Find the highest z-index on the Page using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Find the highest z-index on the Page in JavaScript
To find the highest z-index on the page:
- Get an array containing all DOM elements.
- Use the
window.getComputedStyle()method to get thez-indexof each element. - Return the highest of all the
z-indexvalues.
Here is the HTML for the example.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <div style="position: relative; z-index: 3">Bobby Hadz Com</div> <span style="position: relative; z-index: 5">One two three</span> <p style="position: relative; z-index: 8">Apple banana kiwi</p> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
function getMaxZIndex() { return Math.max( ...Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('body *'), el => parseFloat(window.getComputedStyle(el).zIndex), ).filter(zIndex => !Number.isNaN(zIndex)), 0, ); } console.log(getMaxZIndex()); // 👉️ 8
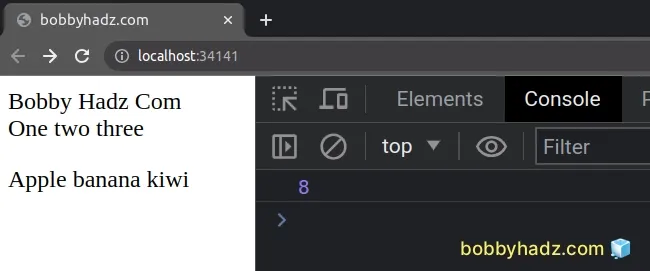
The getMaxZIndex function finds and returns the highest z-index on the page.
The first step is to use the
document.querySelectorAll method to get
a NodeList containing all of the DOM elements.
We used the Array.from() method to
convert the NodeList to an array.
We passed the following 2 arguments to the Array.from() method:
- An array-like object that we want to convert to an array.
- A
mapfunction to call on every element of the array.
The function we call on every element uses the window.getComputedStyle() method to get an object containing the values of all CSS properties of the DOM element.
style.zIndex property on the element because style.zIndex doesn't consider z-indexes set in external stylesheets, whereaswindow.getComputedStyle() does.We passed the result to the parseFloat function, however, the z-index
property is not guaranteed to return a value that can be parsed as a number, it
might return a string - "auto".
If we pass a value of "auto" to the parseFloat function, we would get NaN
(not a number) back.
console.log(parseFloat('auto')); // 👉️ NaN
This is why we used the
Array.filter()
method to remove all NaN values from the array.
function getMaxZIndex() { return Math.max( ...Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('body *'), el => parseFloat(window.getComputedStyle(el).zIndex), ).filter(zIndex => !Number.isNaN(zIndex)), 0, ); }
Now that the array contains only numbers, we are able to use the spread syntax (...) to unpack the values from the array into a call to the Math.max() method
The Math.max() method takes two or more comma-separated numbers and returns
the max value.
console.log(Math.max(3, 5, 8)); // 👉️ 8 console.log(Math.max(-5, 10, 3)); // 👉️ 10
Notice that after unpacking the numbers from the array returned from the
filter() method, we also added a 0 as a parameter to the Math.max()
function.
function getMaxZIndex() { return Math.max( ...Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('body *'), el => parseFloat(window.getComputedStyle(el).zIndex), ).filter(zIndex => !Number.isNaN(zIndex)), 0, ); }
This serves as a default value in case none of the elements on the page have a
z-index set.
If none of the elements on the page have a z-index set the getMaxZIndex
function will return 0.
I've also written an article on how to override an element's !important styles.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

