Windows Equivalent of the 'ls', 'which' and 'ln' commands
Last updated: Apr 4, 2024
Reading time·9 min

# Table of Contents
- Windows Equivalent of the 'ls' command - CMD & PowerShell
- Windows: Equivalent of the 'which' command - CMD & PowerShell
- The Windows equivalent of the 'ln' command (symbolic link)
# Windows Equivalent of the 'ls' command - CMD & PowerShell
The Unix ls command is used to list the names of the files and subdirectories
in a specific directory.
The dir command is the Windows equivalent of the ls command. The dir
command displays a list of a directory's files and subdirectories. The command
also displays the date and time each file or directory was modified.
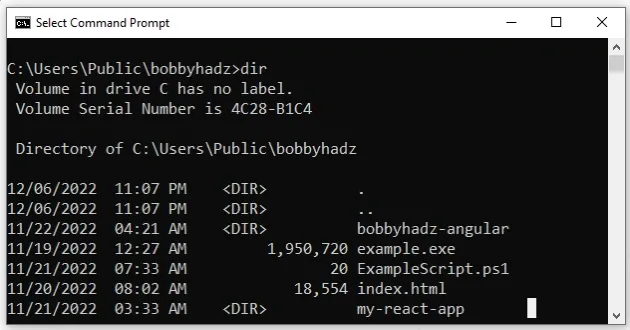
dir
Here is an example output of running the dir command in CMD.
You can also use the wildcard character * with the dir command to substitute
for any string of characters.
dir *.txt
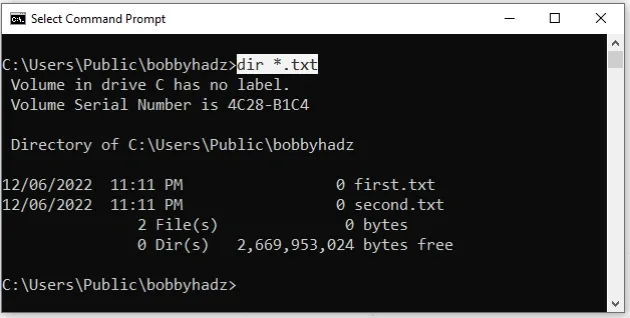
The command in the example lists all files in the current directory that have an
extension that begins with .txt extension, e.g. a.txt, b.txt, c.txt1,
etc.
Here is another example of using the wildcard * character with the dir
command.
dir abc*.txt
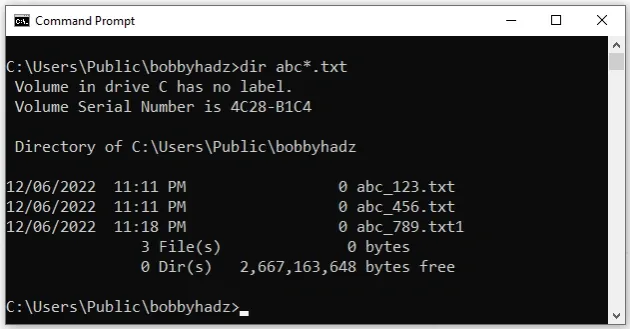
The command lists all files in the current directory that begin with abc and
have an extension that begins with .txt.
You can use the dir/? command to print all of the parameters that can be
passed to the dir command.
dir/?
