How to Redirect to an Internal/External URL in React
Last updated: Apr 6, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Redirect to an External URL in React.js
- Use an anchor tag if you need to link to an external URL
- Redirect to an External URL using
window.location.href - Redirect to an internal URL using React Router
- Using the equivalent of
history.replace()
# Redirect to an External URL in React.js
Use the window.location.replace() method to redirect to an external URL in
React.
If a certain condition is met, you can programmatically replace the current
resource with the provided URL by calling the replace() method.
export default function App() { const handleClick = () => { window.location.replace('https://bobbyhadz.com'); }; return ( <div> <button onClick={handleClick}>Click to redirect</button> </div> ); }
The code sample redirects to an external URL when the user clicks on the button.
The call to window.location.replace() does the redirect.
window.location.replace('https://bobbyhadz.com');
This could be any other condition and can also be used in an if statement.
You can use the location.replace() method to replace the current resource with the provided URL.
replace() method, the current page will not be saved in session history.In other words, the user won't be able to use the back button to navigate to it.
We want to avoid this behavior because if the user navigates back to the
webpage, they would get redirected to bobbyhadz.com again and they wouldn't be
able to use the back button functionality.
# Use an anchor tag if you need to link to an external URL
If you need to simply link to an external URL, you can use an <a> tag.
export default function App() { return ( <a href="https://bobbyhadz.com" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"> bobbyhadz.com </a> ); }
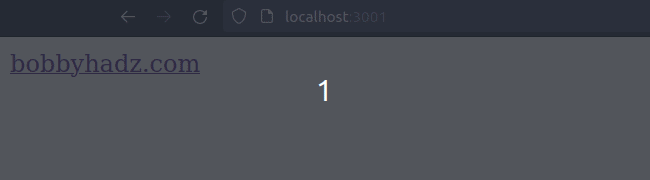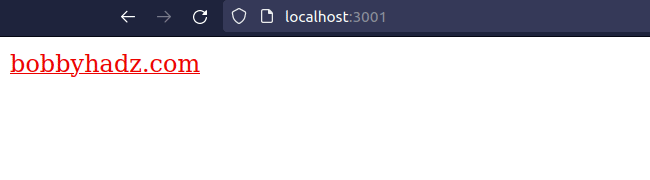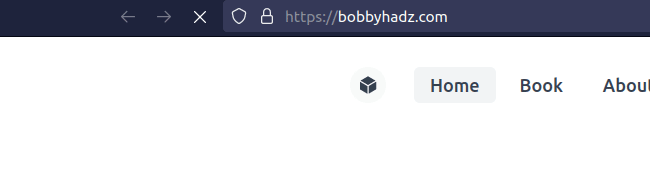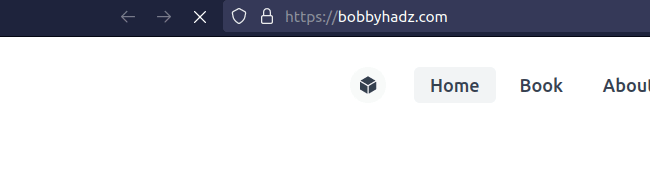
When the target prop of the <a> element is set to _blank, the resource is
loaded into a new tab.
You can remove the attribute if you want to open the external URL in the same tab.
We set the rel prop to noopener noreferrer for security purposes.
The
noopener
keyword of the rel attribute instructs the browser to navigate to the target
resource without granting the new browsing context access to the document that
opened it.
# Redirect to an External URL using window.location.href
If you want to enable the user to go back to the page that redirected them, use
window.location.href instead of window.location.replace.
