Sort the Keys of an Object in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 6, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Sort the Keys of an Object in JavaScript
To sort the keys of an object:
- Use the
Object.keys()method to get an array of the object's keys. - Call the
sort()method on the array. - Call the
reduce()method to get an object with sorted keys.
const obj = {z: 'three', a: 'one', b: 'two'}; const sorted = Object.keys(obj) .sort() .reduce((accumulator, key) => { accumulator[key] = obj[key]; return accumulator; }, {}); console.log(sorted); // 👉️ {a: 'one', b: 'two', z: 'three'}
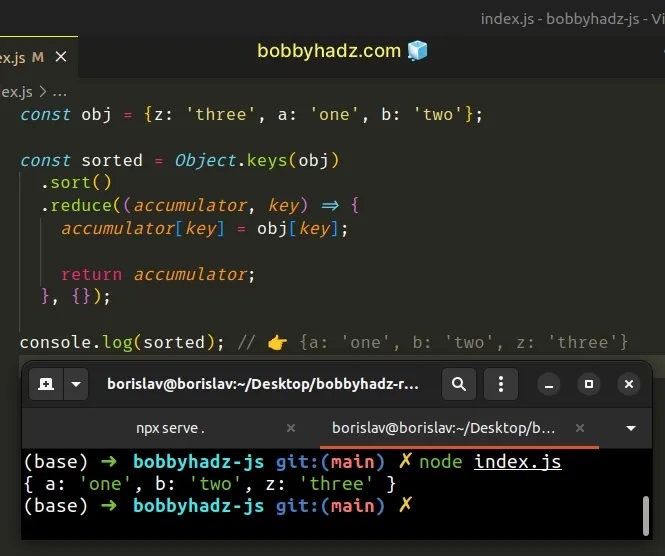
We used the Object.keys() method to get an array of the object's keys.
const obj = {z: 'three', a: 'one', b: 'two'}; // 👇️ ['z', 'a', 'b'] console.log(Object.keys(obj));
The next step is to use the Array.sort() method to sort the array of keys.
const obj = {z: 'three', a: 'one', b: 'two'}; // 👇️ ['a', 'b', 'z'] console.log(Object.keys(obj).sort());
At this point, we have a sorted array containing the object's keys.
The last thing we have to do is use the Array.reduce() method to iterate over the sorted array of keys and assign each key-value pair to an object.
const obj = {z: 'three', a: 'one', b: 'two'}; // 👇️ ['a', 'b', 'z'] console.log(Object.keys(obj).sort()); const sorted = Object.keys(obj) .sort() .reduce((accumulator, key) => { accumulator[key] = obj[key]; return accumulator; }, {}); console.log(sorted); // 👉️ {a: 'one', b: 'two', z: 'three'}
The function we passed to the reduce() method gets called with each element
(key) in the array.
We provided an empty object as the initial value for the accumulator
variable.
On each iteration, we assign the key-value pair to the accumulator object and
return the result.
The value we return from the callback function gets passed as the accumulator
on the next iteration.
After the last iteration, the object contains all of the key-value pairs in a sorted order.
Make sure to pass an empty object as the second parameter to the reduce
method. This is the initial value for the accumulator variable.
Now you can iterate over the sorted object by using the Object.keys() and the
forEach() methods.
const obj = {z: 'three', a: 'one', b: 'two'}; // 👇️ ['a', 'b', 'z'] console.log(Object.keys(obj).sort()); const sorted = Object.keys(obj) .sort() .reduce((accumulator, key) => { accumulator[key] = obj[key]; return accumulator; }, {}); Object.keys(sorted).forEach(key => { console.log(key, sorted[key]); // 👉️ a one, b two, z three });
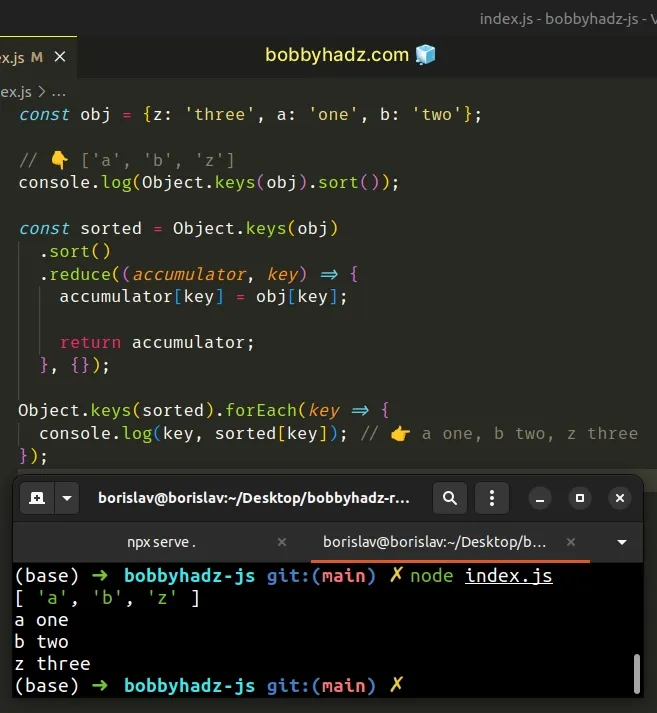
The function we passed to the forEach() method gets called with each element
(key) in the array.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to sort a Set in JavaScript
- Sort an Array of Objects by Boolean property in JavaScript
- Sort an Array of Objects by Date property in JavaScript
- Sort an Array of Strings in Descending order in JavaScript
- Sort an Array with NULL values coming last in JavaScript
- Sort an Array without Mutation using JavaScript
- Sort an Array of strings ignoring the Case in JavaScript
- How to sort a Map in JavaScript
- Convert JSON object to Buffer and vice versa in Node.js

