Check if a Map or a Set is Empty in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
# Check if a Map is Empty in JavaScript
Use the size property to check if a Map is empty, e.g. map.size === 0. The
size property returns the number of elements in the Map.
When accessed on an empty Map, the size property returns 0.
const map1 = new Map(); console.log(map1.size); // 👉️ 0 if (map1.size === 0) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ map is empty'); } else { console.log('⛔️ map is not empty'); }
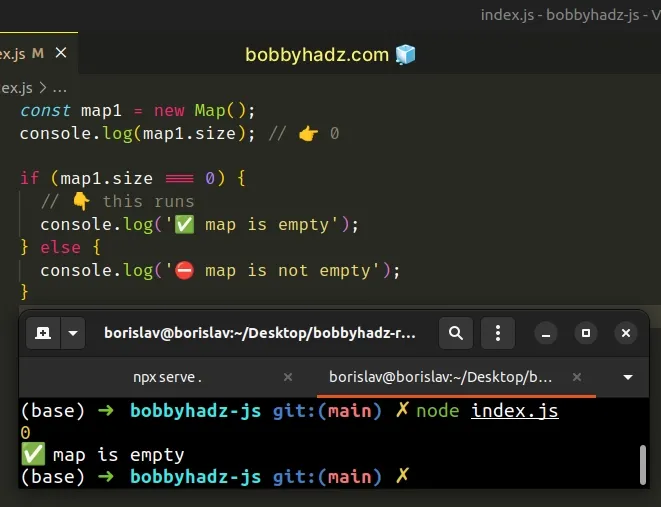
We used the Map.size property on the Map
to check if it's empty.
The property returns the number of elements the Map stores.
const map2 = new Map(); map2.set('country', 'Chile'); console.log(map2.size); // 👉️ 1
The property is very similar to an array's length property, however, it is
read-only and cannot be changed.
const map = new Map(); map.set('country', 'Chile'); console.log(map.size); // 👉️ 1 // ⛔️ TypeError: Cannot set property size of #<Map> which has only a getter map.size = 5;
Even though we attempted to set the size property on the Map, we were unable
to.
This behavior is different when working with arrays.
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c']; console.log(arr.length); // 👉️ 3 arr.length = 1; console.log(arr.length); // 👉️ 1 console.log(arr); // 👉️ ['a']
size property, we were able to change the array's length.We set the array's length to 1 which automatically
removed the last 2 elements from the array.
Map objects also have keys() and values() methods.
const map1 = new Map(); map1.set('name', 'bobby hadz'); map1.set('country', ['Chile', 'ab']); map1.set('age', 30); const keys = [...map1.keys()]; console.log(keys.length); // 👉️ 3 console.log(keys.length === 0); // 👉️ false const values = [...map1.values()]; console.log(values.length); // 👉️ 3 console.log(values.length === 0); // 👉️ false
The Map.keys method returns an
iterator object that contains the keys of the Map.
The Map.values() method returns
an iterator object containing the values for each element in the Map.
We used the spread syntax (...) to convert the iterator objects to an array and
accessed the length property on the arrays to check if the Map is empty.
However, using the size property on the Map object is more convenient and
direct.
If you need to empty a Map object, use the Map.clear() method.
const map1 = new Map(); map1.set('name', 'bobby hadz'); map1.set('country', ['Chile', 'ab']); map1.set('age', 30); console.log(map1.size); // 👉️ 3 map1.clear(); console.log(map1.size); // 👉️ 0 console.log(map1); // 👉️ Map(0) {}
The Map.clear() method removes all elements from a Map object.
If you have to check if a Map object is empty often, define a reusable
function.
function mapIsEmpty(map) { return map.size === 0; } // 👇️ false console.log( mapIsEmpty( new Map([ ['name', 'bobby'], ['age', 30], ]), ), ); // 👇️ true console.log(mapIsEmpty(new Map()));
The mapIsEmpty() function takes a Map object as a parameter and returns
true if it is empty and false otherwise.
# Check if a Set is Empty in JavaScript
Use the size property to check if a Set is empty, e.g. set.size === 0. The
size property returns the number of elements in the Set.