export default function App() { const handleClick = () => { window.location.href = 'https://bobbyhadz.com'; }; return ( <div> <button onClick={handleClick}>Click to redirect</button> </div> ); }
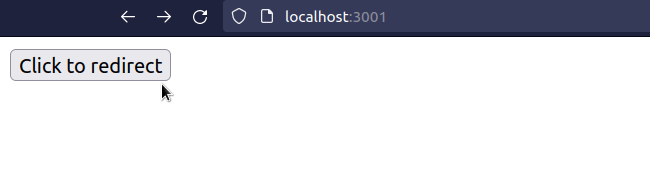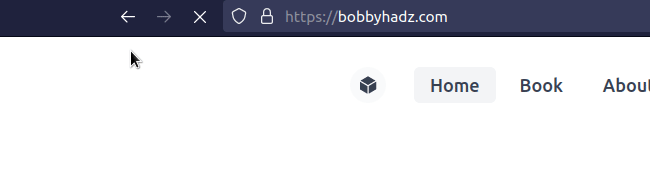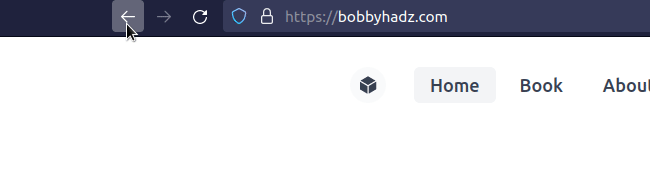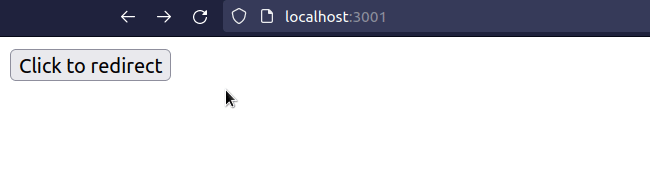
Using window.location.href instead of window.location.replace is different
because it allows the user to go back to the route that redirected them.
window.location.href = 'https://google.com';
If the route simply redirects the user to a different page, that wouldn't make much sense since they'd go back only to get redirected again.
# Redirect to an internal URL using React Router
You can use the useNavigate hook of React Router to navigate to a different
route in your App.
Here is an example of wrapping your React app in a Router in your index.js
file.
import {createRoot} from 'react-dom/client'; import App from './App'; import {BrowserRouter as Router} from 'react-router-dom'; const rootElement = document.getElementById('root'); const root = createRoot(rootElement); // 👇️ Wrap App in Router root.render( <Router> <App /> </Router>, );
Now you can use the useNavigate hook in your App.js file.
import React from 'react'; import {useNavigate} from 'react-router-dom'; export default function App() { const navigate = useNavigate(); const handleClick = () => { // 👇️ Navigate programmatically navigate('/about'); }; return ( <div> <button onClick={handleClick}>Navigate to About</button> </div> ); }
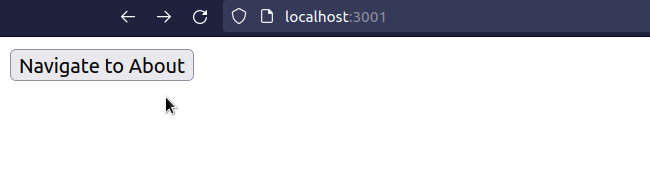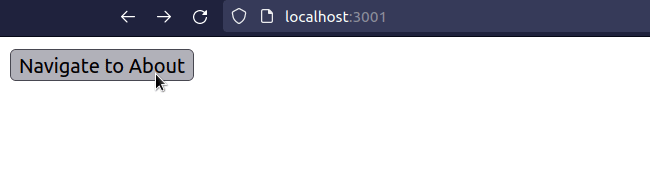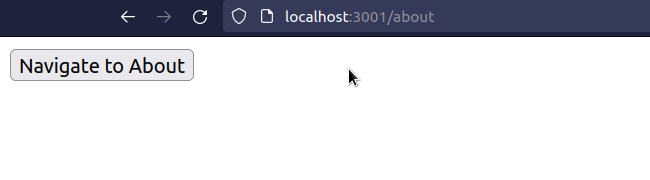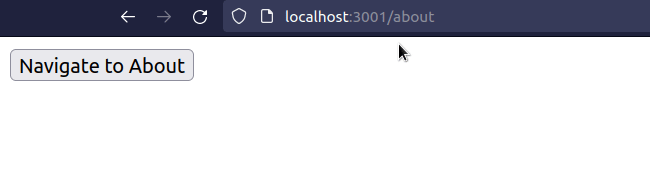
We programmatically navigate to the /about page when the button is clicked.
The useNavigate hook returns a function that lets us navigate
programmatically, e.g. after a form is submitted.
I've written a detailed guide on how to redirect to another page on button click.
# Using the equivalent of history.replace()
The parameter we passed to the navigate function is the same as the to prop
on a <Link to="/about"> component.
