Pip install a specific version of a Python package
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·7 min

# Table of Contents
# Pip install a specific version of a Python package
Use two equal signs to pip install a specific version of a Python package,
e.g. pip install requests==2.28.1.
If you already have the package installed, run the command with the
--ignore-installed option to ignore the installed package and overwrite it.
# 👇️ In a virtual environment or using Python 2 pip install requests==2.28.1 # 👇️ for Python 3 pip3 install requests==2.28.1 # 👇️ If you don't have pip in your PATH environment variable python3 -m pip install requests==2.28.1
The example commands install a specific version of the requests package.
# Uninstall the package and then install a specific version
If you already have the package installed, it's best to uninstall it and rerun the command scoped to the specific version.
# 👇️ Uninstall package pip uninstall requests pip3 uninstall requests python3 -m pip uninstall requests # 👇️ install a specific version of the package pip install requests==2.28.1
As an alternative to uninstalling the package prior to installing a specific version, you can also use the --ignore-installed option.
pip install requests==2.28.0 --ignore-installed
The --ignore-installed option ignores the installed packages and overwrites
them.
requests module, make sure to replace requests with the actual package you need to install.# Checking the versions of a package
You can view all of the versions of a package by entering the
pip install example== command, where you replace example with the actual
name of the package.
pip install example== pip3 install example==
Here is a screenshot of issuing the command in my terminal.
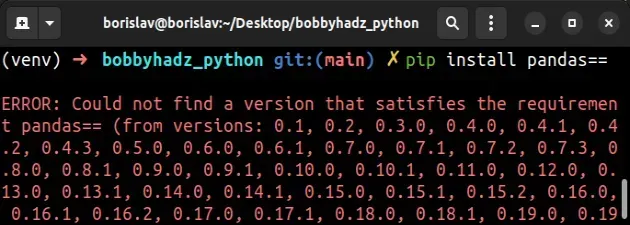
The output contains a tuple of all of the versions of the package from the oldest to the most recent.
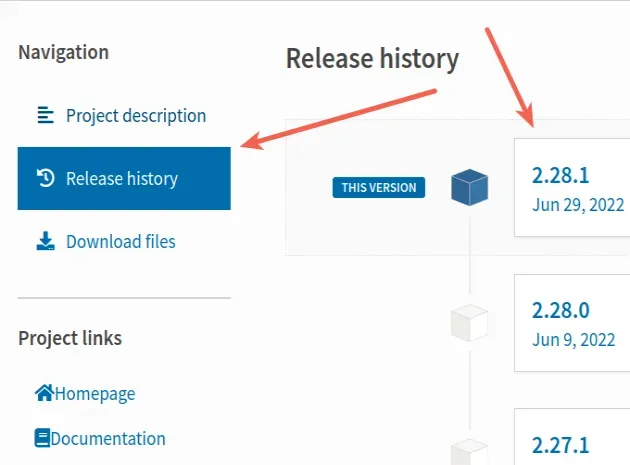
You can also view all of the versions of a package by:
- Googling "package-name pypi".
- Clicking on the pypi page of the package.
- Clicking on "Release history"
# Creating a virtual environment
If you don't have a virtual environment, it is recommended to create one as they make management of packages a lot simpler.
# 👇️ Use the correct version of Python when creating VENV python3 -m venv venv # 👇️ Activate on Unix or MacOS source venv/bin/activate # 👇️ Activate on Windows (cmd.exe) venv\Scripts\activate.bat # 👇️ Activate on Windows (PowerShell) venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 # 👇️ install a specific version of the package pip install requests==2.28.1
# Check which version of the package is installed
You can check the version of a specific package with the pip show package_name
command.
pip show requests
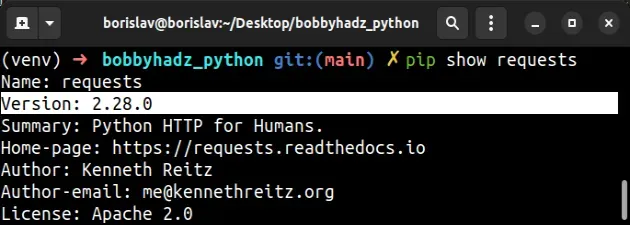
The pip show package_name command will either state that the package is not
installed or show a bunch of information about the package, including the
version and the location where the package is installed.
--force-reinstall option to install a specific version of a module.pip install requests==2.28.0 --force-reinstall
The --force-reinstall option reinstalls all packages even if they are up-to-date.