When accessed on an empty Set, the size property returns 0.
const set1 = new Set(); console.log(set1.size); // 👉️ 0 if (set1.size === 0) { // 👇️ this runs console.log('✅ Set is empty'); } else { console.log('⛔️ Set is NOT empty'); }
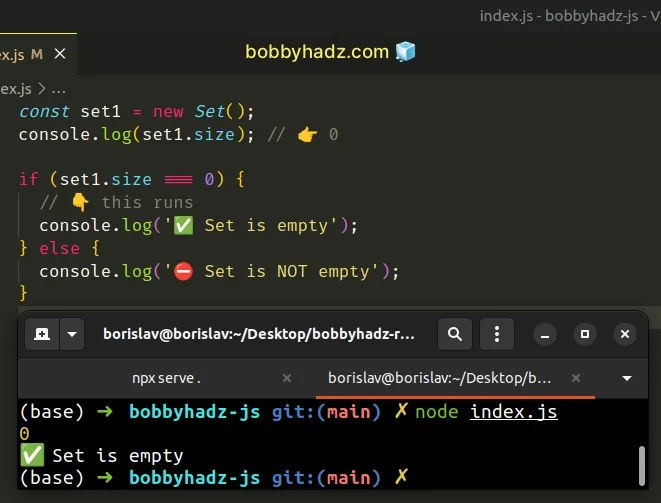
We used the Set.size property to check if
a Set is empty.
Set stores.const set2 = new Set(['a', 'b']); console.log(set2.size); // 👉️ 2
The property is similar to an array's length property, however, it is
read-only and cannot be changed.
const set1 = new Set(['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']); console.log(set1.size); // 👉️ 3 // ⛔️ TypeError: Cannot set property size of #<Set> which has only a getter set1.size = 1;
We attempted to change the size property on the Set, however, we were unable
to.
This is different when working with arrays, where the value of the length
property can be set by the user.
const arr = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']; console.log(arr.length); // 👉️ 3 arr.length = 1; console.log(arr.length); // 👉️ 1 console.log(arr); // 👉️ [ 'bobby' ]
As opposed to a Set's size property we were able to set the array's length
property and change the array's contents.
If you need to empty a Set object, use the
Set.clear()
method.
const set1 = new Set(['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']); console.log(set1.size); // 👉️ 3 set1.clear(); console.log(set1.size); // 👉️ 0 console.log(set1); // 👉️ Set(0) {}
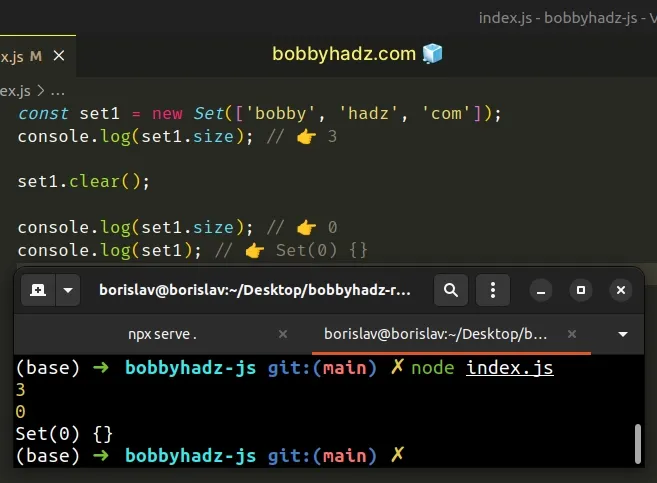
The Set.clear() method removes all elements from a Set object.
If you have to check if a Set object is empty often, define a reusable
function.
function setIsEmpty(set) { return set.size === 0; } // 👇️ false console.log(setIsEmpty(new Set(['bobby', 'hadz']))); // 👇️ true console.log(setIsEmpty(new Set()));
The setIsEmpty function takes a Set object as a parameter and returns true
if it is empty and false otherwise.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Check if an Object is of type Map or Set in JavaScript
- How to convert an Array to a Map in JavaScript
- Convert a Map to an Array of Objects in JavaScript
- How to Convert a Map to JSON in JavaScript
- Convert a Map to an Object in JavaScript
- Convert Map Keys and Values to an Array in JavaScript
- How to Clear an Object in JavaScript