If you want to use the equivalent of the history.replace() method, pass an
options parameter to the navigate function.
import {useNavigate} from 'react-router-dom'; export default function App() { const navigate = useNavigate(); const handleClick = () => { // 👇️ Replace set to true navigate('/about', {replace: true}); }; return ( <div> <button onClick={handleClick}>Navigate to About</button> </div> ); }
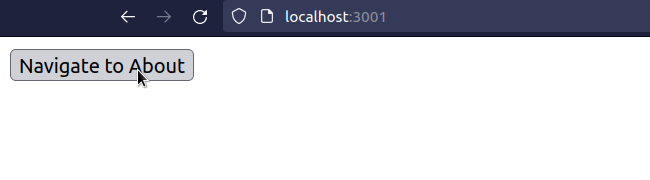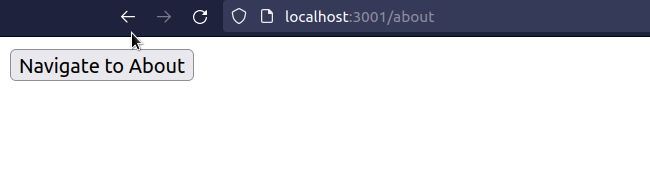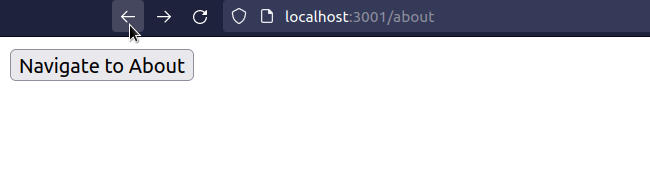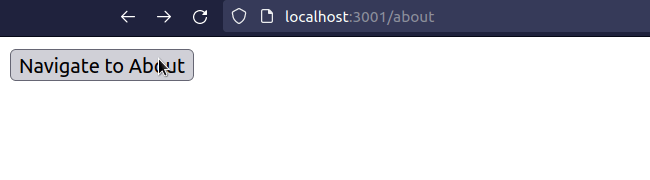
When the replace property is set to true on the options object, the current
entry in the history stack gets replaced with the new one.
This is useful, for example, when a user logs in - you don't want them to be able to click the back button and get back to the login page.
Or if you have a route that redirects users to a different page - you don't want users to click the back button and get redirected again.
You can also call the navigate function with a delta to go back in the history
stack, e.g. navigate(-1) is the same as hitting the back button.
# Redirect to an external URL using React Router
If you need to redirect to an external URL with React Router, you have to use
the window.location.replace() method.
import {Link, Route, Routes} from 'react-router-dom'; export default function App() { return ( <div> <div> <Link to="/about">About</Link> </div> <Routes> <Route path="/about" element={<About />} /> </Routes> </div> ); } function About() { // 👇️ Redirect to external URL window.location.replace('https://bobbyhadz.com'); return null; }
The code snippet redirects to an external URL when the user navigates to the
/about route.
This could be any other condition and can also be used in an if statement.
replace() method, the current page will not be saved in session history.In other words, the user won't be able to use the back button to navigate to it.
We want to avoid this behavior because if the user navigates back to the
/about route, they would get redirected to bobbyhadz.com again and they
wouldn't be able to use the back button functionality.
# Redirect to an external URL with React Router using window.location.href
If you want to enable the user to go back to the page that redirected them, use
window.location.href instead of window.location.replace.
import {Link, Route, Routes} from 'react-router-dom'; export default function App() { return ( <div> <div> <Link to="/about">About</Link> </div> <Routes> <Route path="/about" element={<About />} /> </Routes> </div> ); } function About() { // 👇️ Using window.location.href 👇️ window.location.href = 'https://bobbyhadz.com'; return null; }
Using window.location.href instead of window.location.replace is different
because it allows the user to go back to the route that redirected them.
window.location.href = 'https://bobbyhadz.com';
In this particular case, if the user clicks back, they would get redirected to
bobbyhadz.com again.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Redirect on form submit using React Router
- Set a Default route with redirect using React Router
- Get the current URL and Route in React and React Router
- How to remove query params using React router
- Get the ID from a URL in React and React Router
- How to Go back to the previous Page with React Router
- Handling 404 page not found in React Router
- Programmatically update query params in React router

