useEffect must not return anything besides a function [Fix]
Last updated: Apr 7, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- useEffect must not return anything besides a function
- Write the async function inside your useEffect hook
- Returning a clean-up function from your useEffect hook
# useEffect must not return anything besides a function
The warning "useEffect must not return anything besides a function, which is
used for clean-up." occurs when you return a value that is not a function from
your useEffect hook.
To solve the error, define an async function within your useEffect hook
and call it.
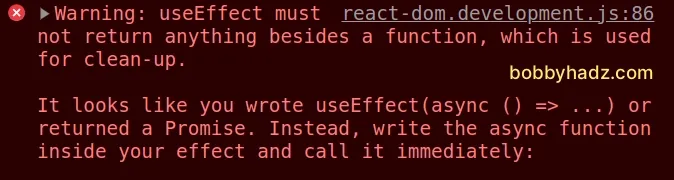
Here is the complete stack trace.
Warning: useEffect must not return anything besides a function, which is used for clean-up. It looks like you wrote useEffect(async () => ...) or returned a Promise. Instead, write the async function inside your effect and call it immediately:
Here is a code sample that causes the warning.
import {useState, useEffect} from 'react'; function App() { const [users, setUsers] = useState([]); // ⛔️ Effect callbacks are synchronous to prevent race conditions. Put the async function inside: // ⛔️ defining the function as async causes the issue useEffect(async () => { const response = await fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/'); const data = await response.json(); setUsers(data.results); }, []); console.log(users); return ( <div> {users.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> </div> ))} </div> ); } export default App;
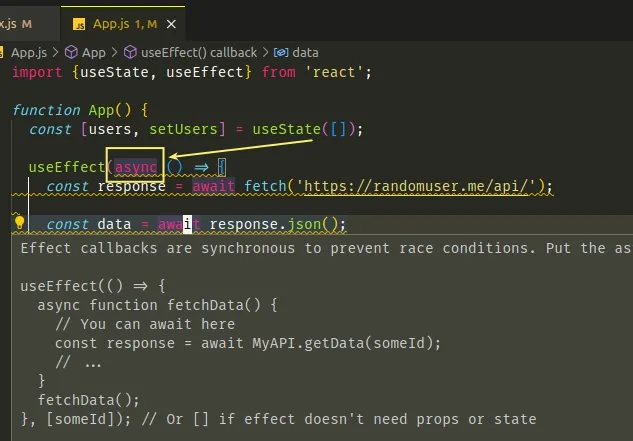
Notice that we defined the function we passed to the useEffect hook as async.
async return a Promise object.This is an issue because the useEffect hook should only return a function that
is used for clean-up.
The clean-up function is called when the component unmounts and is often used to remove event listeners and carry out other tasks that allow you to avoid memory leaks.
Make sure you don't have a return statement that returns anything other than a
clean-up function in your useEffect hook (e.g. a Promise).
# Write the async function inside your useEffect hook
To solve the error, write the async function inside your useEffect hook and
call it.
import {useState, useEffect} from 'react'; function App() { const [users, setUsers] = useState([]); // 👇️ Notice that this function is no longer async useEffect(() => { // ✅ Define the async function here async function getUsers() { const response = await fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/'); const data = await response.json(); setUsers(data.results); } // 👇️ Call the function here getUsers(); }, []); console.log(users); return ( <div> {users.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> </div> ))} </div> ); } export default App;
Notice that the function we passed to the useEffect hook is no longer async.
async functions return a Promise even if you don't explicitly use a return statement.Instead, we defined the async function inside of the useEffect hook and
called it.
When the component mounts, the useEffect hook runs and the getUsers()
function is invoked.
The function fetches data from a remote API and updates the state.
Here is a complete example that sets a loading spinner and error state.
import {useState, useEffect} from 'react'; function App() { const [users, setUsers] = useState([]); const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false); const [err, setErr] = useState(''); useEffect(() => { async function getUsers() { setIsLoading(true); try { const response = await fetch( 'https://randomuser.me/api/', ); const data = await response.json(); console.log('data is: ', JSON.stringify(data, null, 4)); setUsers(data.results); } catch (err) { setErr(err.message); } finally { setIsLoading(false); } } getUsers(); }, []); return ( <div> {err && <h2>{err}</h2>} {isLoading && <h2>Loading...</h2>} {users.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> </div> ))} </div> ); } export default App;
We added 2 more state variables - isLoading and err.
The isLoading boolean is used to track the loading state and the err state
variable tracks the error state.
Once we start fetching data, we immediately set the loading state to true.
async function getUsers() { setIsLoading(true); try { const response = await fetch( 'https://randomuser.me/api/', ); const data = await response.json(); console.log('data is: ', JSON.stringify(data, null, 4)); setUsers(data.results); } catch (err) { setErr(err.message); } finally { setIsLoading(false); } }
We added a try/catch statement to handle a potential error.
If the fetch request succeeds, the users state variable gets set to the
users from the remote API.
If an error occurs, the catch block runs where we set the error state.
The finally block is run regardless if the HTTP request is successful or not.
In the finally block, we simply set the loading state to false.
# Returning a clean-up function from your useEffect hook
As the warning states, "useEffect must not return anything besides a function, which is used for clean-up".
Let's look at an example that returns a clean-up function from the useEffect
hook to fully understand how it works.
As previously noted, the clean-up function is most commonly used to remove event listeners, track whether the component is mounted and in general to help us avoid memory leaks.
The following example uses the clean-up function to set an isMounted variable
to false.
import {useState, useEffect} from 'react'; function App() { const [users, setUsers] = useState([]); useEffect(() => { // 👇️ Initialize `isMounted` to `true` let isMounted = true; async function getUsers() { const response = await fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/'); const data = await response.json(); console.log('data is: ', JSON.stringify(data, null, 4)); // 👇️ Only update the state if the component is mounted if (isMounted) { setUsers(data.results); } } getUsers(); return () => { // 👇️ When the component unmounts, set isMounted to false isMounted = false; }; }, []); return ( <div> {users.map(user => ( <div key={user.id.value}> <h2> Name: {user.name.first} {user.name.last} </h2> </div> ))} </div> ); } export default App;
We initialized the isMounted variable to true inside our useEffect hook.
// 👇️ Initialize `isMounted` to `true` let isMounted = true;
We'll use the variable to track whether the component is mounted or not.
This is useful because if you try to update the state of an unmounted component you'd get the "Can't perform a react state update on an unmounted component" warning.
The getUsers function uses the value of the isMounted variable to determine
whether it should update the state.
async function getUsers() { const response = await fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/'); const data = await response.json(); console.log('data is: ', JSON.stringify(data, null, 4)); // 👇️ Only update the state if the component is mounted if (isMounted) { setUsers(data.results); } }
If the component is no longer mounted, we don't want to attempt to update the state because it is pointless and a sign of a memory leak.
The function we returned from the useEffect hook is run when the component
unmounts.
return () => { // 👇️ When the component unmounts, set isMounted to false isMounted = false; };
The function simply sets the isMounted variable to false.
If the getUsers function runs after the component is unmounted, the condition
in the if statement is not met and we don't attempt to update the state.
I've also written an article on how to fetch data on button click in React.js.
The article shows examples that use the built-in fetch and the third-party
axios modules.
I've also written an article on
how to run a React hook when a component unmounts
with an example that uses the removeEventListener method.
# Conclusion
To resolve the "useEffect must not return anything besides a function, which is
used for clean-up." warning, make sure the function you've passed to the
useEffect hook is not marked as async.
All async functions return a promise, even if you don't use an explicit
return statement.
Instead, define the async function inside the useEffect hook and call the
async function.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

