How to read a CSV file from a URL using Python [4 Ways]
Last updated: Apr 11, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Reading a CSV file from a URL using Python and Pandas
- Reading only a subset of the columns of the CSV file from a URL
- Reading a CSV file from a URL using csv and urllib
- Reading a CSV file from a URL using requests
# Reading a CSV file from a URL using Python and Pandas
To read a CSV file from a URL using Python and Pandas:
- First, make sure that
you have the
pandasmodule installed.
Open your terminal in your project's root directory and run the following command.
pip install pandas # or with pip3 pip3 install pandas # for Anaconda conda install -c anaconda pandas # for Jupyter Notebook !pip install pandas
- Import the
pandasmodule and use the pandas.read_csv() method. - The
pandas.read_csv()method will read the CSV file from the URL into aDataFrame.
import pandas as pd url = "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/bobbyhadz/9061dd50a9c0d9628592b156326251ff/raw/381229ffc3a72c04066397c948cf386e10c98bee/employees.csv" data = pd.read_csv( url, sep=',', encoding='utf-8', ) # first_name last_name date # 0 Alice Smith 2023-01-05 # 1 Bobby Hadz 2023-03-25 # 2 Carl Lemon 2021-01-24 print(data)
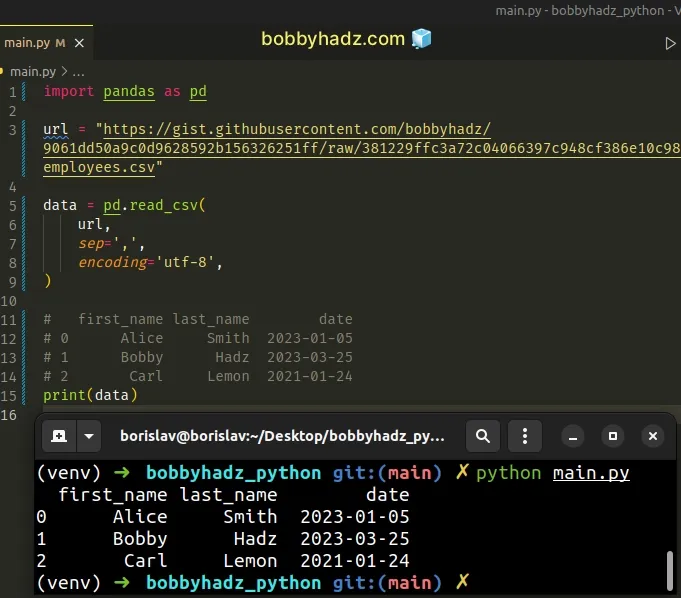
You can open the CSV file by clicking on the following link.
Here are the contents of the example CSV file.
first_name,last_name,date Alice,Smith,2023-01-05 Bobby,Hadz,2023-03-25 Carl,Lemon,2021-01-24
We imported the pandas module and used the
pandas.read_csv() method
to read the CSV file from the URL.
import pandas as pd # ... data = pd.read_csv( url, sep=',', encoding='utf-8', )
We passed the following 3 arguments to the pandas.read_csv method:
- The URL where the CSV file is accessible (make sure the filename and extension and specified).
- The delimiter that is used between the CSV values (a comma
,in the example). - The encoding of the CSV file.
The pandas.read_csv method returns a DataFrame object.
import pandas as pd url = "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/bobbyhadz/9061dd50a9c0d9628592b156326251ff/raw/381229ffc3a72c04066397c948cf386e10c98bee/employees.csv" data = pd.read_csv( url, sep=',', encoding='utf-8', ) # first_name last_name date # 0 Alice Smith 2023-01-05 # 1 Bobby Hadz 2023-03-25 # 2 Carl Lemon 2021-01-24 print(data) print('-' * 50) print(data['first_name']) print('-' * 50) print(data['last_name'])
Running the code sample with python main.py produces the following output.
