How to convert an Object to FormData in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 7, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- How to convert an Object to FormData in JavaScript
- Making an HTTP request after converting the object to FormData
- Converting FormData to a JSON object in JavaScript
- How to convert an Object to FormData using Array.reduce()
- Handle nested objects and files when converting an object to FormData
# How to convert an Object to FormData in JavaScript
To convert an object to FormData in JavaScript:
- Use the
FormData()constructor to initialize a newFormDatainstance. - Use the
Object.entries()method to iterate over the object. - Use the
FormData.append()method to add each key-value pair of the object to theFormDatainstance.
function objectToFormData(obj) { const formData = new FormData(); Object.entries(obj).forEach(([key, value]) => { formData.append(key, value); }); return formData; } const employee = { id: 1, first: 'bobby', last: 'hadz', age: 30, tasks: ['develop', 'test', 'ship'], }; const fData = objectToFormData(employee); console.log(fData); console.log(fData.get('first')); // 👉️ bobby console.log(fData.get('tasks')); // 👉️ develop,test,ship
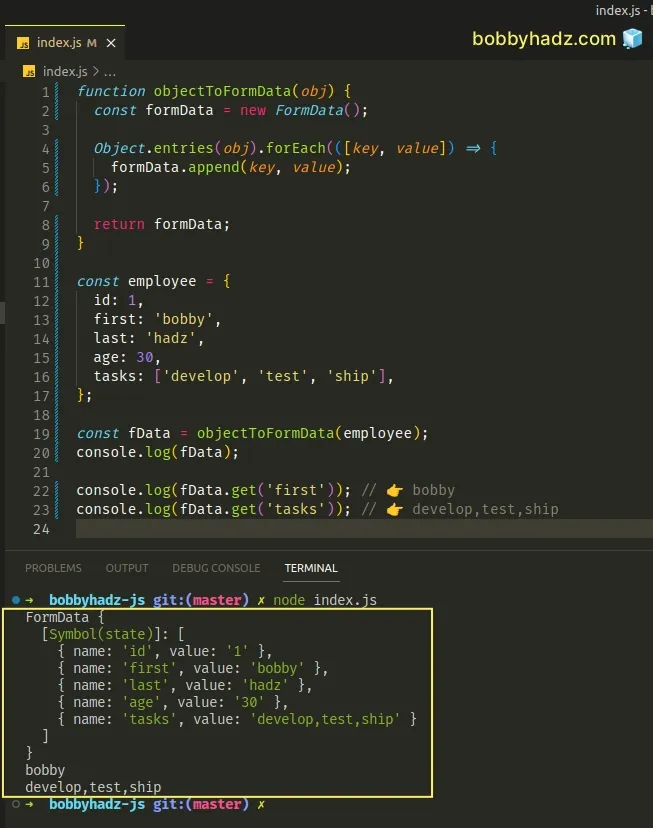
The objectToFormData() function takes an object as a parameter and converts
the object to FormData.
The
FormData()
constructor creates a new FormData object.
function objectToFormData(obj) { const formData = new FormData(); Object.entries(obj).forEach(([key, value]) => { formData.append(key, value); }); return formData; }
The object stores a set of key-value pairs that represent form fields and their values.
We used the Object.entries method to get an array of the object's key-value pairs.
const employee = { id: 1, first: 'bobby', last: 'hadz', age: 30, tasks: ['develop', 'test', 'ship'], }; // [ // [ 'id', 1 ], // [ 'first', 'bobby' ], // [ 'last', 'hadz' ], // [ 'age', 30 ], // [ 'tasks', [ 'develop', 'test', 'ship' ] ] // ] console.log(Object.entries(employee));
The function we passed to the Array.forEach() method gets called with each key-value pair from the array.
function objectToFormData(obj) { const formData = new FormData(); Object.entries(obj).forEach(([key, value]) => { formData.append(key, value); }); return formData; }
On each iteration, we use
destructuring assignment to assign
the key and value to variables and append the key-value pair to the formData
object.
