Check if specific Text exists on the Page in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 5, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Check if Text exists on the Page using JavaScript
To check if specific text exists on the page, use the document.body property
to access the body element and check if the text content of the body contains
the text.
Here is the HTML for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <div id="box" style=" background-color: salmon; width: 150px; height: 150px; " > bobby hadz tutorial </div> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
const text = 'bobby hadz tutorial'; if (document.body.textContent.includes(text)) { console.log('✅ text exists on page'); } else { console.log('⛔️ text does not exist on page'); }
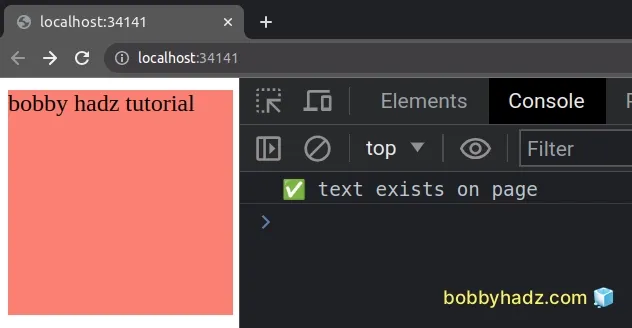
We used the document.body property to get access to the body element.
The textContent property returns the text content of a node and its descendants.
body element, the textContent property returns the text content of all nodes on the page.We used the String.includes() method to check if the text content on the page contains the specified string.
# Check if Text exists on the Page in a case-insensitive manner
Note that the includes method performs a case-sensitive search to determine if
the substring is contained in the string the method was called on.
If you need to ignore the case when comparing the text content and the specific string, convert both of them to lowercase.
const text = 'BOBBY HADZ TUTORIAL'; if ( document.body.textContent .toLowerCase() .includes(text.toLowerCase()) ) { console.log('✅ text exists on page'); } else { console.log('⛔️ text does not exist on page'); }
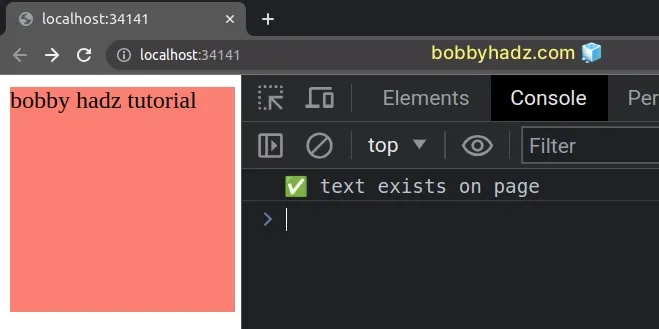
By converting both of the values to lowercase, we are able to perform a case-insensitive comparison.
For example, this code snippet checks if the div element contains the specific
text.
const text = 'BOBBY HADZ TUTORIAL'; const box = document.getElementById('box'); if (box.textContent.toLowerCase().includes(text.toLowerCase())) { console.log('text exists on page'); } else { console.log('text does not exist on page'); }
Since the textContent property returns the text content of the element and all
of its descendants, chances are you can select a specific element and check if
it contains the text.
Accessing the textContent property on the body element means that we append
the text content of every single node on the page to a string, which can be slow
on pages with a lot of nested elements.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

