How to Convert an Array to a Set in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 2, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Convert an Array to Set in JavaScript
- Convert an Array of Objects to a Set
- Add Array of Values to an Existing Set using spread syntax
- Add an Array of Values to an Existing Set using a
for...ofloop
# Convert an Array to Set in JavaScript
Use the Set() constructor to convert an array to a Set, e.g.
const set = new Set(arr);.
The Set() constructor is used to create Set objects that store unique
values of any type.
// ✅ Convert an Array to a Set const arr = ['a', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'c']; // 👇️ {'a', 'b', 'c'} const set = new Set(arr); console.log(set.size); // 👉️ 3 console.log(set.has('c')); // 👉️ true // ------------------------------------------ // ✅ Convert an Array of Objects to a Set const arr2 = [ {id: 1, letter: 'a'}, {id: 2, letter: 'b'}, {id: 3, letter: 'c'}, ]; const set2 = new Set(arr2.map(obj => obj.letter)); // 👇️ Set(3) { 'a', 'b', 'c' } console.log(set2);
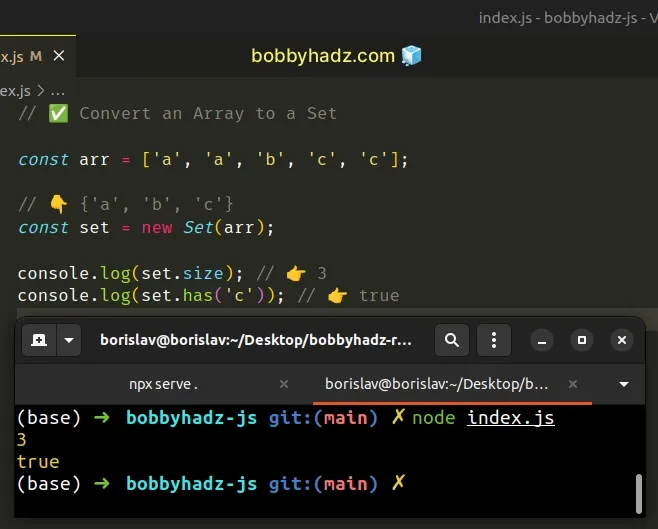
The
Set
object only stores unique values. Even if the supplied array contains
duplicates, they don't get added to the Set.
const arr = ['a', 'a', 'a']; const set = new Set(arr); console.log(set); // 👉️ Set(1) { 'a' } console.log(set.size); // 👉️ 1
The only parameter the Set() constructor takes is an iterable.
Set() constructor, all of the array's elements get added to the Set (without the duplicates).If you need to convert the Set back to an array, use the
spread syntax (...).
const arr = ['a', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'c']; // 👇️ {'a', 'b', 'c'} const set = new Set(arr); const newArr = [...set]; // 👇️ ['a', 'b', 'c'] console.log(newArr);
The spread syntax (...) unpacks the values of the Set into the new array.
You can also use the Array.from() method to convert the Set back to an
array.
const arr = ['a', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'c']; // 👇️ {'a', 'b', 'c'} const set = new Set(arr); const newArr = Array.from(set); // 👇️ ['a', 'b', 'c'] console.log(newArr);
The Array.from() method creates an array from the provided iterable.
If you need to convert an array of objects to a Set containing only the values
of a specific property, use the Array.map() method.
# Convert an Array of Objects to a Set
To convert an Array of objects to a Set:
- Use the
Array.map()method to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, access a specific property and return its value.
- Use the
Set()constructor to convert the array to aSetobject.
const arr = [ {id: 1, letter: 'a'}, {id: 2, letter: 'b'}, {id: 3, letter: 'c'}, ]; const set = new Set(arr.map(obj => obj.letter)); // 👇️ Set(3) { 'a', 'b', 'c' } console.log(set);
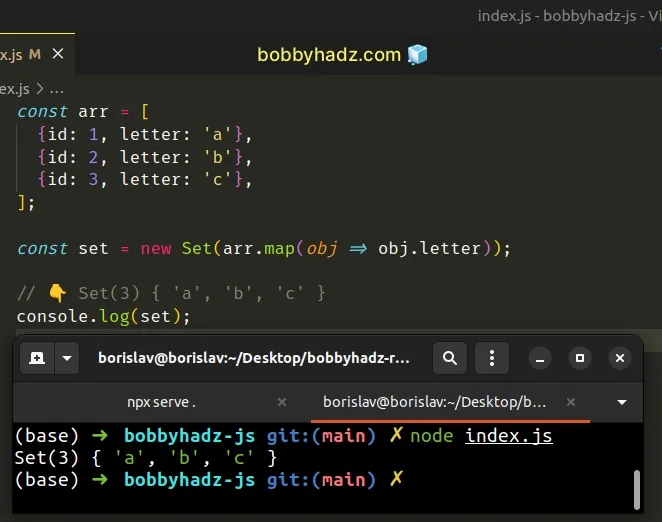
The function we passed to the Array.map() method gets called with each element (object) in the array.
On each iteration, we access the letter property on the object and return the
result.
const arr = [ {id: 1, letter: 'a'}, {id: 2, letter: 'b'}, {id: 3, letter: 'c'}, ]; // 👇️ ['a', 'b', 'c'] console.log(arr.map(obj => obj.letter)); const set = new Set(arr.map(obj => obj.letter)); // 👇️ Set(3) { 'a', 'b', 'c' } console.log(set);
The output of the Array.map() method is an array containing all of the values
of the letter property.
