TypeError: Failed to execute 'fetch' on 'Window' [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 4, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# TypeError: Failed to execute 'fetch' on 'Window' [Solved]
The JavaScript fetch TypeError "Failed to execute 'fetch' on 'Window'" occurs for multiple reasons:
- Having a newline (
\n) character in any of your header values (e.g. theAuthorizationheader). - Having an invalid character in one of your header names (e.g. a colon
:). - Misspelling the names of one of your HTTP headers.
- Supplying a request body when issuing a GET request.
- Having other syntactical errors in your
fetchrequest.
# Make sure you don't have a newline character \n in your header keys and values
The first thing you should check is that you don't have any newline characters
\n in your header keys and values.
// ⛔️ header value contains \n newline character { 'Authorization': '\nBearer YOUR_TOKEN' }
You might also be using a template literal string to interpolate a variable.
// ⛔️ header value contains \n newline character const value = 'some\nheader\nvalue'; headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Authorization': `Bearer ${token}`, }
Here is an example of a valid HTTP GET fetch() request that sets headers.
function getUser() { return fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts', { method: 'GET', headers: { Accept: 'application/json', Authorization: 'Bearer YOUR_TOKEN', }, }) .then(response => { if (!response.ok) { throw new Error(`Error! status: ${response.status}`); } return response.json(); }) .catch(error => { console.log('error: ', error); }); } getUser().then(data => { console.log(data); });
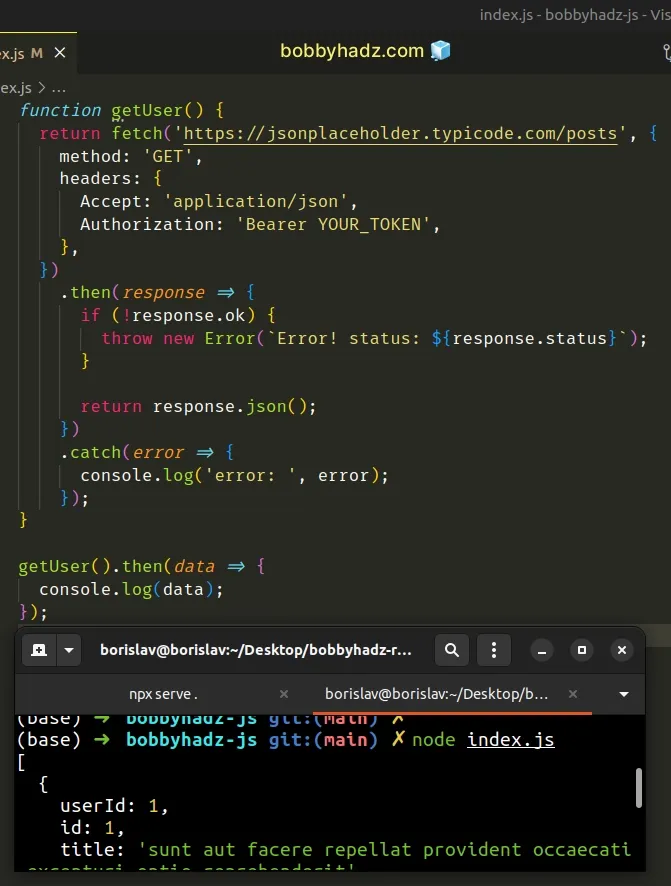
- Make sure you don't have any misspelled header names.
- Your headers shouldn't contain any special characters, e.g. newlines
\nor spaces. - You shouldn't provide a request body when issuing a GET request.
Also, make sure that your headers property is set to an object.
The error also occurs when you try to set the headers property to a string.