The
FormData.append
method adds the given key-value pair to the FormData object or updates the
corresponding value if the key exists.
# Making an HTTP request after converting the object to FormData
Here is an example of making an HTTP request after converting the object to
FormData.
function objectToFormData(obj) { const formData = new FormData(); Object.entries(obj).forEach(([key, value]) => { formData.append(key, value); }); return formData; } const employee = { id: 1, first: 'bobby', last: 'hadz', age: 30, tasks: ['develop', 'test', 'ship'], }; const response = fetch('https://reqres.in/api/users', { method: 'POST', // 👇️ set body to FormData body: objectToFormData(employee), headers: { Accept: 'application/json', }, }) .then(res => res.json()) .then(data => { console.log('data: ', data); }) .catch(err => { console.log('error: ', err); });
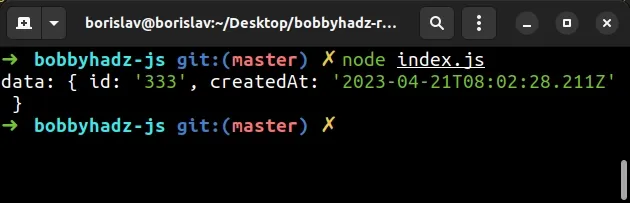
Notice that we set the body property to the result of calling the
objectToFormData() function.
# Converting FormData to a JSON object in JavaScript
If you need to convert the FormData object to a JSON object:
- Declare a new variable that stores an empty object literal.
- Use the
formData.forEach()method to iterate over theformDataobject - Add each key-value pair to the object.
- Use the
JSON.stringify()method to convert the object to a JSON string.
function objectToFormData(obj) { const formData = new FormData(); Object.entries(obj).forEach(([key, value]) => { formData.append(key, value); }); return formData; } const employee = { id: 1, first: 'bobby', last: 'hadz', age: 30, tasks: ['develop', 'test', 'ship'], }; const formData = objectToFormData(employee); // 1) Declare new empty object const object = {}; formData.forEach((value, key) => { // 2) Assign each key-value pair to the object object[key] = value; }); // { // id: '1', // first: 'bobby', // last: 'hadz', // age: '30', // tasks: 'develop,test,ship' // } console.log(object); // 3) Convert the object to a JSON string const jsonString = JSON.stringify(object); // {"id":"1","first":"bobby","last":"hadz","age":"30","tasks":"develop,test,ship"} console.log(jsonString);
We used the formData.forEach() method to iterate over the FormData object
and added each key-value pair to the newly initialized object variable.
The last step is to use the JSON.stringify() method to convert the object to a JSON string.
You can then send the JSON string over the network in an HTTP request by setting
the Content-Type HTTP request header to application/json.
# How to convert an Object to FormData using Array.reduce()
You can also use the Array.reduce() method.
- Use the
Object.entries()method to get an array of key-value pairs. - Use the
Array.reduce()method to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, append a new key-value pair to the
FormDataobject.
function objectToFormData(obj) { return Object.entries(obj).reduce((formData, [key, value]) => { formData.append(key, value); return formData; }, new FormData()); } const employee = { id: 1, first: 'bobby', last: 'hadz', age: 30, tasks: ['develop', 'test', 'ship'], }; const fData = objectToFormData(employee); console.log(fData); console.log(fData.get('first')); // 👉️ bobby console.log(fData.get('tasks')); // 👉️ develop,test,ship

We used the Object.entries() method to get an array of key-value pairs just
like in the previous subheading.
const employee = { id: 1, first: 'bobby', last: 'hadz', age: 30, tasks: ['develop', 'test', 'ship'], }; // [ // [ 'id', 1 ], // [ 'first', 'bobby' ], // [ 'last', 'hadz' ], // [ 'age', 30 ], // [ 'tasks', [ 'develop', 'test', 'ship' ] ] // ] console.log(Object.entries(employee));
However, instead of using Array.forEach(), we used the
Array.reduce() method.
function objectToFormData(obj) { return Object.entries(obj).reduce((formData, [key, value]) => { formData.append(key, value); return formData; }, new FormData()); }
The formData argument is set to a FormData object because that's what we
passed as the second argument to reduce().