This is only necessary if you are installing a specific version of a module that is already installed in the environment.
You can also use the pip freeze command to get the versions of your installed packages.
pip freeze
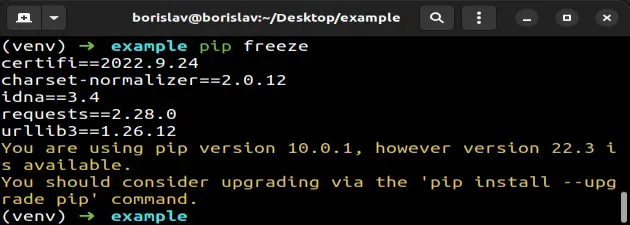
The command also shows the versions of the dependencies of the packages you installed.
If you get a warning that your pip version is out of date, run the
pip install --upgrade pip command.
pip install --upgrade pip
You can also redirect the output of the pip freeze command to a
requirements.txt file.
pip freeze > requirements.txt
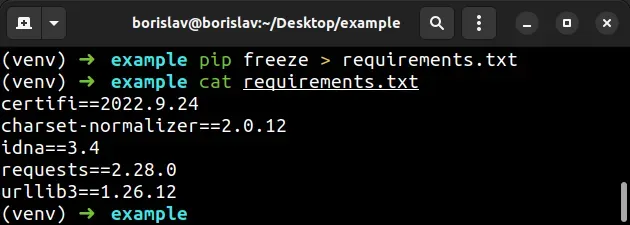
Here are the contents of my requirements.txt file.
certifi==2022.9.24 charset-normalizer==2.0.12 idna==3.4 requests==2.28.0 urllib3==1.26.12
The file contains the versions of the installed package (requests) and its
dependencies.
# Installing the packages from the requirements.txt file
You can run the pip install -r requirements.txt command if you need to install
the specified versions of the packages.
pip install -r requirements.txt
The command installs all of the packages in the file.
If you simply pip install the package, e.g. pip install requests, you are
installing the latest version.
You can also specify a version range.
pip install "requests>=2.26.0,<=2.27.0" --force-reinstall
The command installs a version of requests greater than or equal to 2.26.0
and less than or equal to 2.27.0.
Make sure to wrap the range in double quotes if you are on Windows.
# Install a specific version of pip
Use the pip install --upgrade pip command to install a specific version of
pip.
# ✅ install a specific version of `pip` pip install --upgrade pip==8.1.2 # ✅ install a specific version of a package using `pip` pip install requests==2.28.0 --ignore-installed # ✅ upgrade pip to the latest version pip install --upgrade pip
The first command installs a specific version of pip.
The pip install command will install the version of pip that is specified
after the two equal signs.
You might also have to use pip3 to scope the command to Python 3.
pip install --upgrade pip==8.1.2 pip3 install --upgrade pip==8.1.2 python -m pip install --upgrade pip==8.1.2 python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip==8.1.2
If you need to check all of the available versions of pip, use the
pip install pip== command.
pip install pip== pip3 install pip==
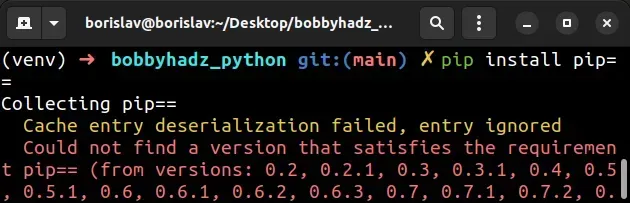
pip from the oldest to the most recent version.You can pick a version and specify it after the two equal signs.
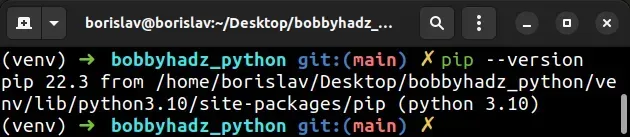
You can use the pip --version command to check your pip version.
pip --version pip3 --version
# Using the --ignore-installed flag
The same approach can be used to install a specific version of a package.
pip install requests==2.28.1 --ignore-installed pip3 install requests==2.28.1 --ignore-installed python -m pip install requests==2.28.1 --ignore-installed python3 -m pip install requests==2.28.1 --ignore-installed
The --ignore-installed option ignores the installed packages and overwrites
them.
