Get the Min/Max Values in a Map or a Set in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
# Get the Min/Max Values in a Map in JavaScript
To get the min and max values in a Map:
- Use the
values()method to get an iterator of the Map's values. - Pass the iterator to the
Math.min()andMath.max()methods. - The
Math.min()andMath.max()methods return the lowest and highest of the passed-in numbers.
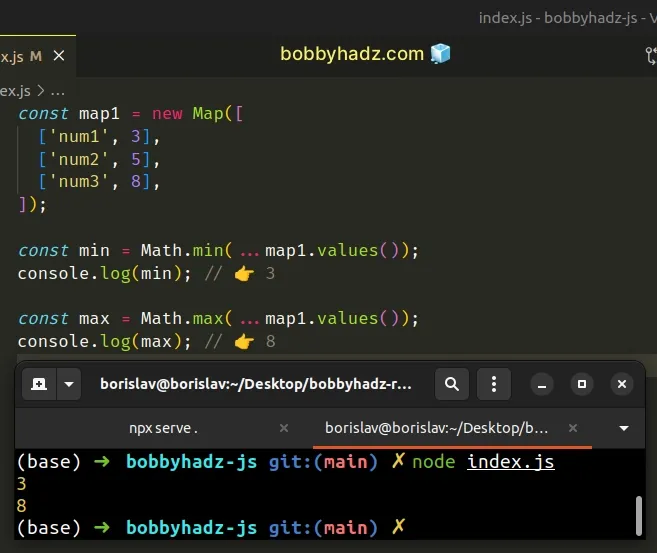
const map1 = new Map([ ['num1', 3], ['num2', 5], ['num3', 8], ]); const min = Math.min(...map1.values()); console.log(min); // 👉️ 3 const max = Math.max(...map1.values()); console.log(max); // 👉️ 8
The Map.values() method returns an iterator object containing the Map's values.
const map1 = new Map([ ['num1', 3], ['num2', 5], ['num3', 8], ]); // 👇️ [Map Iterator] { 3, 5, 8 } console.log(map1.values());
We can't pass the iterator object directly to the Math.max() and Math.min() methods because they expect multiple, comma-separated numbers and not an iterator.
const min = Math.min(3, 5, 8); console.log(min); // 👉️ 3 const max = Math.max(3, 5, 8); console.log(max); // 👉️ 8
We used the
spread syntax (...) to
unpack the values of the iterator objects in the call to the Math.min() and
Math.max() methods.
const map1 = new Map([ ['num1', 3], ['num2', 5], ['num3', 8], ]); const min = Math.min(...map1.values()); console.log(min); // 👉️ 3 const max = Math.max(...map1.values()); console.log(max); // 👉️ 8
You can imagine that the spread syntax passes the values of the iterator object as comma-separated arguments to the methods.
The Math.min() method returns the smallest of the supplied parameters.
The Math.max() method returns the largest of the given numbers.
If you need to get the min and max values in a Map and the corresponding keys,
use the Array.reduce() method.
# Get the Min/Max Values in a Map using reduce()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
reduce()method to iterate over the Map's entries. - Check if each value is the
minormaxvalue. - Return the corresponding key-value pair.
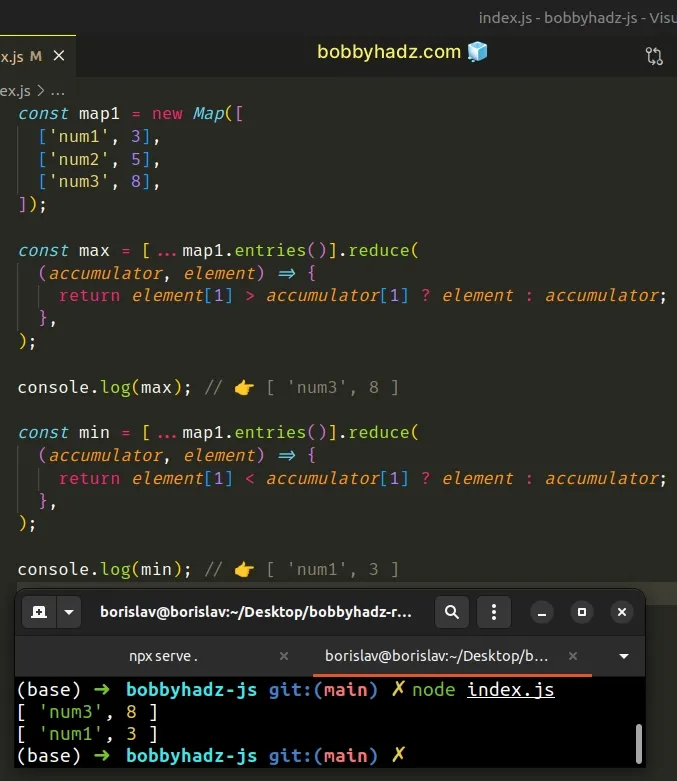
const map1 = new Map([ ['num1', 3], ['num2', 5], ['num3', 8], ]); const max = [...map1.entries()].reduce( (accumulator, element) => { return element[1] > accumulator[1] ? element : accumulator; }, ); console.log(max); // 👉️ [ 'num3', 8 ] const min = [...map1.entries()].reduce( (accumulator, element) => { return element[1] < accumulator[1] ? element : accumulator; }, ); console.log(min); // 👉️ [ 'num1', 3 ]
The
Map.entries()
method returns an iterator object containing the [key, value] pairs for each
element in the Map.
