Create a Role with AWS CLI - Complete Guide
Last updated: Sep 19, 2021
Reading time·8 min

# Table of Contents
- Create an IAM role with AWS CLI
- Attach an Inline Policy to an IAM role with AWS CLI
- Attach a Managed Policy to an IAM role with AWS CLI
- Update a Role's Inline Policies with AWS CLI
- Update a Role's Managed Policies with AWS CLI
- Delete an Inline Policy of a Role with AWS CLI
- Delete a Managed Policy of a Role with AWS CLI
# Create an IAM role with AWS CLI
An IAM role is a collection of policies that grant specific permissions to access AWS resources.
Before we create the role, we must define a trust policy for it. The trust policy specifies which IAM entities (accounts, users, roles, services) can assume the role.
In our case, we will create a role that is to be assumed by the lambda service.
Let's create a trust policy that allows lambda to assume the role. Create a file
called trust-policy.json:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": "lambda.amazonaws.com" }, "Action": "sts:AssumeRole" } ] }
To create an IAM role, open your terminal in the directory where
trust-policy.json is stored and use the
create-role
command.
aws iam create-role --role-name role-example --assume-role-policy-document file://trust-policy.json
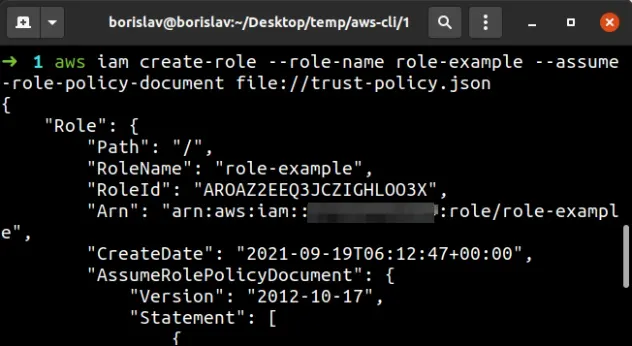
--parameters to an AWS CLI command, prefix human-readable files with file:// and binary (non human-readable) files with fileb://.# Attach an Inline Policy to an IAM role with AWS CLI
At this point, our role can be assumed by the lambda service, but it does not grant any permissions.
To grant permissions to an IAM role we must attach a policy to the role.
IAM policies define specific permissions needed to access AWS resources and can be associated with roles, users or groups.
To attach an inline policy to an IAM role, we have to:
- write and store the policy in a
jsonfile on the local file system - run the AWS CLI put-role-policy command
This is an example inline policy that grants permissions to List* and
GetItem actions on all Dynamodb tables. Save
the contents of the policy in a file named read-dynamodb.json:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "dynamodb:List*", "dynamodb:GetItem" ], "Effect": "Allow", "Resource": "*" } ] }
* characters makes the policies too broad and grants more permissions than necessary.The next step is to attach the policy to our IAM role. Open your terminal in the
directory where the read-dynamodb.json file is stored and run the
put-role-policy
command:
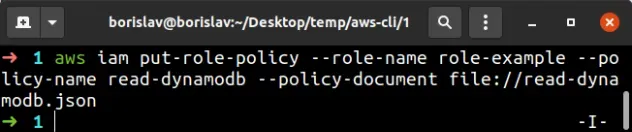
aws iam put-role-policy --role-name role-example --policy-name read-dynamodb --policy-document file://read-dynamodb.json
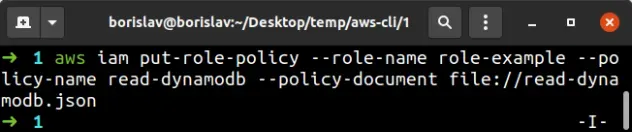
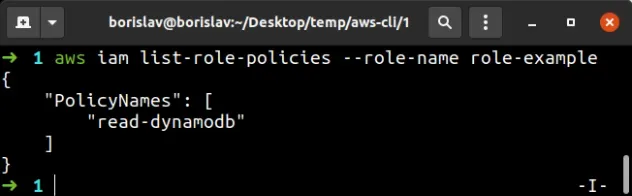
Let's verify that the inline policy is successfully attached to the role, by running the list-role-policies command:
aws iam list-role-policies --role-name role-example
# Attach a Managed Policy to an IAM role with AWS CLI
Managed policies are of 2 types:
- AWS-managed policies - created and managed by AWS. They aim to provide permissions for the most common use cases.
