Convert JSON object to Buffer and vice versa in Node.js
Last updated: Apr 5, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Convert JSON object to Buffer and vice versa in Node.js
To convert JSON to a Buffer in Node.js:
- Use the
JSON.stringify()method to convert the JavaScript object to a JSON string. - Use the
Buffer.from()method to convert the JSON string to a buffer.
const obj = { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500, }; const buf = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(obj)); // 👇️ <Buffer 7b 22 69 64 22 3a 31 2c 22 6e 61 6d 65 22 3a 22 62 6f 62 62 79 20 68 61 64 7a 22 2c 22 73 61 6c 61 72 79 22 3a 35 30 30 7d> console.log(buf); // 👇️ {"id":1,"name":"bobby hadz","salary":500} console.log(buf.toString());
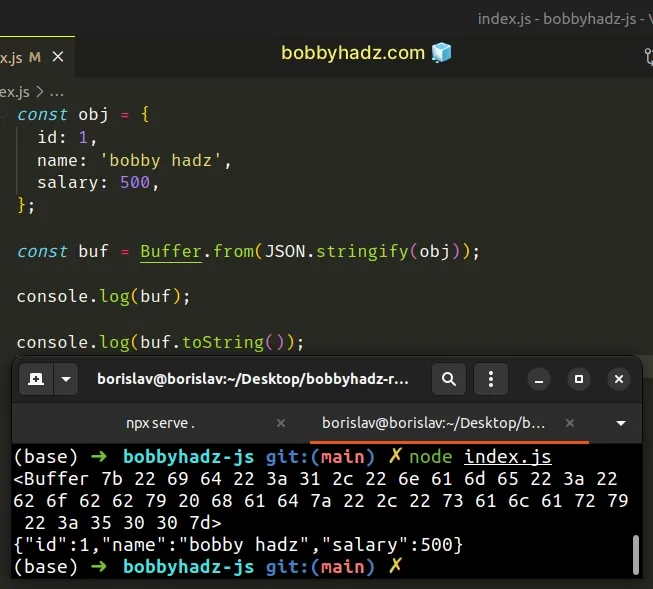
The JSON.stringify() method converts a JavaScript value to a JSON string.
const obj = { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500, }; // 👇️ {"id":1,"name":"bobby hadz","salary":500} console.log(JSON.stringify(obj));
The Buffer.from method takes the following 2 parameters:
- a string - A string to encode.
- encoding - The encoding of the string. Defaults to
utf8if not specified.
We didn't specify an encoding and used the default of utf8.
The Buffer.from() method creates a new Buffer that contains the string.
If you need to print the Buffer in a readable format, call the toString()
method.
const obj = { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500, }; const buf = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(obj)); console.log(buf); // 👇️ {"id":1,"name":"bobby hadz","salary":500} console.log(buf.toString());
Buffers store binary data, so in order to print the contents of a buffer in a readable format, we convert the buffer to a string.
# Converting the Buffer back to an object
If you need to convert the Buffer back to an object, use the
JSON.parse method.
const obj = { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500, }; const buf = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(obj)); // 👇️ convert buffer back to object const objAgain = JSON.parse(buf); console.log(objAgain); // 👉️ { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500 } console.log(typeof objAgain); // 👉️ object console.log(objAgain.id); // 👉️ 1 console.log(objAgain.name); // 👉️ bobby hadz console.log(objAgain.salary); // 👉️ 500
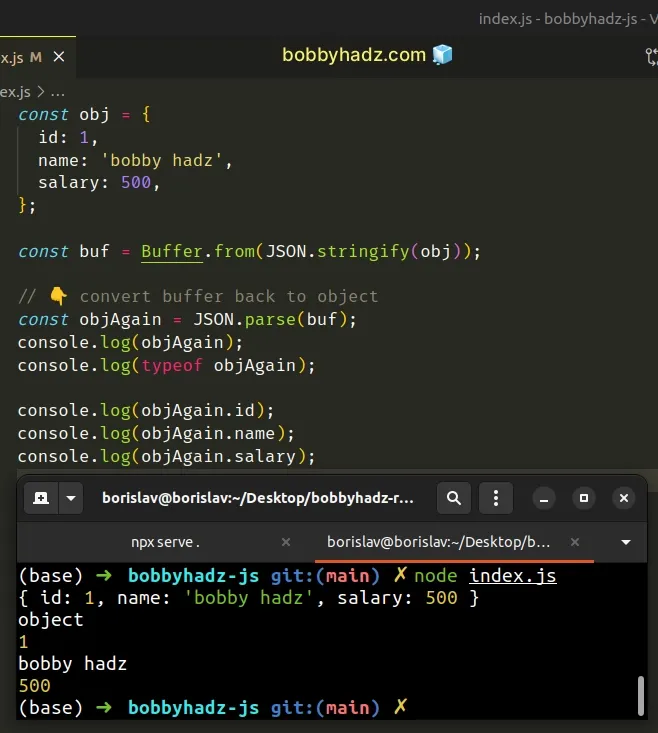
The JSON.parse() method can be called with a Buffer and converts the buffer
to a JavaScript object.