Alternatively, you can view the syntax and the parameters for the dir command
in
this section
of the docs.
The PowerShell equivalent of the ls command is Get-ChildItem.
# Windows equivalent of the ls command in PowerShell
The Windows equivalent of the ls command in PowerShell is the
Get-ChildItem command.
The Get-ChildItem command lists the filenames and the subdirectory names in
the current directory.
Get-ChildItem
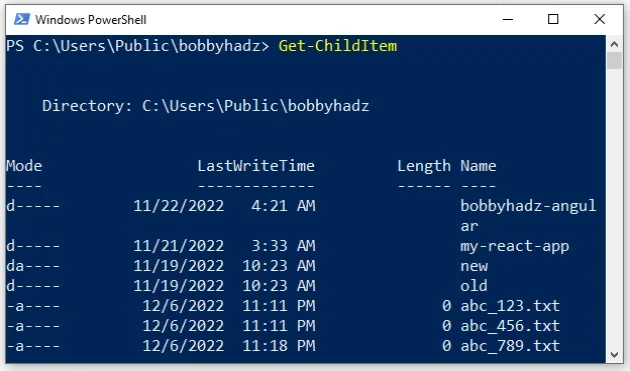
Note that there is also an ls alias for the Get-ChildItem command in
PowerShell.
ls
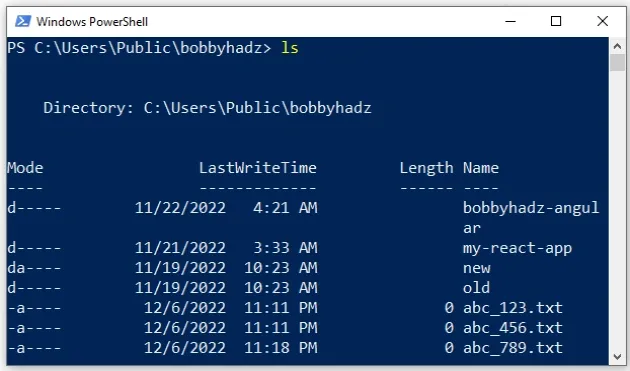
If you need to open PowerShell in a specific folder:
- Open the folder in a window.
- Press
Shiftand right-click in Explorer.
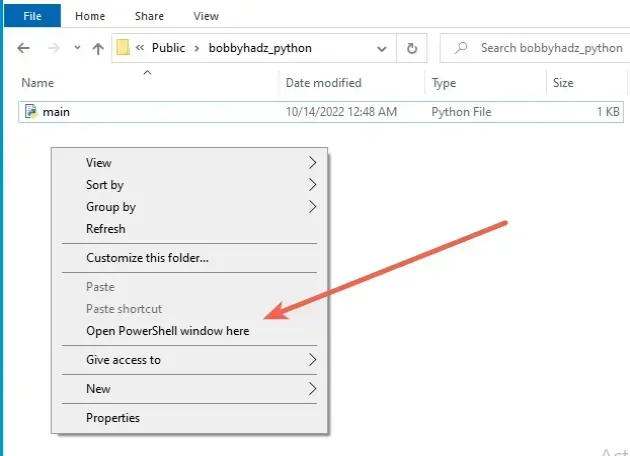
- Click on "Open PowerShell window here".
- Run the
lsorGet-ChildItemcommand.
Get-ChildItem ls
You can use the -Path parameter to specify a path. Wildcards are accepted and
the default location is the current directory.
Get-ChildItem -Path 'C:\Users\Public\bobbyhadz\'
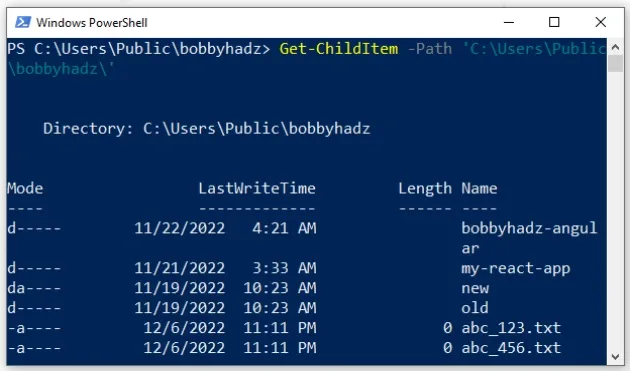
The command lists the files and directories under the path
C:\Users\Public\bobbyhadz.
Make sure to update the path according to your requirements.
The output includes information about the mode, when the file or directory was last updated, its size, etc.
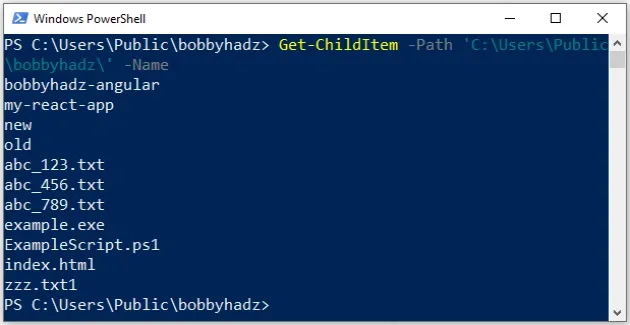
-Name parameter.Get-ChildItem -Path 'C:\Users\Public\bobbyhadz\' -Name
You can use the Get-Help Get-ChildItem command to display the help page of
Get-ChildItem with information about the syntax, the command's aliases and
