How to change the Base URL in Axios [4 ways]
Last updated: Mar 7, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Setting the
axiosBase URL globally - Overwriting the current base URL for a specific
axiosrequest - Setting the
axiosBase URL by creating an instance - Setting the
axiosBase URL dynamically
# Setting the axios Base URL globally
One way to change the axios base URL is to set the defaults.baseURL
property on the imported axios object.
Properties set on the defaults object are applied to every request.
import axios from 'axios'; axios.defaults.baseURL = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/'; axios .get('posts') .then(response => { console.log(response.data); }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
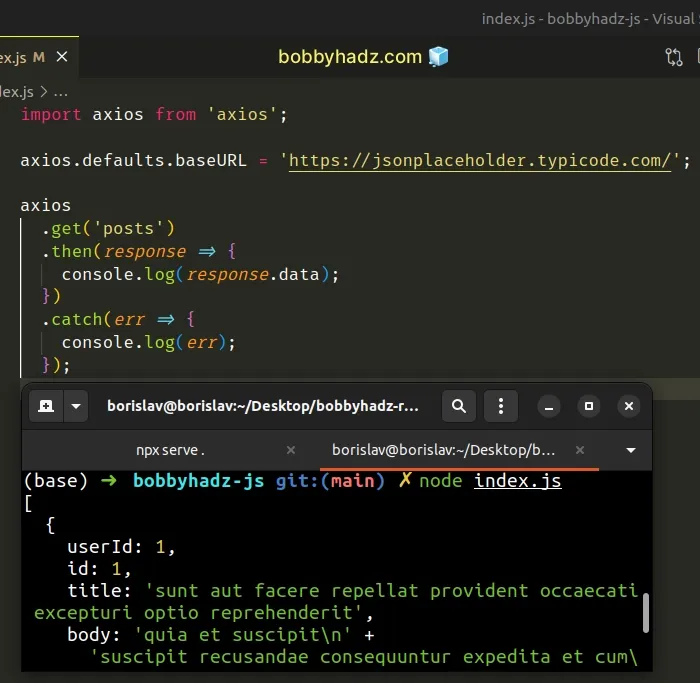
You can import the axios module and set
the defaults.baseURL property in your main .js file (e.g. index.js).
import axios from 'axios'; axios.defaults.baseURL = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/';
You might also be making requests to the same origin and just want to set a path that you don't want to repeat every time.
import axios from 'axios'; axios.defaults.baseURL = '/api/'; axios .get('posts') .then(response => { console.log(response.data); }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
The example sets the base URL to /api/, so it would make an HTTP request to
/api/posts on the same origin.
axios and have the base URL configured.When you set properties on the defaults object, they are applied to every
request as shown in
this section of the axios
docs.
# Overwriting the current base URL for a specific axios request
You can also overwrite the current base URL for a specific axios request.
Here is an example.
import axios from 'axios'; axios.defaults.baseURL = 'https://google.com'; axios({ method: 'GET', url: 'posts', baseURL: 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/', }) .then(response => { console.log(response.data); }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
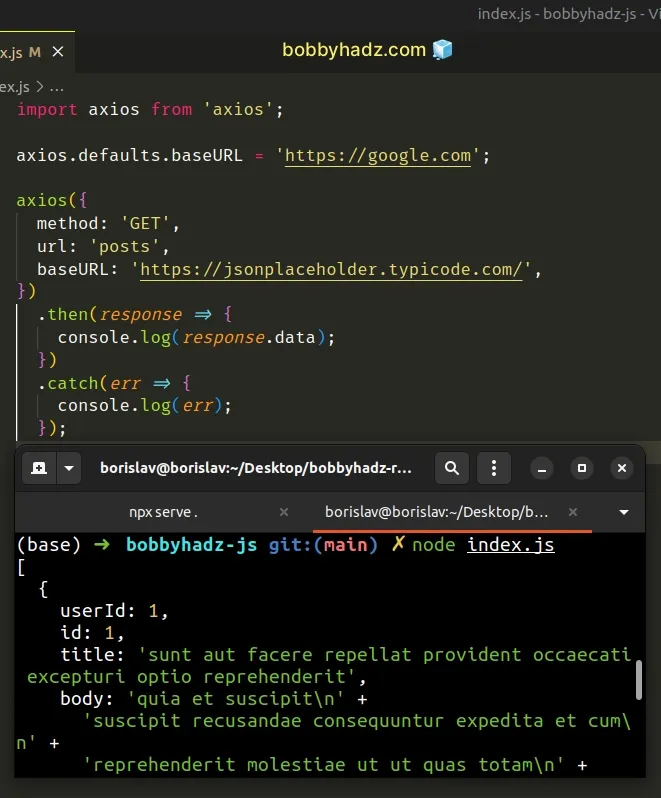
We initially set the baseUrl property to google.com.
axios.get() method.Instead, we called the axios() method and passed it an object containing 3
properties:
method- the request method that is used when making the HTTP request.url- the server URL to which the request is madebaseURL-baseURLwill be prepended tourl, unlessurlis absolute.