- Customer-managed policies - created and managed by the user. Like AWS- managed policies, they can be reused and attached to multiple principal entities, as opposed to inline policies.
Let's attach an AWS-managed policy that grants read and write permissions to access the CloudWatch service to our role.
To attach an AWS-managed policy to an IAM role with the AWS CLI, use the attach-role-policy command.
aws iam attach-role-policy --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole --role-name role-example
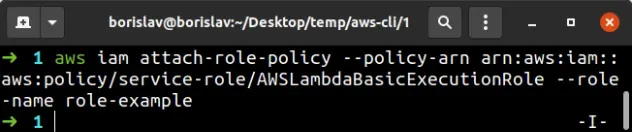
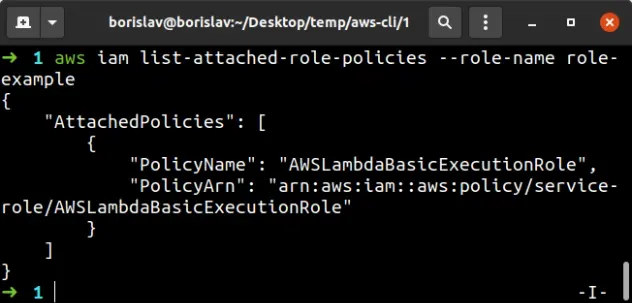
To verify the AWS-managed policy has been successfully attached to an IAM role, run the list-attached-role-policies command.
aws iam list-attached-role-policies --role-name role-example
To attach a customer-managed policy to an IAM role with the AWS CLI, we have to:
- Create the managed policy and take note of the policy's ARN
- Use the attach-role-policy command to attach the policy to the role
Let's create a customer-managed policy that grants S3 read permissions to all buckets in the account.
Store the following json into a file called read-s3.json:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:Get*", "s3:List*" ], "Resource": "*" } ] }
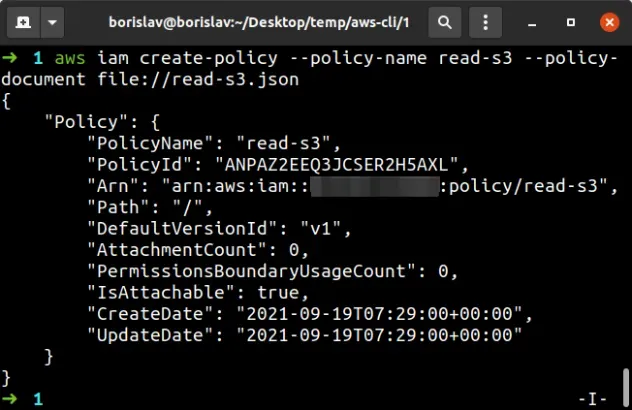
To create the customer-managed policy, open your terminal in the directory
where you stored the read-s3.json file and run the
create-policy
command:
aws iam create-policy --policy-name read-s3 --policy-document file://read-s3.json
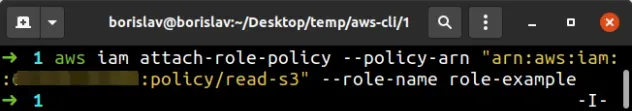
To attach a customer-managed policy to an IAM role, using the AWS CLI, run the attach-role-policy command.