some helpful remarks.
Get-Help Get-ChildItem
You can also check out the command's syntax and some examples in the official docs.
Alternatively, you can use the ls command in Git Bash on Windows.
If you already have git installed, you can search for Git Bash and use the
ls command, otherwise, you have to install git first.
# Running the ls command in Git Bash
To download git and be able to use Git Bash:
- Open the git downloads page and download the installer for Windows.
- Start the installer.
- You will be prompted to select a destination location. You can leave the
default option and click
Next.
- You will be prompted to select components on the next screen. Leave the
default options and click
Next.
Click
Nexton the screen that prompts you to "Select Start Menu Folder".On the next screen, you can choose the default editor for
Git, e.g.Notepad,Notepad++or any other editor you prefer.
- On the "Adjust the name of the initial branch in new repositories screen",
click
Next.
- On the "Adjust your PATH environment" screen, make sure you have the default option of "Git from the command line and also from 3rd-party software" option selected and click "Next".
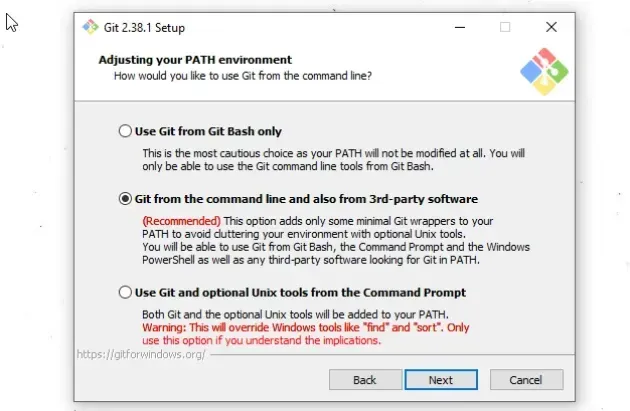
- For all the remaining screens, leave the default option selected and click
Next. - Lastly, click on the
Installbutton to installgit.
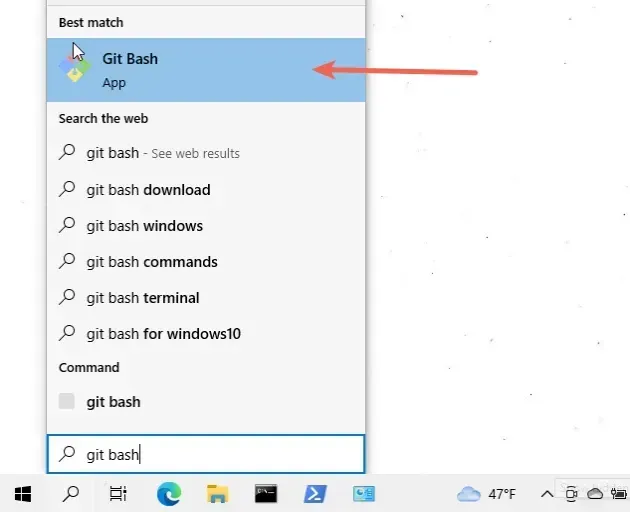
Once you have git installed, click on the Search field, type "Git Bash"
