The difference between pip freeze and pip list in Python
Last updated: Apr 10, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# The difference between pip freeze and pip list in Python
The difference between pip freeze and pip list is that:
pip freezeoutputs the installed by the user packages in a requirements format that can be used to generate arequirements.txtfile.pip listoutputs all installed packages, including editables.
# pip freeze is used to generate a requirements.txt file
You will most often use the pip freeze command to generate a
requirements.txt file.
pip freeze > requirements.txt pip3 freeze > requirements.txt
pip freeze to a file called requirements.txt.The requirements.txt file can be used to install the packages and recreate the environment.
pip install -r requirements.txt pip3 install -r requirements.txt
A requirements.txt file can only be generated from the output of the
pip freeze command, not from
the output of pip list.
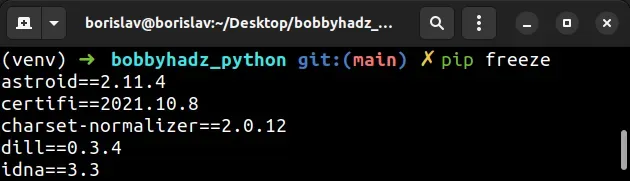
The names of packages and the specific versions are separated by two equal signs
which is the syntax used by pip to install a specific version of a package.
pip install requests==2.28.0 pip3 install requests==2.28.0
# The pip list command outputs the packages in a different format
The pip list command also shows the installed packages and their versions but in a different format.
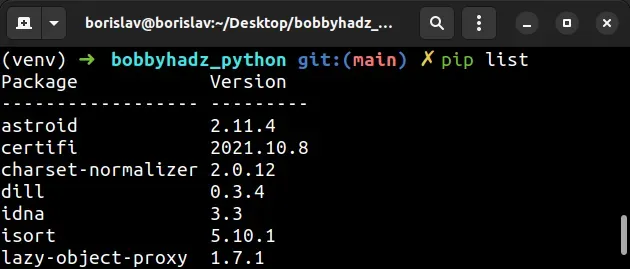
pip freeze command doesn't output packages that pip depends on by default, e.g. wheel and setuptools, whereas the pip list command does.You can use the --all option if you need to include the
pip,
setuptools, distrubute and
wheel packages in the
output of pip freeze.
pip freeze --all
The pip list outputs all installed packages, including editables, whereas
pip freeze shows the packages the user installed and their dependencies.
If you don't use a virtual environment, it is recommended to create one as they make management of packages much easier.
# 👇️ optionally store currently installed packages in a file pip freeze > requirements.txt pip3 freeze > requirements.txt # 👇️ Use the correct version of Python when creating VENV python -m venv venv # 👇️ Activate on Unix or MacOS source venv/bin/activate # 👇️ Activate on Windows (cmd.exe) venv\Scripts\activate.bat # 👇️ Activate on Windows (PowerShell) venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 # 👇️ Upgrade pip pip install --upgrade pip # 👇️ Install the package in your virtual environment pip install requests # 👇️ Optionally install packages from a `requirements.txt` file pip install -r requirements.txt pip3 install -r requirements.txt
If the python -m venv venv command doesn't work, try one of the following
commands:
python3 -m venv venvpy -m venv venv
Make sure to use the correct activation command depending on your operating system.
Note that the name requirements.txt is just a convention. You can use any to
store the output of the pip freeze command and you can have as many
requirements files as necessary.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Pip install multiple requirements files in Python
- How to pip install a package Globally instead of Locally
- Pip install and uninstall in silent, non-interactive mode
- Pip install a specific version of a Python package
- Pip list all available versions of a Python package
- The purpose of pip's
--no-cache-diroption