aws iam attach-role-policy --policy-arn YOUR_POLICY_ARN --role-name role-example
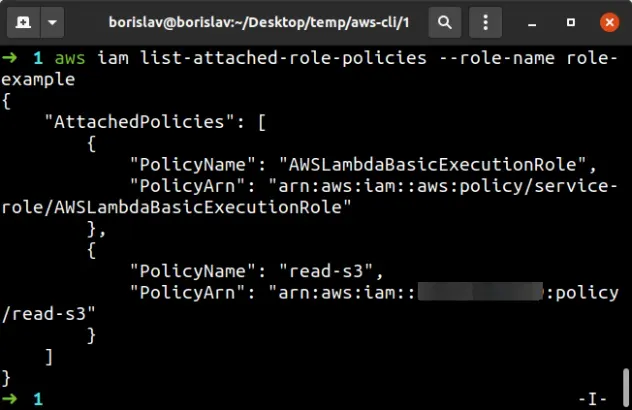
To verify the customer-managed policy has been successfully attached to the IAM role, run the list-attach-role-policies command.
aws iam list-attached-role-policies --role-name role-example
# Update a Role's Inline Policies with AWS CLI
To update a role's inline policy using the AWS CLI, we have to know the name of the inline policy. Let's get the name by running the list-role-policies command:
aws iam list-role-policies --role-name role-example

Let's remove the List* action from our read-dynamodb.json. Update the file
to look like:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "dynamodb:GetItem" ], "Effect": "Allow", "Resource": "*" } ] }
Now open your terminal in the directory where the read-dynamodb.json file is
stored and run the
put role policy command
to update the inline policy attached to the role:
aws iam put-role-policy --role-name role-example --policy-name read-dynamodb --policy-document file://read-dynamodb.json
To verify the inline policy of the role has been updated, run the get role policy command:
aws iam get-role-policy --role-name role-example --policy-name read-dynamodb
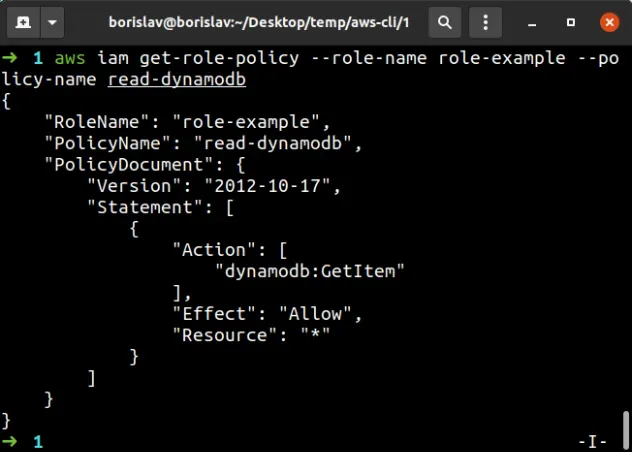
The output of the command shows that the List* action has successfully been
removed from the inline policy.
# Update a Role's Managed Policies with AWS CLI
We can only update customer-managed AWS Policies.
To update a customer-managed policy with AWS CLI, we have to:
- Get the ARN of the policy
- update the
jsonfile that stores the contents of the customer-managed policy - update the policy by running the create policy version command
Let's get the ARN of the customer-managed policy that's attached to our role by running the list-attached-role-policies command:
aws iam list-attached-role-policies --role-name role-example

read-s3 policy to a notepad.Let's update the contents of the read-s3.json file to delete the List*
action:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:Get*" ], "Resource": "*" } ] }
Open your terminal in the directory where you stored the read-s3.json file and
execute the
create-policy-version
command to update the managed policy:
aws iam create-policy-version --policy-arn "YOUR_S3_POLICY_ARN" --policy-document file://read-s3.json --set-as-default
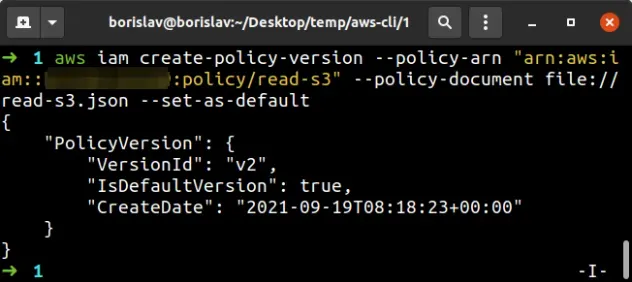
--set-as-default parameter specifies that the policy's version should be set as default and applied to all IAM users, groups, and roles that the policy is attached to.The output shows that the policy's VersionId is v2 after the update.