first_name last_name date 0 Alice Smith 2023-01-05 1 Bobby Hadz 2023-03-25 2 Carl Lemon 2021-01-24 -------------------------------------------------- 0 Alice 1 Bobby 2 Carl Name: first_name, dtype: object -------------------------------------------------- 0 Smith 1 Hadz 2 Lemon Name: last_name, dtype: object
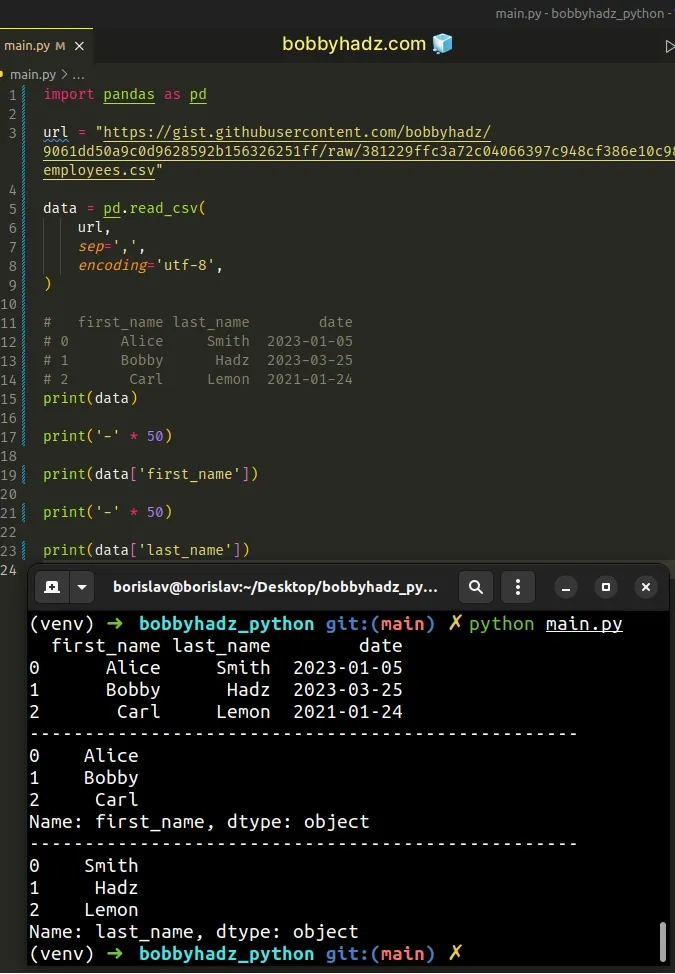
Notice that we can use bracket notation to access specific columns.
# Reading only a subset of the columns of the CSV file from a URL
If you only need to read a subset of the columns of the CSV file from the URL,
specify the usecols argument when calling pandas.read_csv().
import pandas as pd url = "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/bobbyhadz/9061dd50a9c0d9628592b156326251ff/raw/381229ffc3a72c04066397c948cf386e10c98bee/employees.csv" data = pd.read_csv( url, sep=',', encoding='utf-8', usecols=['first_name', 'last_name'] ) # first_name last_name # 0 Alice Smith # 1 Bobby Hadz # 2 Carl Lemon print(data) print('-' * 50) print(data['first_name']) print('-' * 50) print(data['last_name'])
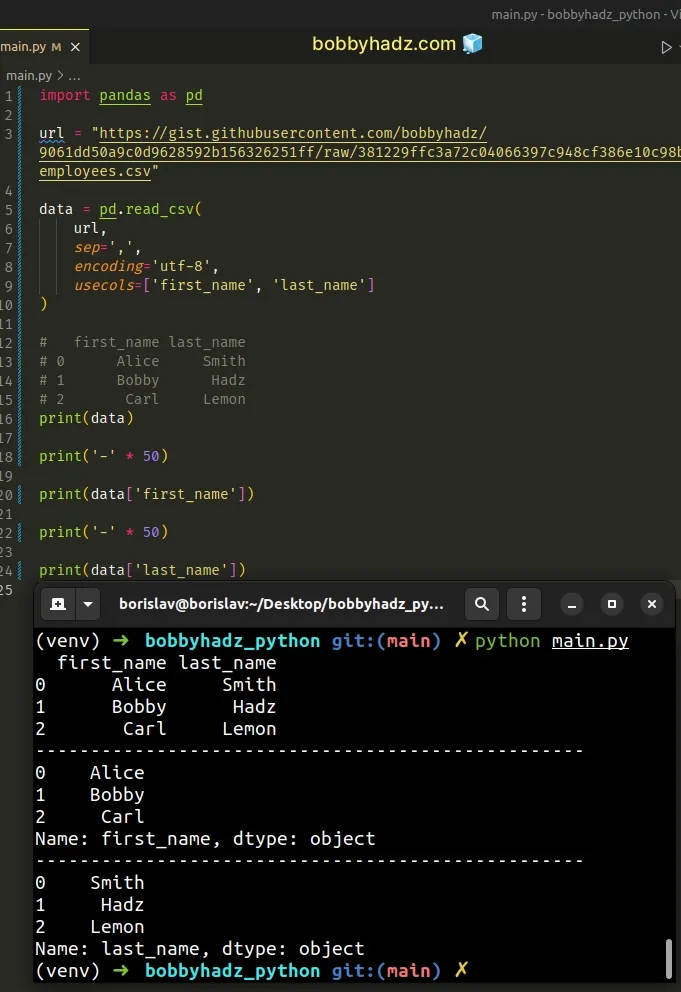
We set the usecols argument to an array that contains the first_name and
last_name columns.