The last step is to pass the array of values to the Set() constructor.
# Convert an Array to a Set using Array.forEach()
This is a three-step process:
- Declare a new variable that stores an empty
Setobject. - Use the
Array.forEach()method to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, use the
Set.add()method to add the element to theSet.
const arr = ['a', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'c']; const set = new Set(); arr.forEach(element => { set.add(element); }); // 👇️ Set(3) { 'a', 'b', 'c' } console.log(set);
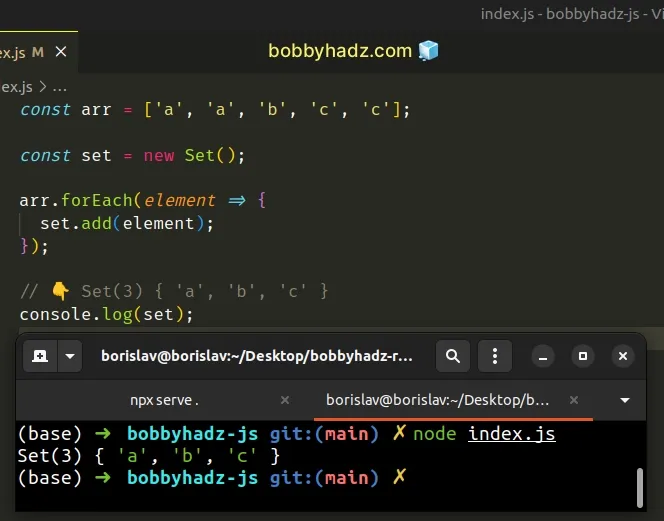
The function we passed to the Array.forEach() method gets called with each element in the array.
On each iteration, we use the set.add() method to add the element to a new
Set object.
The Set.add() method inserts a new element
with the supplied value into a Set object, if the value is not already in the
Set.
Set constructor, but it is useful when you need to process the values before adding them to the Set.You can also use the Array.reduce() method to convert an array to a Set
object.
# Convert an Array to a Set using Array.reduce()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array.reduce()method to iterate over the array. - Initialize the
accumulatorvariable to an emptySet. - On each iteration, add the element to the
Set.
const arr = ['a', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'c']; const set = arr.reduce((accumulator, current) => { accumulator.add(current); return accumulator; }, new Set()); // 👇️ Set(3) { 'a', 'b', 'c' } console.log(set);
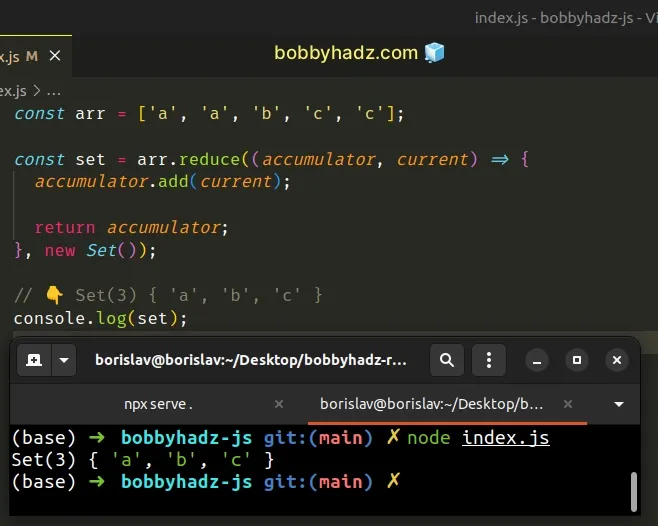
The function we passed to the Array.reduce() method gets called for each element in the array.
The initial value of the accumulator variable is an empty Set because that's
what we passed as the second argument to the Array.reduce() method.
On each iteration, we use the Set.add() method to add the current element to
the Set object.
# Add Array of Values to an Existing Set using spread syntax (...)
This is a three-step process:
- Create a new
Setusing theSet()constructor. - Unpack the values of the existing
Setand the array into a newSet. - The new
Setwill contain the values of the originalSetand the array.
const set1 = new Set(); const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']; const newSet = new Set([...set1, ...arr]); console.log(newSet); // 👉️ Set(3) { 'bobby', 'hadz', 'com' }
We created a new Set using the Set() constructor and used the spread syntax
(...) to unpack the values of the existing set and the array into the new Set.
Set objects and arrays are iterable, so we are able to use the spread syntax
(...) to unpack them into a new Set.
You can also use a for...of loop to add an array of values to an existing
Set.
# Add an Array of Values to an Existing Set using a for...of loop
This is a two-step process:
- Use a
for...ofloop to iterate over the array. - Use the
Set.add()method to add each array element to theSetobject.
const set1 = new Set(); const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']; for (const element of arr) { set1.add(element); } console.log(set1); // 👉️ Set(3) { 'bobby', 'hadz', 'com' }
The for...of statement is
used to loop over iterable objects like arrays, strings, Map, Set and
NodeList objects and generators.
On each iteration, we use the Set.add() method to add the current element to
the Set object.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Convert an Array of Objects to an Array of Values in JS
- How to convert an Array to a Map in JavaScript
- Convert Array of Strings to Array of Numbers in JavaScript
- Convert Array to String (with and without Commas) in JS
- Convert an Array to an Object using JavaScript
- Convert Bytes to KB, MB, GB or TB using JavaScript