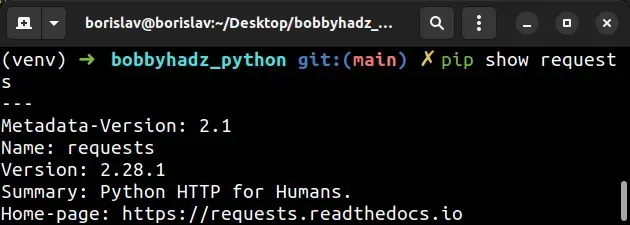
If you need to get the version of an installed package, use the
pip show <package-name> command.
pip show requests pip3 show requests python -m pip show requests python3 -m pip show requests
Make sure to replace requests with the name of your specific package.
If you need to upgrade pip to the latest version, use the
pip install --upgrade pip command.
Here are the commands for upgrading pip on all operating systems.
Which command works depends on your operating system and your version of Python.
# 👇️ If you have pip already installed pip install --upgrade pip # 👇️ If your pip is aliased as pip3 (Python 3) pip3 install --upgrade pip # 👇️ If you don't have pip in your PATH environment variable python -m pip install --upgrade pip # 👇️ If you don't have pip in your PATH environment variable python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip # 👇️ If you have easy_install easy_install --upgrade pip # 👇️ If you get a permissions error sudo easy_install --upgrade pip # 👇️ If you get a permissions error when upgrading `pip` pip install --upgrade pip --user # 👇️ Upgrade pip scoped to the current user (if you get a permissions error) python -m pip install --user --upgrade pip python3 -m pip install --user --upgrade pip # 👇️ Installing directly from get-pip.py (MacOS and Linux) curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python # 👇️ If you get permissions issues curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | sudo python # 👇️ Alternative for Ubuntu/Debian sudo apt-get update && apt-get upgrade python-pip # 👇️ Alternative for Red Hat / CentOS / Fedora sudo yum install epel-release sudo yum install python-pip sudo yum update python-pip
After you upgrade pip, upgrade setuptools and wheels as well.
pip install --upgrade setuptools wheel pip3 install --upgrade setuptools wheel python3 -m pip install --upgrade setuptools wheel
If your issue persists, run the following command.
# 👇️ On Linux or MacOS python -m ensurepip --upgrade # 👇️ Using python 3 python3 -m ensurepip --upgrade # 👇️ On Windows py -m ensurepip --upgrade
ensurepip package enables us to bootstrap the pip installer into an existing Python installation or virtual environment.Alternatively, you can use the official get-pip script to install pip.
Download the script from https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py by clicking on the link, right-clicking and selecting "Save as" in your browser.
Open your terminal in the location where the get-pip.py file is downloaded and
run the following command.
# 👇️ On Linux or MacOS python get-pip.py # 👇️ Using python 3 python3 get-pip.py # 👇️ On Windows py get-pip.py
The get-pip.py script uses bootstrapping logic to install pip.
If none of the suggestions helped, try to install pip with a command that's
specific to your operating system.
# 👇️ On Debian / Ubuntu sudo apt update sudo apt install python3-venv python3-pip # 👇️ On MacOS brew install python # 👇️ On Fedora / CentOS sudo dnf install python3-pip python3-wheel
Try upgrading pip by running:
# 👇️ on MacOS or Linux python -m pip install --upgrade pip # 👇️ for Python 3 python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip # 👇️ on Windows py -m pip install --upgrade pip
If that didn't help and you're using a virtual environment, try recreating it.
# 👇️ optionally store installed packages in a file pip freeze > requirements.txt # 👇️ deactivate deactivate # 👇️ remove the old virtual environment folder rm -rf venv # 👇️ initialize a new virtual environment python3 -m venv venv # 👇️ Activate on Unix or MacOS source venv/bin/activate # 👇️ Activate on Windows (cmd.exe) venv\Scripts\activate.bat # 👇️ Activate on Windows (PowerShell) venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 pip install --upgrade pip # 👇️ install the modules in your requirements.txt file pip install -r requirements.txt
Your virtual environment will use the version of Python that was used to create it.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- The difference between pip freeze and pip list in Python
- Pip install multiple requirements files in Python
- How to pip install a package Globally instead of Locally
- Pip install and uninstall in silent, non-interactive mode
- Pip list all available versions of a Python package
- The purpose of pip's
--no-cache-diroption - AttributeError: module 'ffmpeg' has no attribute 'input'
- How to find the dependencies of a Python package
- Check the syntax of a Python script without executing it
- 'EntryPoints' object has no attribute 'get' error [Solved]

