How to fetch Data on Button click in React
Last updated: Apr 7, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
# Fetch data on Button click using fetch in React
To fetch data on button click in React:
- Set the
onClickprop on a button element. - Every time the button is clicked, make an HTTP request.
- Update the state variables and render the data.
import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const [data, setData] = useState({data: []}); const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false); const [err, setErr] = useState(''); const handleClick = async () => { setIsLoading(true); try { const response = await fetch('https://reqres.in/api/users', { method: 'GET', headers: { Accept: 'application/json', }, }); if (!response.ok) { throw new Error(`Error! status: ${response.status}`); } const result = await response.json(); console.log('result is: ', JSON.stringify(result, null, 4)); setData(result); } catch (err) { setErr(err.message); } finally { setIsLoading(false); } }; console.log(data); return ( <div> {err && <h2>{err}</h2>} <button onClick={handleClick}>Fetch data</button> {isLoading && <h2>Loading...</h2>} {data.data.map(person => { return ( <div key={person.id}> <h2>{person.email}</h2> <h2>{person.first_name}</h2> <h2>{person.last_name}</h2> <br /> </div> ); })} </div> ); }; export default App;

We set the onClick prop on a button element, so every time the button gets
clicked, the handleClick function gets invoked.
<button onClick={handleClick}>Fetch data</button>
We marked the handleClick function as async, so we are able to use the
await keyword to await Promises inside of it.
const handleClick = async () => { setIsLoading(true); try { const response = await fetch('https://reqres.in/api/users', { method: 'GET', headers: { Accept: 'application/json', }, }); if (!response.ok) { throw new Error(`Error! status: ${response.status}`); } const result = await response.json(); console.log('result is: ', JSON.stringify(result, null, 4)); setData(result); } catch (err) { setErr(err.message); } finally { setIsLoading(false); } };
handleClick function, we wait for the HTTP request to finish and update the state variables.At the start of the request, the isLoading state is set to true to show a
loading spinner if the request takes time.
We used the finally block to set the isLoading state back to false,
regardless if the request is successful or has failed.
finally { setIsLoading(false); }
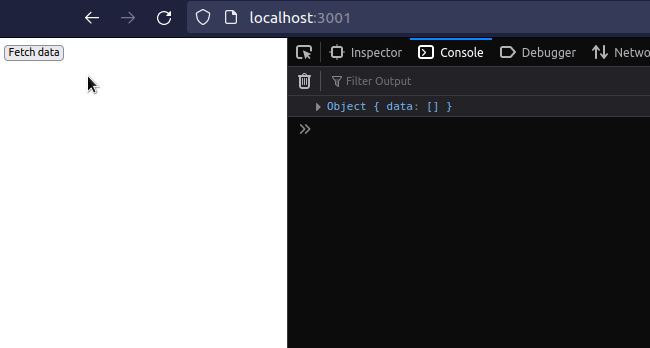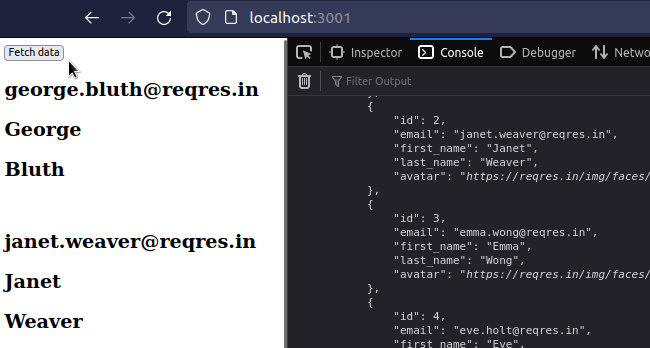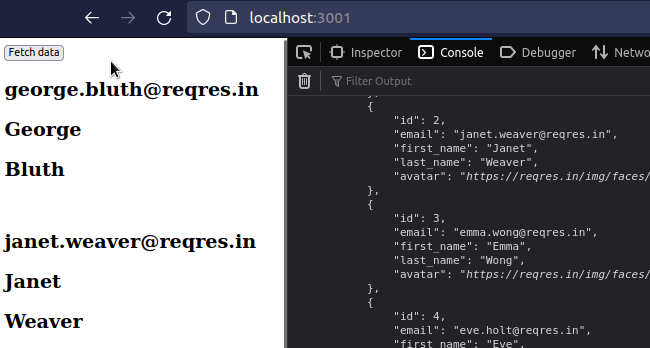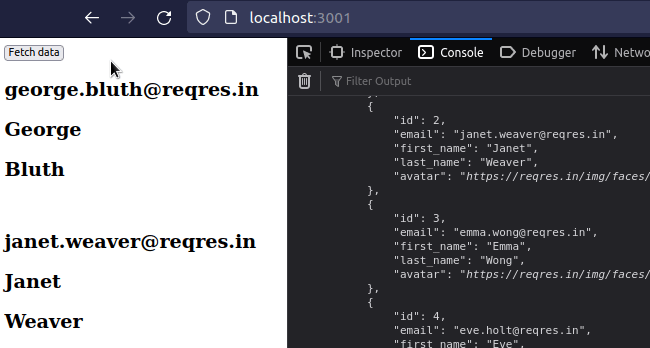
If the request is successful, the data state variable gets set to the data
from the response, otherwise, the err state gets set.