We can use the policy's ARN and VersionId to verify that the
customer-managed policy has been updated successfully:
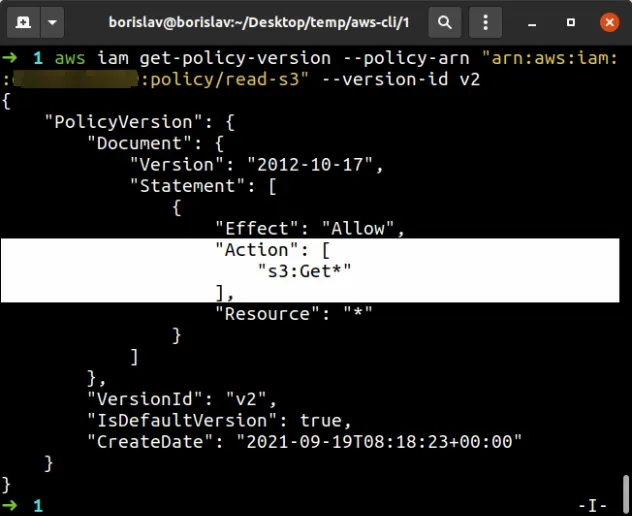
The output of the
get-policy-version
command shows that the List* action has been successfully removed from the
policy.
# Delete an Inline Policy of a Role with AWS CLI
To delete an inline policy attached to an IAM role with AWS CLI, we have to:
- Get the name of the inline policy
- run the delete-role-policy command
Let's list the names of the inline policies attached to our IAM role:
aws iam list-role-policies --role-name role-example

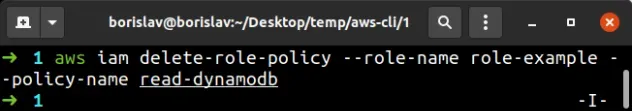
And finally let's delete the read-dynamodb inline policy from the role, by
using the delete-role-policy command:
aws iam delete-role-policy --role-name role-example --policy-name read-dynamodb
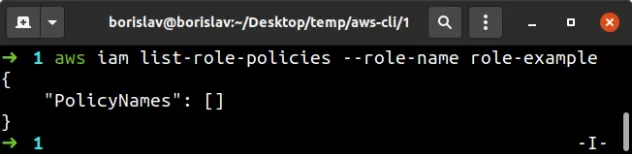
To verify the inline policy has been deleted from the role, run the list-role-policies command again:
aws iam list-role-policies --role-name role-example
# Delete a Managed Policy of a Role with AWS CLI
The process of deleting a customer-managed policy is a lot more complicated than with inline policies.
That's because customer-managed policies:
- Can be attached to multiple users, groups and roles.
- Can have multiple versions, which have to be deleted.
The process of deleting a customer-managed policy with AWS CLI consists of the following steps:
- Detach the policy from all users, groups and roles
- Delete all versions of the policy
- Delete the policy
Let's grab the ARN of the managed policy we're trying to delete by running the
list-attached-role-policies command:
aws iam list-attached-role-policies --role-name role-example

Copy the PolicyArn of the read-s3 managed policy and store it in a notepad.
The next step is to list all users, roles and groups that the managed policy is attached to, by running the list-entities-for-policy command:
aws iam list-entities-for-policy --policy-arn "YOUR_S3_POLICY_ARN"
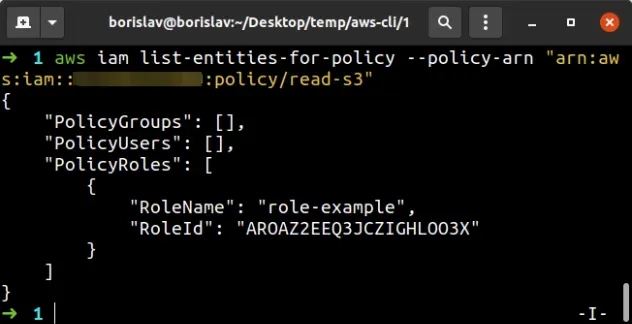
The output shows that the policy is only attached to the role-example role.
