How to sort a Set in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Sort a Set in JavaScript
To sort a Set in JavaScript:
- Use the
Array.from()method to convert theSetto an array. - Use the
Array.sort()method to sort the array. - Convert the array back to a
Setobject.
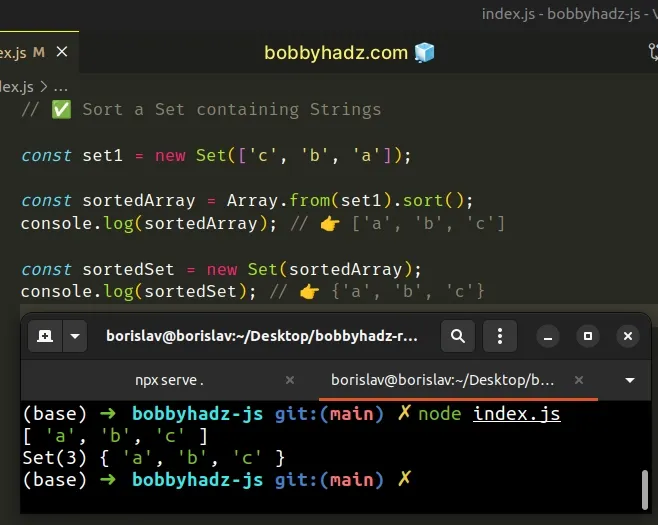
// ✅ Sort a Set containing Strings const set1 = new Set(['c', 'b', 'a']); const sortedArray = Array.from(set1).sort(); console.log(sortedArray); // 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c'] const sortedSet = new Set(sortedArray); console.log(sortedSet); // 👉️ {'a', 'b', 'c'}
If you need to sort a Set containing numbers, you have to pass a function to
the Array.sort() method.
// ✅ Sort a Set containing Numbers const set1 = new Set([300, 100, 700]); // 👇️ sorts numbers in Ascending order const sortedArray = Array.from(set1).sort((a, b) => a - b); console.log(sortedArray); // 👉️ [100, 300, 700] const sortedSet = new Set(sortedArray); console.log(sortedSet); // 👉️ {100, 300, 700}
We used the Array.from() method to
convert the Set object to an array, so we can call the
Array.sort() method on the
array.
Notice that when sorting numbers, we have to pass a function as a parameter to
the sort() method, whereas with strings, we don't.
The parameter we passed to the sort() method is a function that defines the
sort order.
If you don't provide the parameter, the array elements get converted to strings and sorted according to their UTF-816 code unit values.
This is not what we want when working with Set objects that contain numbers,
however, it is exactly what we want when comparing strings.
After we have sorted the array, we pass it to the
Set() constructor to convert it back to
a Set.
If you have to do this often, define reusable functions.
function sortStringSet(set) { const sortedArray = Array.from(set).sort(); const sortedSet = new Set(sortedArray); return sortedSet; } // 👇️ Set(3) { 'a', 'b', 'c' } console.log(sortStringSet(new Set(['c', 'b', 'a']))); // 👇️ Set(3) { 'a', 'c', 'z' } console.log(sortStringSet(new Set(['c', 'z', 'a'])));
The sortStringSet() function takes a Set containing strings as a parameter
and sorts the Set.
You can also define a sortNumbersSet() function.
function sortNumbersSet(set) { const sortedArray = Array.from(set).sort((a, b) => a - b); const sortedSet = new Set(sortedArray); return sortedSet; } // 👇️ Set(3) { 100, 300, 700 } console.log(sortNumbersSet(new Set([700, 100, 300]))); // 👇️ Set(3) { 100, 500, 600 } console.log(sortNumbersSet(new Set([500, 600, 100])));
The function takes a numeric Set as a parameter and sorts the Set.
# Sort a Set using spread syntax (...)
Alternatively, you can use the
spread syntax (...) to
convert the Set to an array.
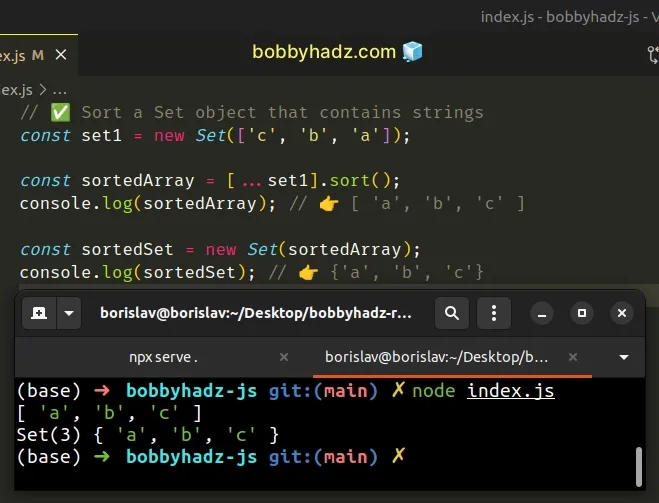
// ✅ Sort a Set object that contains strings const set1 = new Set(['c', 'b', 'a']); const sortedArray = [...set1].sort(); console.log(sortedArray); // 👉️ [ 'a', 'b', 'c' ] const sortedSet = new Set(sortedArray); console.log(sortedSet); // 👉️ {'a', 'b', 'c'}
If your Set object contains numbers, pass a function to the Array.sort()
method.
const numbersSet = new Set([300, 100, 700]); const sortedNumbers = [...numbersSet].sort((a, b) => a - b); console.log(sortedNumbers); // 👉️ [100, 300, 700] const sortedNumbersSet = new Set(sortedNumbers); console.log(sortedNumbersSet); // 👉️ {100, 300, 700}
The code samples achieve the same result as the ones that used the
Array.from() method.
The spread syntax (...) simply unpacks the elements of the Set into an array.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Sort an Array of Objects by Boolean property in JavaScript
- Sort an Array of Objects by Date property in JavaScript
- Sort an Array of Strings in Descending order in JavaScript
- Sort an Array with NULL values coming last in JavaScript
- Sort an Array without Mutation using JavaScript
- Sort an Array of strings ignoring the Case in JavaScript
- How to sort a Map in JavaScript
- Sort the Keys of an Object in JavaScript