On a successful response, the data gets rendered, otherwise, the error is
shown.
This example uses the native fetch API, but the concept applies if you're
using the axios package as well.
# Fetch data on Button click using axios in React
If you decide to use axios, make sure you have the package installed by
running npm install axios.
# 👇️ If you use NPM npm install axios # 👇️ If you use YARN yarn add axios
Here is how you would fetch data on button click using the axios package.
import {useState} from 'react'; import axios from 'axios'; const App = () => { const [data, setData] = useState({data: []}); const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false); const [err, setErr] = useState(''); const handleClick = async () => { setIsLoading(true); try { const {data} = await axios.get('https://reqres.in/api/users', { headers: { Accept: 'application/json', }, }); console.log('data is: ', JSON.stringify(data, null, 4)); setData(data); } catch (err) { setErr(err.message); } finally { setIsLoading(false); } }; console.log(data); return ( <div> {err && <h2>{err}</h2>} <button onClick={handleClick}>Fetch data</button> {isLoading && <h2>Loading...</h2>} {data.data.map(person => { return ( <div key={person.id}> <h2>{person.email}</h2> <h2>{person.first_name}</h2> <h2>{person.last_name}</h2> <br /> </div> ); })} </div> ); }; export default App;
If you use axios, make sure you have the package installed by running
npm install axios in the root directory of your project.
The syntax when using the axios package is a bit cleaner and we have to deal
with less implementation details, but the concept is the same.
We have to set the onClick prop on a button element and make an HTTP request
every time the button is clicked.
<button onClick={handleClick}>Fetch data</button>
Every time the button is clicked, the handleClick function is invoked.
The first thing to do in the request handler is to set the isLoading state to
true to show a loading spinner if the request takes time.
const handleClick = async () => { setIsLoading(true); try { const {data} = await axios.get('https://reqres.in/api/users', { headers: { Accept: 'application/json', }, }); console.log('data is: ', JSON.stringify(data, null, 4)); setData(data); } catch (err) { setErr(err.message); } finally { setIsLoading(false); } };
The finally block takes care of setting the loading state back to false.
finally { setIsLoading(false); }
The finally block runs regardless if the request has succeeded or has failed.
If the request succeeds, we set the data state variable to the data from the
API.
setData(data);
If the request fails, we update the error state and render the error message.
catch (err) { setErr(err.message); }
If you need to wait for the state to update, click on the link and follow the instructions.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- React Hook useEffect has a missing dependency error [Fixed]
- useEffect must not return anything besides a function
- Can't perform a react state update on an unmounted component
- How to Remove an Event listener in React
- Fetch API cannot load localhost. URL scheme is not supported
- How to change the favicon in React.js.
- How to download a File in React.js (local or remote file)
- How to change the Base URL in Axios [4 ways]
- How to generate unique IDs in React.js [3 Ways]
- fetch() returns empty Response Body in JavaScript [Solved]
- Chrome: How to Copy an Object or Array from the Console tab
- TypeError: Failed to execute 'fetch' on 'Window' [Solved]
- How to POST Form Data using the JavaScript Fetch API