and start the application.
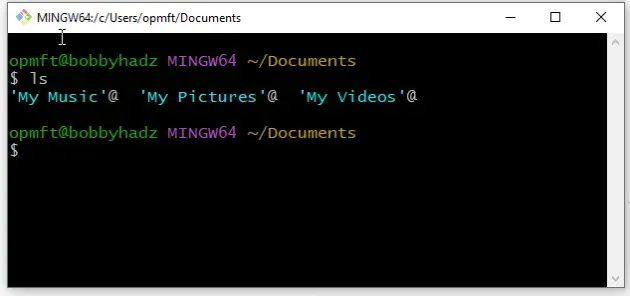
Now you can use the ls command directly in Git Bash.
ls
If you need to open Git Bash in a specific folder:
- Open the folder in a new window.
- Right-click in Explorer.
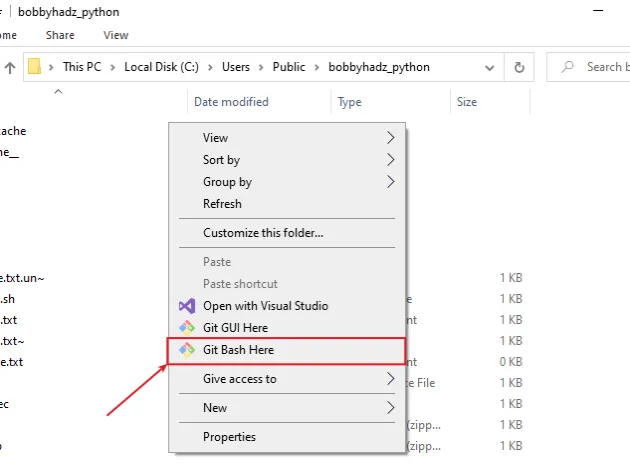
- Click "Git Bash Here".
Now you can use the ls command to display a list of the directory's files and
subdirectories.
ls
# Windows: Equivalent of the 'which' command - CMD & PowerShell
The Unix which command searches the $PATH environment variable and returns
the path to the specified executable.
The where command is the Windows equivalent of the which Unix command.
The where command displays the location of all files that match the given
search pattern, not just executable files.
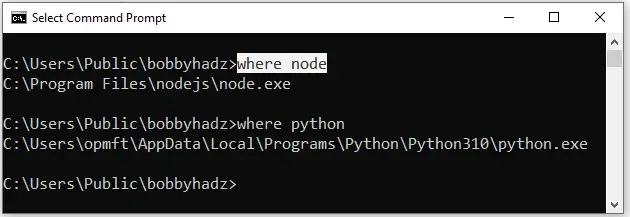
where node where python
Make sure to replace the
node and
python placeholders with the name of your specific command.
You can also use wildcards when issuing the where command.
where pyt*
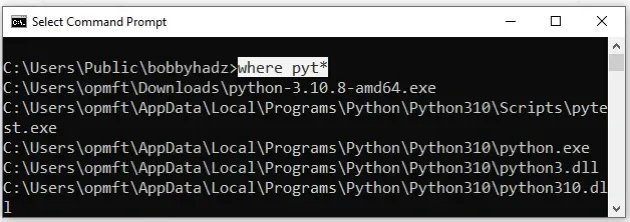
%PATH% environment variable and the current directory whose names start with pyt.You can use the where /? command to display a short description of the
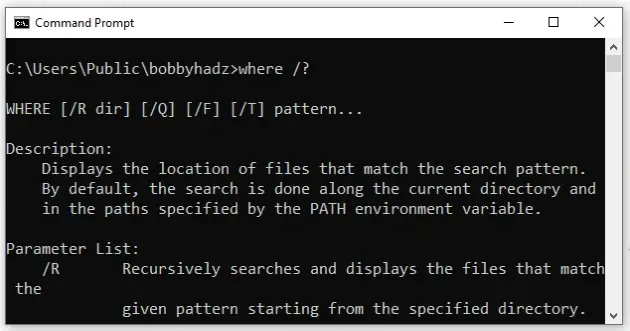
command, its parameter list and a couple of examples.
where /?
You can also check the parameters the where command takes and some examples in
the
official docs.
# Windows equivalent of the which command in PowerShell
The Get-Command is the Windows equivalent of the Unix which command in