// ⛔️ incorrect headers: 'Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN'
Instead, the headers property must be set to an object of header keys and
values.
headers: { 'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_TOKEN', 'Accept': 'application/json', }
And, here is an example of a valid HTTP POST fetch() request that specifies a
request body and headers.
function getUser() { return fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts', { method: 'POST', body: JSON.stringify({ author: 'bobby hadz', title: 'Using fetch correctly in JavaScript', }), headers: { Accept: 'application/json', Authorization: 'Bearer YOUR_TOKEN', 'Content-Type': 'application/json', }, }) .then(response => { if (!response.ok) { throw new Error(`Error! status: ${response.status}`); } return response.json(); }) .catch(error => { console.log('error: ', error); }); } getUser().then(data => { console.log(data); });
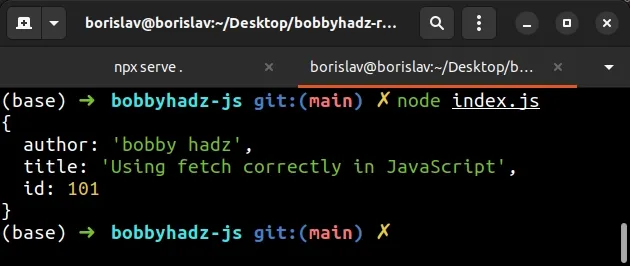
- Notice that we set the HTTP method to
POST. - We used the JSON.stringify() method to convert the body object to a JSON string.
- Make sure you haven't misspelled any header names or header values.
# Having an invalid character in your header names or values
The error also commonly occurs when you have an invalid character in a header name or value, e.g. a colon.
// ⛔️ incorrect - header name contains a colon headers: { "Authorization:": "Bearer YOUR_TOKEN", }
Notice that the header name above contains a colon.
Make sure you don't have any special characters in the names of your headers.
// ✅ correct headers: { "Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_TOKEN", }
Also, make sure you don't have any species in the names of your headers.
// ⛔️ incorrect - header name contains a space headers: { "Content Type": "application/json" }
Misspelling the name of a header commonly causes the error.
The Content-Type header contains a hyphen, not a space.
// ✅ correct - header name is spelled correctly headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" }
The following is also incorrect.
// ⛔️ incorrect - should be Content-Type, not Content/Type headers: { 'Content/Type': 'application/json' }
Make sure you haven't misspelled any of the names of your HTTP headers.
# Make sure you haven't included the body in a GET request
Another common cause of the error is including the request body in a GET request.
The following code sample causes the error because we've set the method
property to GET but we are also sending a request body.
// ⛔️ error: TypeError: Failed to execute 'fetch' on 'Window': Request with GET/HEAD method cannot have body. function getUser() { return fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts', { method: 'GET', body: JSON.stringify({ author: 'bobby hadz', title: 'Using fetch correctly in JavaScript', }), headers: { Accept: 'application/json', Authorization: 'Bearer YOUR_TOKEN', 'Content-Type': 'application/json', }, }) .then(response => { if (!response.ok) { throw new Error(`Error! status: ${response.status}`); } return response.json(); }) .catch(error => { console.log('error: ', error); }); } getUser().then(data => { console.log(data); });
If you meant to send over a POST request, make sure to set the method property
to POST.
fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts', { // 👇️ set method to POST method: 'POST', body: JSON.stringify({ author: 'bobby hadz', title: 'Using fetch correctly in JavaScript', }), headers: { Accept: 'application/json', Authorization: 'Bearer YOUR_TOKEN', 'Content-Type': 'application/json', }, })
If you meant to send a GET request, then you have to remove the body property.
function getUser() { return fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts', { method: 'GET', // ✅ removed body property to send a GET request headers: { Accept: '\napplication/json', Authorization: 'Bearer YOUR_TOKEN', }, }) .then(response => { if (!response.ok) { throw new Error(`Error! status: ${response.status}`); } return response.json(); }) .catch(error => { console.log('error: ', error); }); } getUser().then(data => { console.log(data); });
However, the HTTP method cannot be GET when the body property is set.
Note that the method property defaults to GET when using fetch().
You have to explicitly set the method property if you need to issue a request
of a different type, e.g. POST, PATCH, DELETE, etc.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to fetch Data on Button click in React
- Fetch API cannot load localhost. URL scheme is not supported
- TypeError: Failed to fetch and CORS in JavaScript
- Axios Network Error when making HTTP request
- ReferenceError: fetch is not defined in NodeJs
- How to get the status code of an Axios HTTP error
- Get the Status Code of a Fetch HTTP Response in JavaScript
- fetch() returns empty Response Body in JavaScript [Solved]