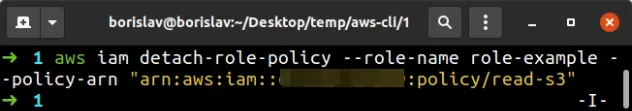
Let's detach the customer-managed policy from the role by using the detach-role-policy command:
aws iam detach-role-policy --role-name role-example --policy-arn "YOUR_S3_POLICY_ARN"
The next step is to delete all versions of the policy other than the default version. The default version is automatically deleted when the managed policy is deleted.
aws iam list-policy-versions --policy-arn "YOUR_S3_POLICY_ARN"
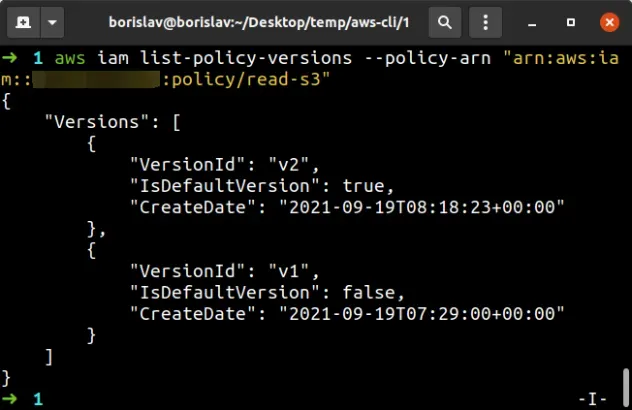
The output from the command shows that v2 of the policy is the default (the
one we can't delete). So let's delete v1 of the customer-managed policy, by
running the
delete-policy-version
command.
aws iam delete-policy-version --policy-arn "YOUR_S3_POLICY_ARN" --version-id v1
To delete a customer-managed policy with AWS CLI, use the delete-policy command.
aws iam delete-policy --policy-arn "YOUR_S3_POLICY_ARN"
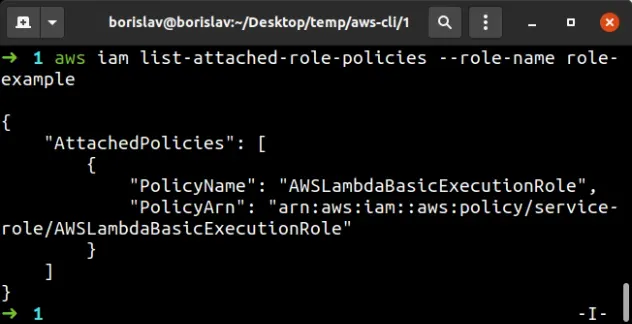
If we run the list-attached-role-policies command we can see that the only
managed policy attached to our IAM role is the AWS-managed policy:
aws iam list-attached-role-policies --role-name role-example
I've also written an article on how to create an IAM role in AWS CDK.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to Get your Account Id with AWS CLI
- How to Get your Default Profile with AWS CLI
- Manage Multiple Accounts with the AWS CLI
- Set your Default Profile's Name in AWS CLI
- How to Clear your AWS CLI Credentials
- View your AWS CLI logs in Real Time (tail)
- How to turn off the Pager in AWS CLI
- Create a Lambda Function with AWS CLI - Complete Guide
- Invoke Lambda Functions with AWS CLI - Complete Guide
- Tag an S3 Bucket with AWS CLI
- AWS CDK Tutorial for Beginners - Step-by-Step Guide
- How to use Parameters in AWS CDK
- How to create a Cloudwatch Alarm in AWS CDK