PowerShell.
The command can be used to get the command type, the name and the path to the specified executable.
Get-Command node | Format-Table CommandType, Name, Definition
node with your specific executable.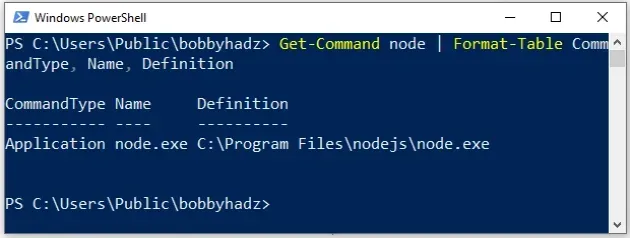
You can also specify the -All parameter when issuing the command.
Get-Command node -All | Format-Table CommandType, Name, Definition
The -All parameter of Get-Command can be used to show all instances of the
specified command on the local computer.
For example, this would be useful if you have multiple instances of node
installed.
You can also use wildcards with Get-Command.
Get-Command no* | Format-Table CommandType, Name, Definition
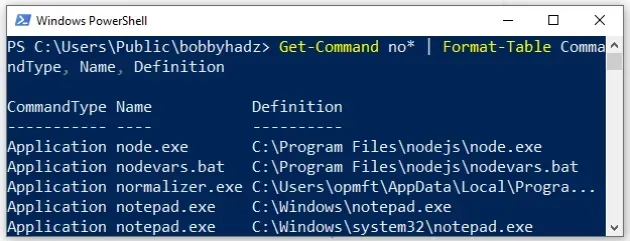
no.You can use the Get-Help Get-Command command to display the help page of
Get-Command with information about the syntax, the command's aliases and some
helpful remarks.
Get-Help Get-Command
You can also check out the command's syntax and some examples in the official docs.
Alternatively, you can use the which command in Git Bash on Windows.
If you already have git installed, you can search for Git Bash and use the
which command, otherwise, you have to install git first.
# Using the which command in Git Bash on Windows
To download git and be able to use Git Bash:
- Open the git downloads page and download the installer for Windows.
- Start the installer.
- You will be prompted to select a destination location. You can leave the
default option and click
Next.