# Converting an Object to a buffer using v8 serialize()
You can also use the serialize() method form the v8 module to convert a
JavaScript object to a Node.js Buffer.
However, there is a caveat that the serialize() method comes from the v8
module.
Therefore the Buffer can only be used in Node.js applications.
import {serialize, deserialize} from 'v8'; const obj = { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500, }; const buf = serialize(obj); // 👇️ <Buffer ff 0f 6f 22 02 69 64 49 02 22 04 6e 61 6d 65 22 0a 62 6f 62 62 79 20 68 61 64 7a 22 06 73 61 6c 61 72 79 49 e8 07 7b 03> console.log(buf); const objAgain = deserialize(buf); // 👇️ { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500 } console.log(objAgain);
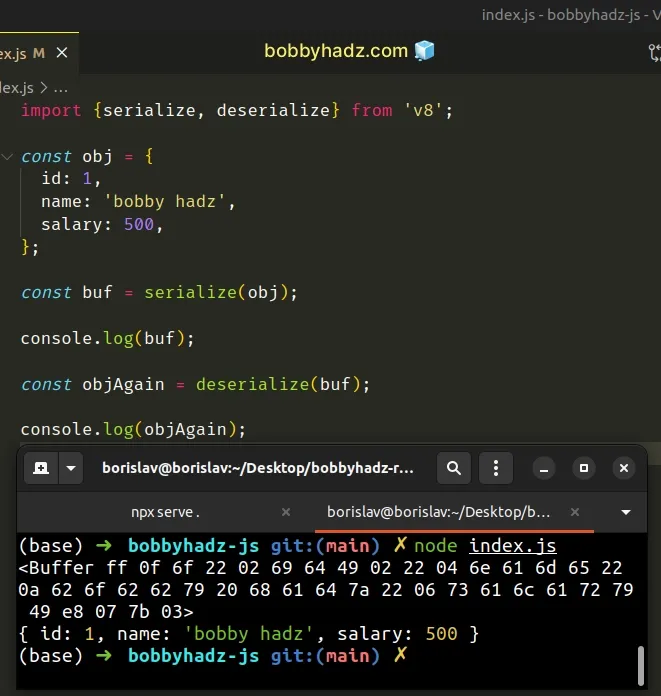
The code sample above uses the ES6 modules import/export syntax.
Use the following import statement if you use CommonJS require().
const {serialize, deserialize} = require('v8'); const obj = { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500, }; const buf = serialize(obj); // 👇️ <Buffer ff 0f 6f 22 02 69 64 49 02 22 04 6e 61 6d 65 22 0a 62 6f 62 62 79 20 68 61 64 7a 22 06 73 61 6c 61 72 79 49 e8 07 7b 03> console.log(buf); const objAgain = deserialize(buf); // 👇️ { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500 } console.log(objAgain);
The serialize method serializes the supplied value into a buffer.
The deserialize method
takes a Buffer that was returned from the serialize() method as a parameter.
The deserialize method reads a JavaScript value from the given Buffer.
Another thing to keep in mind is that you won't get legible results if you call
the toString() method on the Buffer.
import {serialize, deserialize} from 'v8'; const obj = { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500, }; const buf = serialize(obj); // �o"idI"name" // bobby hadz"salaryI�{ console.log(buf.toString());
However, this shouldn't be an issue as you can just console.log the
deserialized value.
# Converting an Object to a buffer using BSON
You can also use the bson (binary JSON) module to convert an object to a buffer.
import {serialize, deserialize} from 'bson'; // or import using CommonJS // const {serialize, deserialize} = require('bson'); const obj = { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500, }; const buf = serialize(obj); // 👇️ <Buffer ff 0f 6f 22 02 69 64 49 02 22 04 6e 61 6d 65 22 0a 62 6f 62 62 79 20 68 61 64 7a 22 06 73 61 6c 61 72 79 49 e8 07 7b 03> console.log(buf); const objAgain = deserialize(buf); // 👇️ { id: 1, name: 'bobby hadz', salary: 500 } console.log(objAgain);
Note that you have to have the bson module installed to be able to run the
code sample.
# with NPM npm install bson # or with YARN yarn add bson
The serialize() method takes an object and returns a Buffer.
The deserialize() method takes a buffer and returns a JavaScript object.
I've also written an article on how to convert a String to a Byte Array in JavaScript.