On each iteration, we append the current key-value pair to the formData object
and return the result.
You can imagine that the formData value we return on each iteration gets
passed as the formData argument on the next iteration.
The value gets accumulated until all key-value pairs of the object are added to
the formData object.
# Handle nested objects and files when converting an object to FormData
If you need to handle nested objects and files when converting an object to
FormData, you have to use a recursive solution.
const buildFormData = (formData, obj, parentKey = '') => { if (Array.isArray(obj)) { obj.forEach(element => { buildFormData(formData, element, parentKey); }); } else if (typeof obj === 'object' && !(obj instanceof File)) { Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => { buildFormData( formData, obj[key], parentKey ? `${parentKey}.${key}` : key, ); }); } else { if (obj == null) { return; } const value = typeof obj === 'number' || typeof obj === 'boolean' ? obj.toString() : obj; formData.append(parentKey, value); } }; export const objectToFormData = obj => { const formData = new FormData(); buildFormData(formData, obj); return formData; }; const employee = { id: 1, first: 'bobby', last: 'hadz', age: 30, tasks: ['develop', 'test', 'ship'], address: { country: 'Belgium', city: 'Ghent', }, }; const fData = objectToFormData(employee); // FormData { // [Symbol(state)]: [ // { name: 'id', value: '1' }, // { name: 'first', value: 'bobby' }, // { name: 'last', value: 'hadz' }, // { name: 'age', value: '30' }, // { name: 'tasks', value: 'develop' }, // { name: 'tasks', value: 'test' }, // { name: 'tasks', value: 'ship' }, // { name: 'address.country', value: 'Belgium' }, // { name: 'address.city', value: 'Ghent' } // ] // } console.log(fData); console.log(fData.get('first')); console.log(fData.get('tasks'));
The buildFormData function does the bulk of the work.
If the function gets called with an array instead of an object, it iterates over the array and calls itself with each element.
if (Array.isArray(obj)) { obj.forEach(element => { buildFormData(formData, element, parentKey); }); }
If the function gets called with an object that is not a file, we iterate over the object's keys and call the function recursively with each key.
else if (typeof obj === 'object' && !(obj instanceof File)) { Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => { buildFormData( formData, obj[key], parentKey ? `${parentKey}.${key}` : key, ); }); }
This takes care of handling nested objects.
Notice that nested object properties are separated by a period . in the
output.
FormData { [Symbol(state)]: [ { name: 'id', value: '1' }, { name: 'first', value: 'bobby' }, { name: 'last', value: 'hadz' }, { name: 'age', value: '30' }, { name: 'tasks', value: 'develop' }, { name: 'tasks', value: 'test' }, { name: 'tasks', value: 'ship' }, // 👇️ nested object properties { name: 'address.country', value: 'Belgium' }, { name: 'address.city', value: 'Ghent' } ] }
If the function gets called with a null value, we return straight away.
if (obj == null) { return; }
Finally, if the function gets called with a number or a boolean, we convert the value to a string and append the key-value pair.
const value = typeof obj === 'number' || typeof obj === 'boolean' ? obj.toString() : obj; formData.append(parentKey, value);
The objectToFormData() function calls the buildFormData function and returns
the constructed FormData object.
export const objectToFormData = obj => { const formData = new FormData(); buildFormData(formData, obj); return formData; };
You should only use this approach if you need to handle nested object properties as it is a bit more involved.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to Make HTTP requests in TypeScript
- Fetch API cannot load localhost. URL scheme is not supported
- TypeError: Failed to fetch and CORS in JavaScript
- Axios Network Error when making HTTP request
- ReferenceError: fetch is not defined in NodeJs
- How to get the status code of an Axios HTTP error
- Get the Status Code of a Fetch HTTP Response in JavaScript