- You will be prompted to select components on the next screen. Leave the
default options and click
Next.

Click
Nexton the screen that prompts you to "Select Start Menu Folder".On the next screen, you can choose the default editor for
Git, e.g.Notepad,Notepad++or any other editor you prefer.

- On the "Adjust the name of the initial branch in new repositories screen",
click
Next.

- On the "Adjust your PATH environment" screen, make sure you have the default option of "Git from the command line and also from 3rd-party software" option selected and click "Next".

- For all the remaining screens, leave the default option selected and click
Next. - Lastly, click on the
Installbutton to installgit.
Once you have git installed, click on the Search field, type "Git Bash"
and start the application.

Now you can use the which command directly in Git Bash.
which node
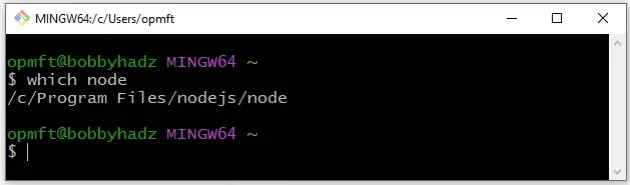
If you need to open Git Bash in a specific folder:
- Open the folder in a new window.
- Right-click in Explorer.

- Click "Git Bash Here".
Finally, issue the which command.
which node
# The Windows equivalent of the 'ln' command (symbolic link)
The Windows mklink command is the equivalent of the Linux/Unix ln command.
The mklink command creates a directory or a file symbolic link.
To create a symbolic link, you must start CMD as an administrator.
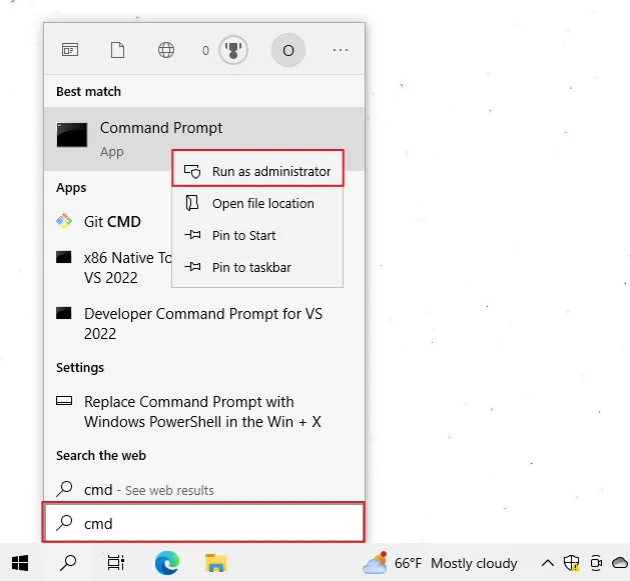
To open CMD as an administrator:
Click on the Search bar and type CMD.
Right-click on the Command Prompt application and click "Run as administrator".
The mklink command is used to create a directory or a file symbolic or hard link.
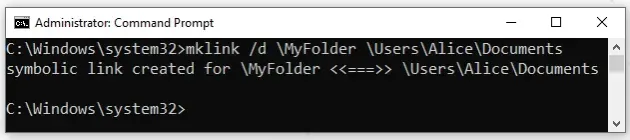
Here is an example that creates a directory symbolic link.
The following command creates a symbolic link named MyFolder from the root
directory to the \Users\Alice\Documents directory.
mklink /d \MyFolder \Users\Alice\Documents
The following command creates a hard link named Myfile.file to
\Alice\Documents\example.file.
mklink /h \MyFile.file \Alice\Documents\example.file
You can check out the parameters the mklink command takes and other examples
in
this section
of the docs.
ln command in Git Bash by installing git on your Windows machine.If you already have git installed:
- Search for "Git Bash".
- Open Git Bash as an administrator.
- Use the
lncommand.
Otherwise, you have to install git first.
# Running the ln command on Windows in Git Bash
To download git and be able to use Git Bash:
- Open the git downloads page and download the installer for Windows.
- Start the installer.
- You will be prompted to select a destination location. You can leave the
default option and click
Next.

- You will be prompted to select components on the next screen. Leave the
default options and click
Next.

Click
Nexton the screen that prompts you to "Select Start Menu Folder".On the next screen, you can choose the default editor for
Git, e.g.Notepad,Notepad++or any other editor you prefer.

- On the "Adjust the name of the initial branch in new repositories screen",
click
Next.

- On the "Adjust your PATH environment" screen, make sure you have the default option of "Git from the command line and also from 3rd-party software" option selected and click "Next".

- For all the remaining screens, leave the default option selected and click
Next. - Lastly, click on the
Installbutton to installgit.
To run Git Bash as an administrator:
- Click on the Search bar and type "Git Bash".
- Right-click on the "Git Bash" application and click "Run as administrator".
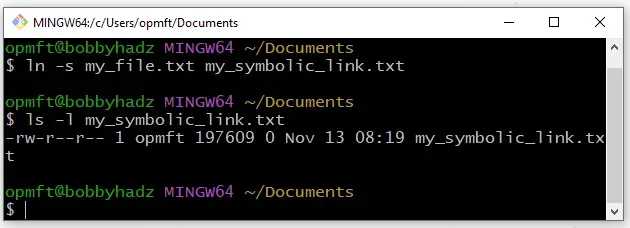
Now you can use the ln command directly in Git Bash.
ln -s my_file.txt my_symbolic_link.txt ln -l my_symbolic_link.txt
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- 'cat' is not recognized as an internal or external command
- 'curl' is not recognized as an internal or external command
- 'grep' is not recognized as an internal or external command
- How to install Homebrew on Windows
- How to install and use 'jq' on Windows
- How to install and use 'AWK' on Windows
- 'nano' is not recognized as an internal or external command
- PowerShell: unable to start ssh-agent service, error :1058
- How to Run Windows (File) Explorer as a Different User

