How to Remove an Element from a Set using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·2 min

# Remove an Element from a Set in JavaScript
Use the Set.delete() method to remove an element from a Set, e.g.
set.delete('element').
If the value exists in the Set, it gets removed from the Set object and
true is returned, otherwise, the method returns false.
const set1 = new Set(['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']); set1.delete('hadz'); console.log(set1); // 👉️ Set(2) { 'bobby', 'com' } console.log(set1.has('hadz')); // 👉️ false
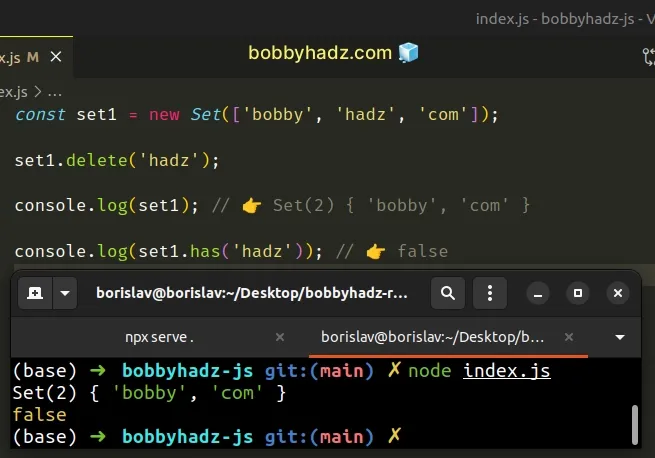
We used the
Set.delete()
method to remove an element from a Set.
The only parameter the method takes is the value we want to remove.
The delete method returns true if the value was in the Set and false
otherwise.
const set1 = new Set(); set1.add('bobby'); set1.add('hadz'); set1.add('com'); console.log(set1); // 👉️ Set(3) { 'bobby', 'hadz', 'com' } console.log(set1.delete('bobby')); // 👉️ true console.log(set1.delete('asdf')); // 👉️ false
# Remove an Object or Array from a Set object in JavaScript
If you need to delete an object or array from a Set, you need to have a
reference to the object or array, or use the forEach() method to get a
reference.
const set1 = new Set([{id: 1}, {id: 2}]); console.log(set1); // 👉️ {{id: 1}, {id: 2}} set1.forEach(obj => { if (obj.id === 2) { set1.delete(obj); } }); console.log(set1); // 👉️ { {id: 1} }
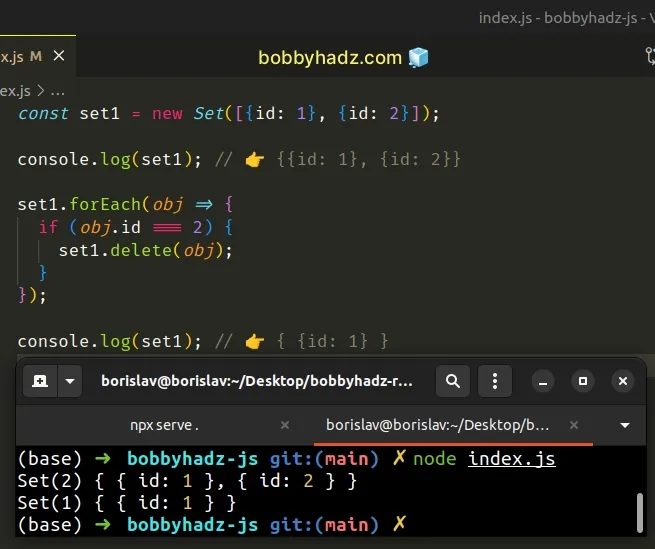
We used the Set.forEach() method
to iterate over the Set and get a reference to the object we wanted to delete.
The function we passed to the forEach() method gets called with each element
in the Set.
On each iteration, we check if the current object is the one we want to delete.
There's an easier way to do this if you have a direct reference to the object.
const obj = {id: 1}; const set1 = new Set([obj, {id: 2}]); set1.delete(obj); console.log(set1); // 👉️ { {id: 2} }
In most situations, you will not have a direct reference to the object or array
you're trying to remove from the Set, so using the forEach() method is a
great alternative.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Check if a Map or a Set is Empty in JavaScript
- How to Convert an Array to a Set in JavaScript
- How to convert a Set to JSON in JavaScript
- How to Convert a Set to a String in JavaScript
- Create a copy of a Map or a Set in JavaScript
- Get the Difference between Two Sets using JavaScript
- How to Get the First Element of a Set in JavaScript
- Get the Intersection of two Arrays or Sets in JavaScript
- How to get the Length of a Set in JavaScript
- Get the Min/Max Values in a Map or a Set in JavaScript