The example makes an HTTP GET request to the following URL:
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts
You can view all the available properties you can set in the request
configuration object in
this section of the axios
docs.
If you need to make a request to the current origin when overwriting the
baseURL property, set baseURL to /.
import axios from 'axios'; axios.defaults.baseURL = 'https://google.com'; axios({ method: 'GET', url: 'posts', baseURL: '/', }) .then(response => { console.log(response.data); }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
The example makes an HTTP GET request to the current origin at /posts.
# Setting the axios Base URL by creating an instance
You can also set the base URL by creating an axios instance.
import axios from 'axios'; // 👇️ export your instance export const placeholderApi = axios.create({ baseURL: 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/', }); placeholderApi .get('posts') .then(response => { console.log(response.data); }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
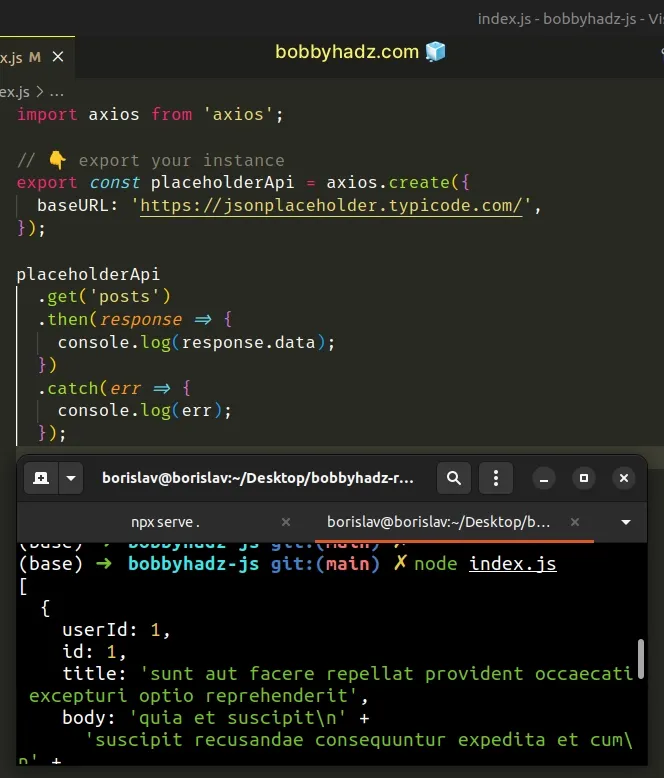
We created an axios instance and set the baseURL property.
Now every time you make an HTTP request to the given URL, you have to import and
use the instance instead of importing axios directly.
// 👇️ import and use the axios instance import {placeholderApi} from './index.js' placeholderApi .get('posts') .then(response => { console.log(response.data); }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
You can create a utility file called axios-instances.js that stores your
axios instances.
import axios from 'axios'; export const placeholderApi = axios.create({ baseURL: 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/', });
You can now import the placeholderApi instance from the axios-instances
module.
import {placeholderApi} from './axios-instances'; placeholderApi .get('posts') .then(response => { console.log(response.data); }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
You can repeat the process and create multiple axios instances if you need to
make HTTP requests to multiple different domains in the same application.
import axios from 'axios'; export const placeholderApi = axios.create({ baseURL: 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/', }); export const randomUserApi = axios.create({ baseURL: 'https://randomuser.me/api/', });
I've written a detailed guide on how to import and export classes and functions in JavaScript.
# Setting the axios Base URL dynamically
In some cases, you might also have to set the axios Base URL dynamically.
import axios from 'axios'; export const axiosInstance = axios.create(); function getBaseUrl() { // some logic to determine base URL here return Promise.resolve( 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/', ); } axiosInstance.interceptors.request.use( async config => { config.baseURL = await getBaseUrl(); return config; }, error => Promise.reject(error), ); axiosInstance .get('posts') .then(response => { console.log(response.data); }) .catch(err => { console.log(err); });
We created an axios instance and used the
interceptors property to
intercept the HTTP request before it is handled.
The request interceptor awaits an async function to determine the base URL.
After the base URL is retrieved, we issue the HTTP GET request.
The example makes an HTTP GET request to the following URL.
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/api
I've also written articles on:

