Windows equivalent of the Unix 'tail' command
Last updated: Apr 4, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
# Windows equivalent of the Unix 'tail' command
The tail Unix command prints the last N lines (10 lines by default) of a file
and terminates.
Use the PowerShell Get-Content command as the Windows equivalent of the Unix
tail command. The Get-Content command is used to print the specified lines
of a certain file and optionally waits for changes.
Open PowerShell and run the following command.
Get-Content my_file.txt -Tail 5
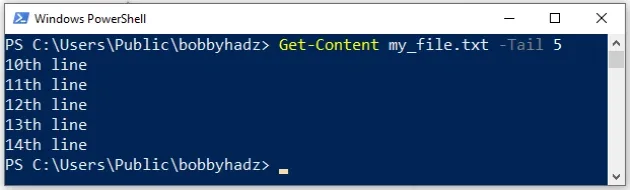
Make sure to replace the my_file.txt with the name of your actual file.
-Tail parameter is used to specify the number of lines from the end of a file to print (5 lines in the example).You can use the
-Wait
parameter as a Windows replacement for the Unix tail -f command.
The -Wait parameter keeps the file open after all existing lines have been
printed.
The Get-Content command checks the file each second and outputs new lines if
present.
Get-Content my_file.txt -Wait -Tail 5
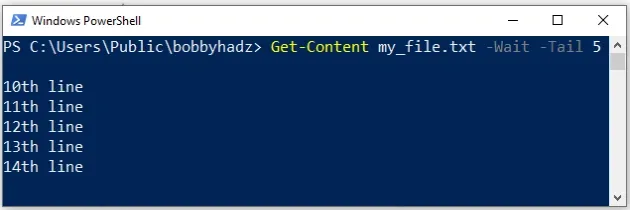
When you issue the Get-Content command with the -Wait parameter, you
basically issue the Unix tail -f command.
You can press CTRL + C to exit.
If you don't know how to open PowerShell:
- Click on the Search bar and type "PowerShell".
- Click on the "Windows PowerShell" application.
If you need to open PowerShell in a specific folder:
- Open the folder in a window.
- Press
Shiftand right-click in Explorer.
- Click on "Open PowerShell window here".
You can also specify an absolute path when issuing the Get-Content command.
Get-Content "C:\Users\Public\bobbyhadz\my_file.txt" -Wait -Tail 5
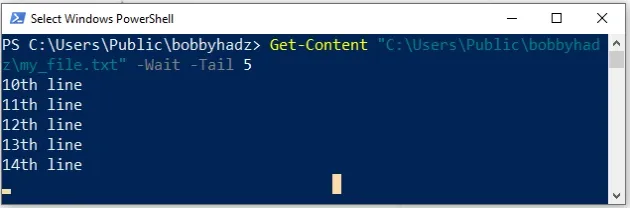
Make sure to replace the path with your specific path to the file.
-Wait parameter.If you want to print the first N lines of a file, use the -TotalCount
parameter.
# 👇️ with a relative path Get-Content -Path my_file.txt -TotalCount 5 # 👇️ with an absolute path Get-Content -Path "C:\Users\Public\bobbyhadz\my_file.txt" -TotalCount 5
You can also use filters with the Get-Content command.
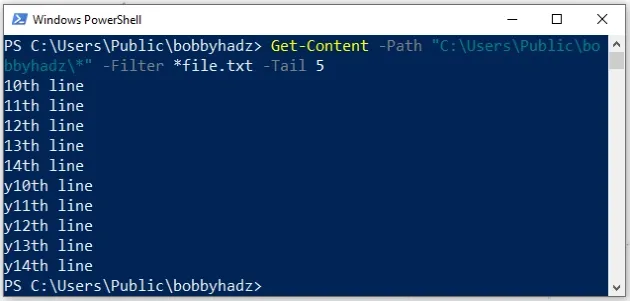
Get-Content -Path "C:\Users\Public\bobbyhadz\*" -Filter *file.txt -Tail 5
When using filters, you have to use a trailing asterisk * when specifying the
path.
The command prints the last 5 lines of all files in the specified directory
whose names end with file.txt, e.g. my_file.txt, your_file.txt, etc.
If you want to only tail the file to print lines that contain a specific string
or pattern, use the Select-String command.
Get-Content my_file.txt -Wait -Tail 3 | Select-String -pattern "th"
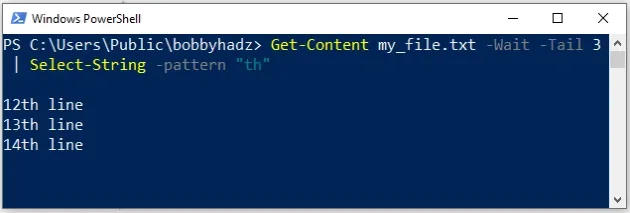
The command tails the file and prints the last 3 lines that contain the string
th.
We specified the -Wait parameter, so the command will keep waiting and
checking if new lines that contain the specified string are written to the file.
You can view more examples of using the Select-String command in
the official docs.
You can use the Get-Help Get-Content command to display the help page of
Get-Content with information about the syntax, the command's aliases and some
helpful remarks.
Get-Help Get-Content
You can also check out the command's syntax and some examples in the official docs.
Alternatively, you can use the tail command in Git Bash on Windows.
If you already have git installed, you can search for Git Bash and use the
tail command, otherwise, you have to install git first.
# Using the tail command on Windows in Git Bash
To download git and be able to use Git Bash:
- Open the git downloads page and download the installer for Windows.
- Start the installer.
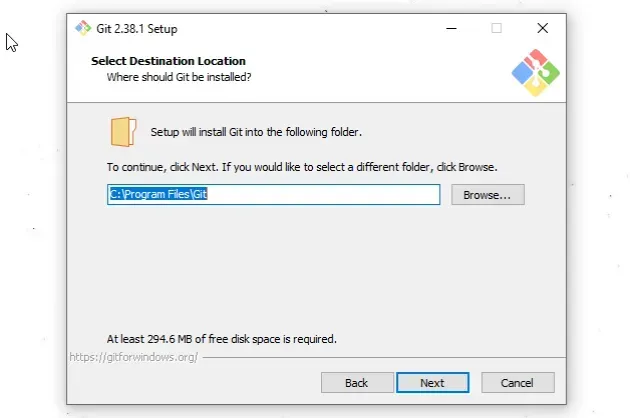
- You will be prompted to select a destination location. You can leave the
default option and click
Next.
- You will be prompted to select components on the next screen. Leave the
default options and click
Next.
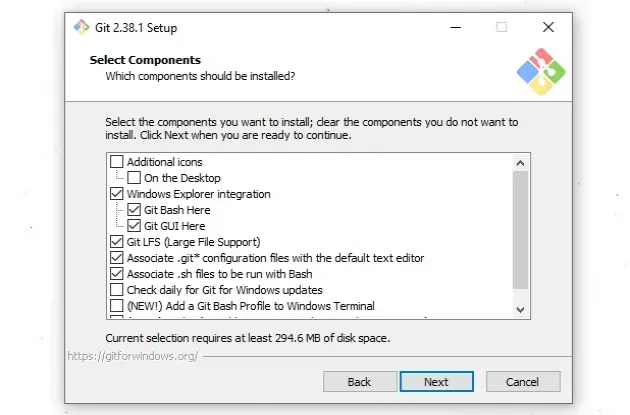
Click
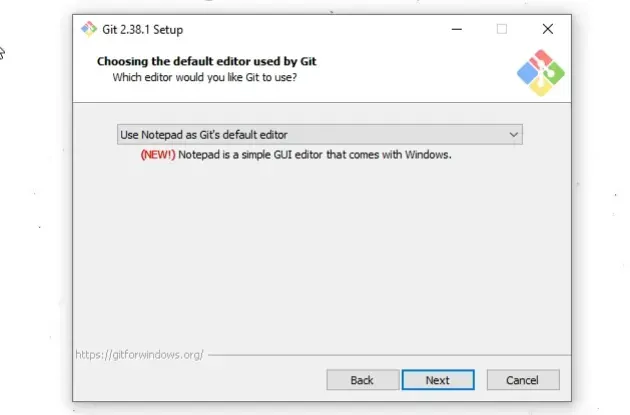
Nexton the screen that prompts you to "Select Start Menu Folder".On the next screen, you can choose the default editor for
Git, e.g.Notepad,Notepad++or any other editor you prefer.
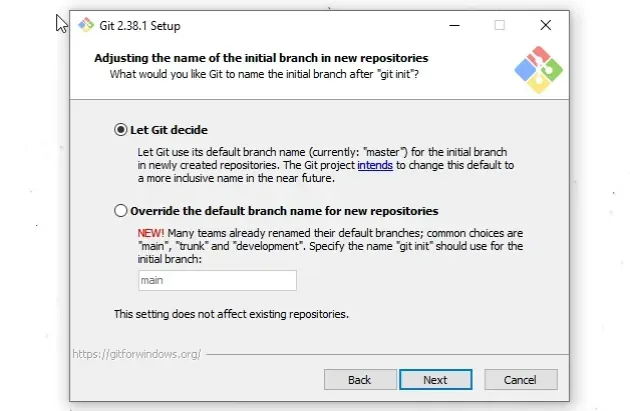
- On the "Adjust the name of the initial branch in new repositories screen",
click
Next.
