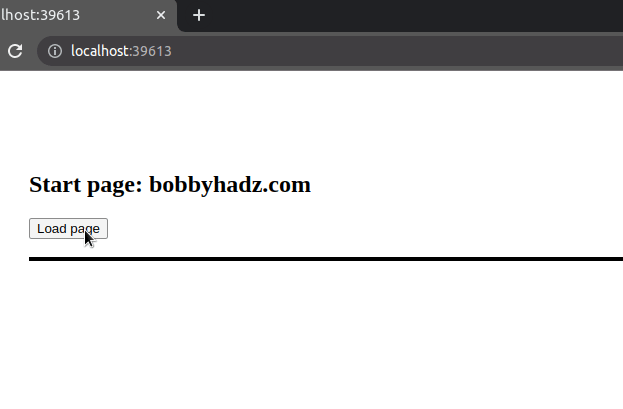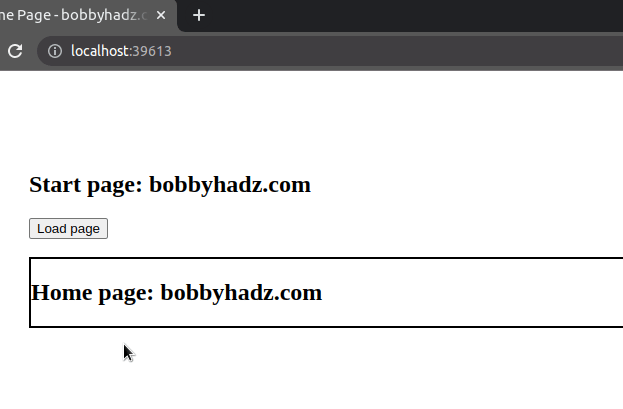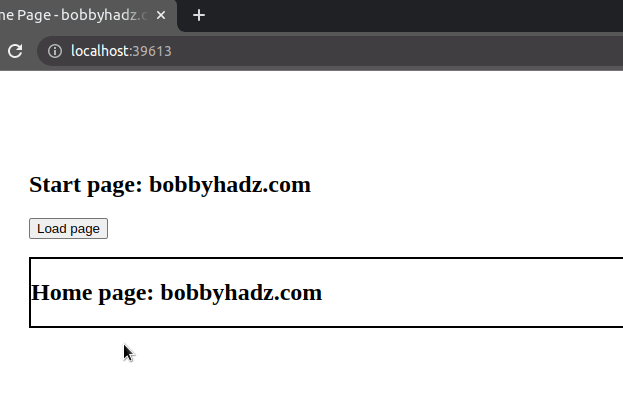
Here is an example that loads an HTML page in a div using jQuery.
Here is the updated code for the index.html file.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <style> body { margin: 100px; } #box { border: 2px solid black; } </style> <script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js" integrity="sha256-/xUj+3OJU5yExlq6GSYGSHk7tPXikynS7ogEvDej/m4=" crossorigin="anonymous" ></script> </head> <body> <h2>Start page: bobbyhadz.com</h2> <button id="btn">Load page</button> <br /> <br /> <!-- 👇️ will load page content in this div --> <div id="box"></div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
Make sure to add the script tag that loads the jQuery library as shown in the
code sample.
The code for the home.html file remains the same.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>Home Page - bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <h2>Home page: bobbyhadz.com</h2> </body> </html>
Here is the updated code for the index.js file.
$(document).ready(function () { $('#btn').on('click', function () { $('#box').load('home.html'); }); });
We added a click event listener to the button element that has an id of
btn.
The last step is to use the jQuery.load() method to load the home.html page
into the div that has an id of box.
If you want to load the HTML page into the div element immediately after the
page loads, remove the click event listener.
$(document).ready(function () { $('#box').load('home.html'); });
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Check if specific Text exists on the Page in JavaScript
- Find the highest z-index on the Page using JavaScript
- How to auto-reload a Page every N seconds using JavaScript
- Fetch API cannot load localhost. URL scheme is not supported
- TypeError: Failed to fetch and CORS in JavaScript
- Axios Network Error when making HTTP request
- How to fetch and display JSON data in HTML using JavaScript
- [DOM] Input elements should have autocomplete attributes