const map1 = new Map([ ['num1', 3], ['num2', 5], ['num3', 8], ]); // 👇️ [Map Entries] { [ 'num1', 3 ], [ 'num2', 5 ], [ 'num3', 8 ] } console.log(map1.entries());
The function we passed to the Array.reduce() method gets called for each element in the array.
On each iteration, we check if the current value is greater than (max) or less than (min) the accumulator and return the element or the accumulator.
Whatever we return from the callback function gets passed as the accumulator
on the next iteration.
The code sample returns arrays containing the key and value of the min and max elements.
# Get the Min/Max Values in a Set in JavaScript
To get the min and max values in a Set:
- Use the spread syntax to unpack the
Setin calls to theMath.minandMath.maxmethods. - The
Math.minmethod will return the min value in theSet. - The
Math.maxmethod will return the max value in theSet.
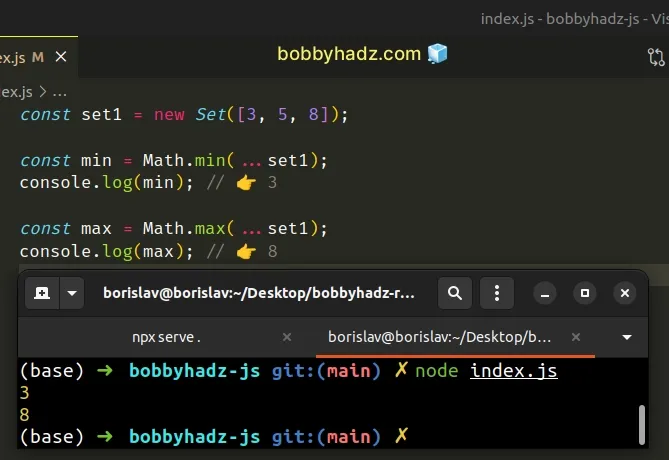
const set1 = new Set([3, 5, 8]); const min = Math.min(...set1); console.log(min); // 👉️ 3 const max = Math.max(...set1); console.log(max); // 👉️ 8
Set objects are iterators, just like arrays.
We can't pass the iterator object directly to the Math.max() and Math.min() methods because they expect multiple, comma-separated numbers and not an iterator.
const min = Math.min(1, 3, 5); console.log(min); // 👉️ 1 const max = Math.max(1, 3, 5); console.log(max); // 👉️ 5
The Math.min() method returns the smallest of the supplied parameters.
The Math.max() method returns the largest of the given numbers.
We used the
spread syntax (...) to
unpack the values of the Set in the calls to the Math.min() and Math.max()
methods.
const set1 = new Set([3, 5, 8]); const min = Math.min(...set1); console.log(min); // 👉️ 3 const max = Math.max(...set1); console.log(max); // 👉️ 8
You can imagine that the spread syntax passes the values of the Set as
multiple, comma-separated arguments to the methods.
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
function setMinMax(set) { const min = Math.min(...set); const max = Math.max(...set); return {min, max}; } const set1 = new Set([3, 5, 8]); const result = setMinMax(set1); console.log(result); // 👉️ { min: 3, max: 8 } console.log(result.min); // 👉️ 3 console.log(result.max); // 👉️ 8
The function takes a Set as a parameter and returns an object with min and
max properties.
The min property stores the min value in the Set and the max property
stores the max value.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