The argument is used to return only a subset of the columns of the CSV file.
# Reading a CSV file from a URL using csv and urllib
You can also use the built-in csv and urllib modules to read a CSV file from
a URL in Python.
import csv from urllib.request import urlopen url = "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/bobbyhadz/9061dd50a9c0d9628592b156326251ff/raw/381229ffc3a72c04066397c948cf386e10c98bee/employees.csv" response = urlopen(url) lines = [line.decode('utf-8') for line in response.readlines()] csv_reader = csv.reader(lines, delimiter=',') for row in csv_reader: print(row)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
['first_name', 'last_name', 'date'] ['Alice', 'Smith', '2023-01-05'] ['Bobby', 'Hadz', '2023-03-25'] ['Carl', 'Lemon', '2021-01-24']
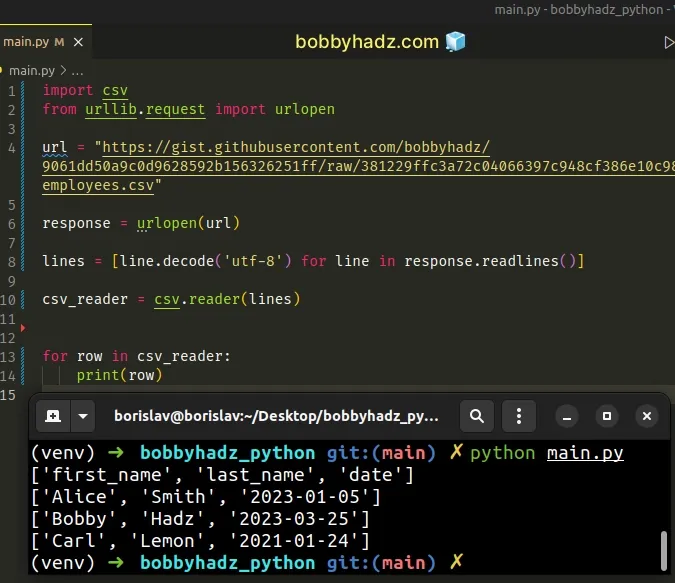
We used the urllib.request.urlopen method to open the URL.
from urllib.request import urlopen url = "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/bobbyhadz/9061dd50a9c0d9628592b156326251ff/raw/381229ffc3a72c04066397c948cf386e10c98bee/employees.csv" response = urlopen(url)
The next step is to use a list comprehension to get a list containing the lines of the CSV file.
# 👇️ ['first_name,last_name,date\n', 'Alice,Smith,2023-01-05\n', 'Bobby,Hadz,2023-03-25\n', 'Carl,Lemon,2021-01-24'] lines = [line.decode('utf-8') for line in response.readlines()]
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
On each iteration, we use the bytes.decode() method to convert the current bytes object to a string.
The csv.reader() method returns a reader object that can be used to iterate over the lines in a CSV file.
csv_reader = csv.reader(lines, delimiter=',') for row in csv_reader: # ['first_name', 'last_name', 'date'] # ['Alice', 'Smith', '2023-01-05'] # ['Bobby', 'Hadz', '2023-03-25'] # ['Carl', 'Lemon', '2021-01-24'] print(row)
If you need to get access to the index of each row, use the enumerate()
function.
csv_reader = csv.reader(lines) for index, row in enumerate(csv_reader): # 0 ['first_name', 'last_name', 'date'] # 1 ['Alice', 'Smith', '2023-01-05'] # 2 ['Bobby', 'Hadz', '2023-03-25'] # 3 ['Carl', 'Lemon', '2021-01-24'] print(index, row)
The enumerate() function takes an iterable and returns an enumerate object containing tuples where the first element is the index and the second is the corresponding item.