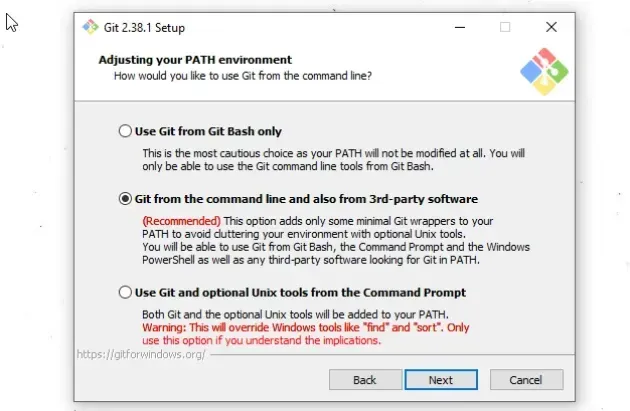
- On the "Adjust your PATH environment" screen, make sure you have the default option of "Git from the command line and also from 3rd-party software" option selected and click "Next".
- For all the remaining screens, leave the default option selected and click
Next. - Lastly, click on the
Installbutton to installgit.
Once you have git installed, click on the Search field, type "Git Bash"
and start the application.
Now you can use the tail command directly in Git Bash.
tail my_file.txt
You can use the tail -f command to follow the file and keep it open to display
changes.
tail -f my_file.txt
The -n parameter is used to specify the number of lines from the end of a file
to print (5 lines in the following example).
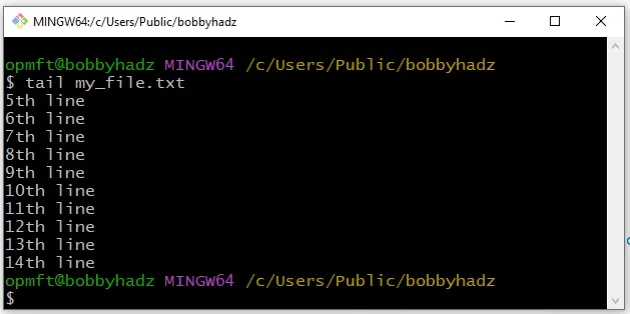
tail my_file.txt -n 5
If you need to open Git Bash in a specific folder:
- Open the folder in a new window.
- Right-click in Explorer.
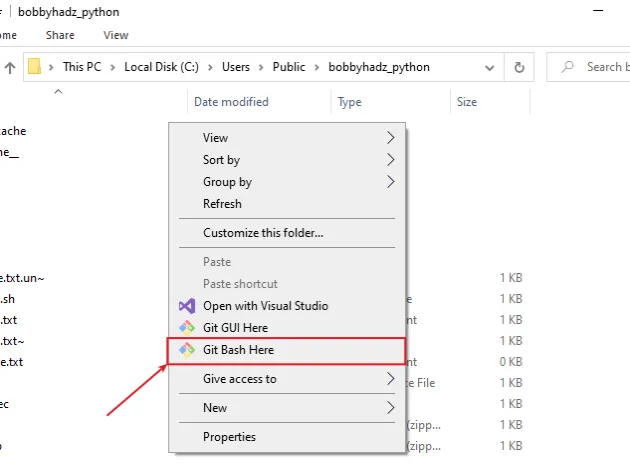
- Click "Git Bash Here".
Finally, issue the tail command.
tail my_file.txt
You can also specify a path to the file you want to tail.
tail "C:/Users/Public/bobbyhadz/my_file.txt" -n 5
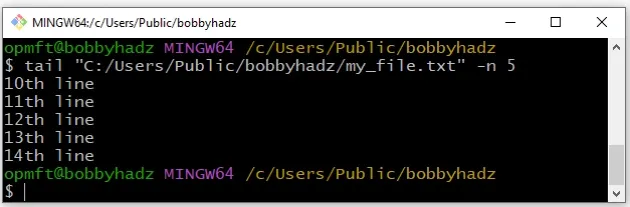
Make sure to replace the path from the example with your specific path.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Windows Equivalent of the 'ls', 'which' and 'ln' commands
- The Windows equivalent of the Unix 'tee' command
- The Windows equivalent of the Unix 'pwd' command
- How to install Homebrew on Windows
- How to install and use 'jq' on Windows
- How to install and use 'AWK' on Windows
- 'grep' is not recognized as an internal or external command
- PowerShell: unable to start ssh-agent service, error :1058
- The token '&&' is not a valid statement separator in this version
- How to Run Windows (File) Explorer as a Different User