# Reading a CSV file from a URL using requests
You can also use the requests module to read a CSV file from a URL in Python.
First, open your terminal in your project's root directory and
install the requests module.
pip install requests pip3 install requests # for Anaconda conda install -c anaconda requests # for Jupyter Notebook !pip install requests
Once you have the module installed, import it and use it as follows.
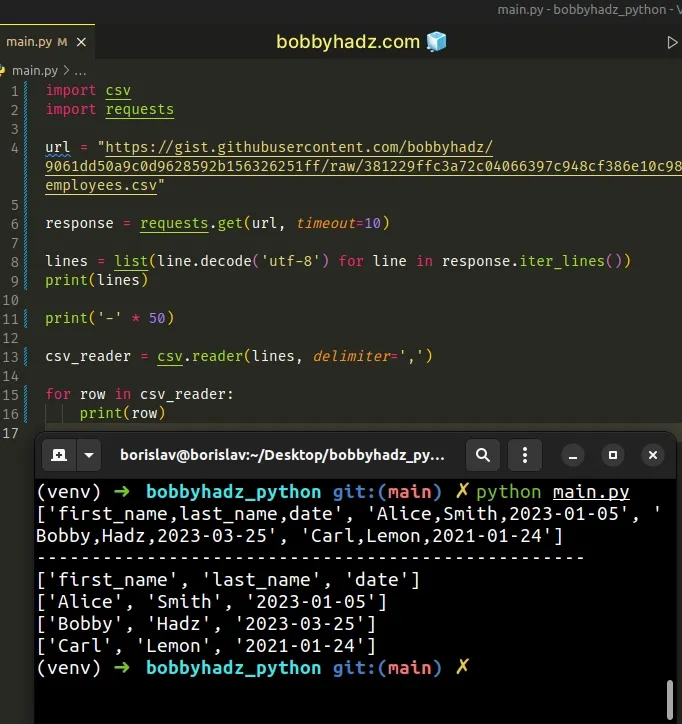
import csv import requests url = "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/bobbyhadz/9061dd50a9c0d9628592b156326251ff/raw/381229ffc3a72c04066397c948cf386e10c98bee/employees.csv" response = requests.get(url, timeout=10) lines = list(line.decode('utf-8') for line in response.iter_lines()) print(lines) print('-' * 50) csv_reader = csv.reader(lines, delimiter=',') for row in csv_reader: print(row)
Running the code sample produces the following output.
['first_name,last_name,date', 'Alice,Smith,2023-01-05', 'Bobby,Hadz,2023-03-25', 'Carl,Lemon,2021-01-24'] -------------------------------------------------- ['first_name', 'last_name', 'date'] ['Alice', 'Smith', '2023-01-05'] ['Bobby', 'Hadz', '2023-03-25'] ['Carl', 'Lemon', '2021-01-24']
We used the requests.get() method to make an HTTP GET request to the URL that
stores the CSV file.
import requests url = "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/bobbyhadz/9061dd50a9c0d9628592b156326251ff/raw/381229ffc3a72c04066397c948cf386e10c98bee/employees.csv" response = requests.get(url, timeout=10)
The timeout argument is used to specify a timeout (in seconds) after which the
request is canceled.
lines = [line.decode('utf-8') for line in response.iter_lines()] # ['first_name,last_name,date', 'Alice,Smith,2023-01-05', 'Bobby,Hadz,2023-03-25', 'Carl,Lemon,2021-01-24'] print(lines)
The next step is to get a list of the lines in the CSV file.
You can instantiate and use a csv.reader object to iterate over the lines.
csv_reader = csv.reader(lines, delimiter=',') for row in csv_reader: # ['first_name', 'last_name', 'date'] # ['Alice', 'Smith', '2023-01-05'] # ['Bobby', 'Hadz', '2023-03-25'] # ['Carl', 'Lemon', '2021-01-24'] print(row)
We used a comma as the delimiter, however, the values in your CSV file might be separated by a different character.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- csv.Error: line contains NULL byte Python error [Solved]
- Module 'csv' has no attribute 'reader' or 'writer' in Python
- How to escape commas in a CSV File [with Examples]
- Module 'lib' has no attribute 'X509_V_FLAG_CB_ISSUER_CHECK'
- _csv.Error: iterator should return strings, not bytes [Fix]
- Skip the header of a file with CSV Reader in Python

