"pip install" causes SyntaxError: invalid syntax [Solved]
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024
Reading time·7 min

# "pip install" causes SyntaxError: invalid syntax [Solved]
If you get a "SyntaxError: invalid syntax" when trying to install a module
using pip, make sure to run the command from your shell, e.g. bash or
PowerShell, and not by running a Python file that contains the
pip install your_module command.
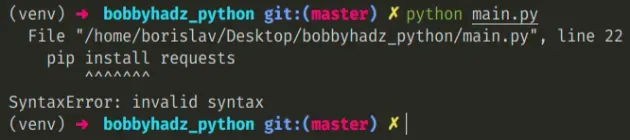
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
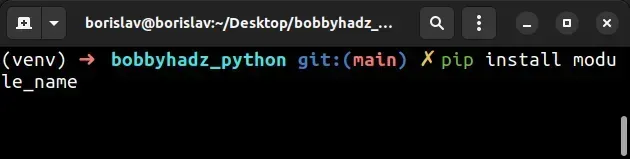
# ⛔️ SyntaxError: invalid syntax pip install requests
# Running pip install from a Python file causes the error
Running the main.py file with python main.py causes the error because we
aren't supposed to run pip commands by running a Python script.
# Don't run pip install from the Python interpreter
You also shouldn't be running the pip install some_module command from the
Python interpreter in your shell.
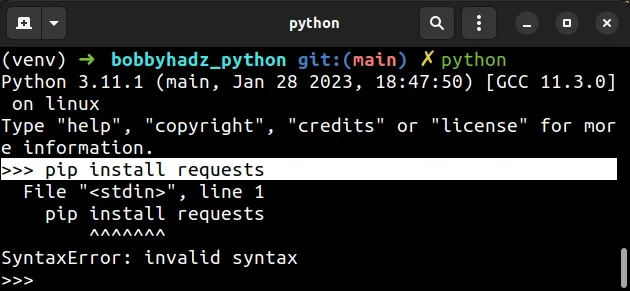
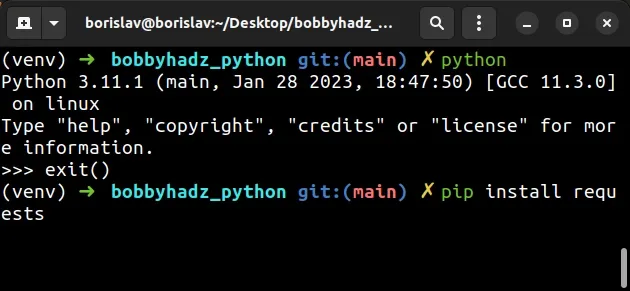
You can press CTRL + D (or Cmd + D on macOS) to exit the Python
interpreter and install the specific module.
If pressing CTRL + D doesn't let you exit the Python interpreter, use the
exit() function.
exit() pip install requests # 👇️ or pip3 pip3 install requests
# Run the pip install command from your shell
Instead, run the pip install your_module command from your shell, e.g. bash,
PowerShell or CMD.
pip install requests # 👇️ or pip3 pip3 install requests # 👇️ or python -m prefix python -m pip install requests python3 -m pip install requests py -m pip install requests
The example above installs the requests module. Make sure to adjust the name of the module if you have to.
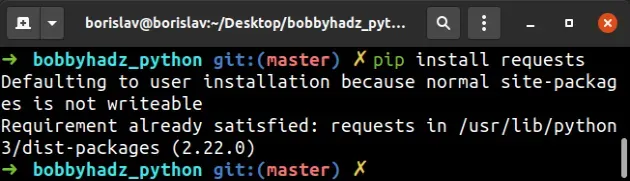
If you get an error when running the pip install some_module command from your
shell, try the following commands.
# 👇️ In a virtual environment or using Python 2 pip install requests # 👇️ For python 3 (could also be pip3.10 depending on your version) pip3 install requests # 👇️ If you get a permissions error sudo pip3 install requests # 👇️ If you don't have pip in your PATH environment variable python -m pip install requests # 👇️ For python 3 (could also be pip3.10 depending on your version) python3 -m pip install requests # 👇️ for Windows py -m pip install requests
The python -m prefix might work in the place of pip when python isn't set up
in your PATH environment variable.
# 👇️ If you don't have pip in your PATH environment variable python -m pip install requests # 👇️ For python 3 (could also be pip3.10 depending on your version) python3 -m pip install requests # 👇️ for Windows py -m pip install requests
Make sure to replace the requests package with the name of the package you're
trying to install.
# Searching for the name of the package to be installed
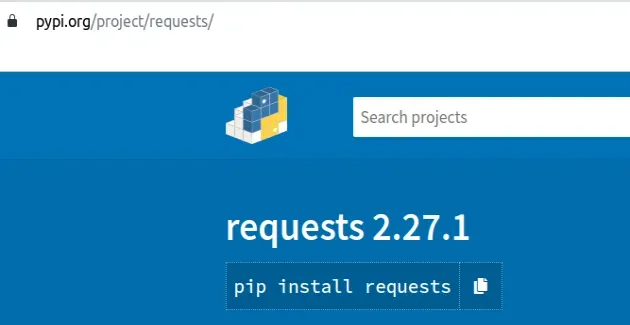
If you aren't sure what command you should run to install the module, google for "Pypi your_module_name", e.g. "Pypi requests".
Click on the pypi.org website and look at the pip install command.
You can also search for a package's name directory on the pypi website.
Once you find the package you are trying to install, copy the pip install X
command and paste it to your terminal.
# Installing a package on Windows
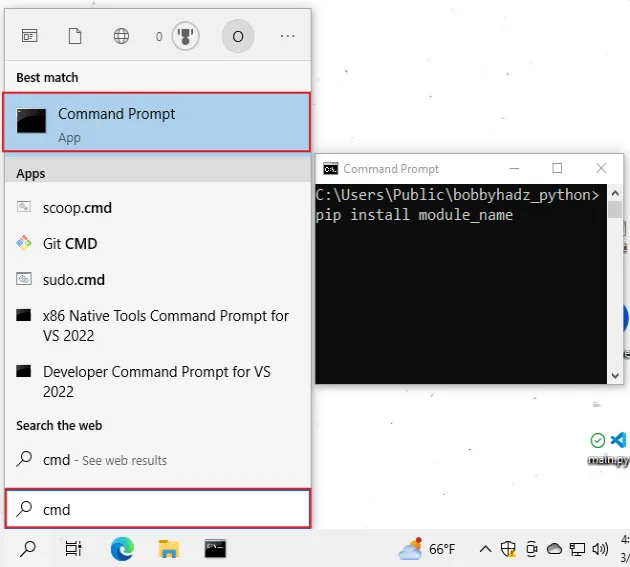
To install a package on Windows:
- Type CMD in the search bar and open the Command Prompt application.
- Type
pip install requestsand press Enter.
pip install requests # 👇️ for Python 3 pip3 install requests
Make sure to replace requests with the name of the package you're trying to
install.
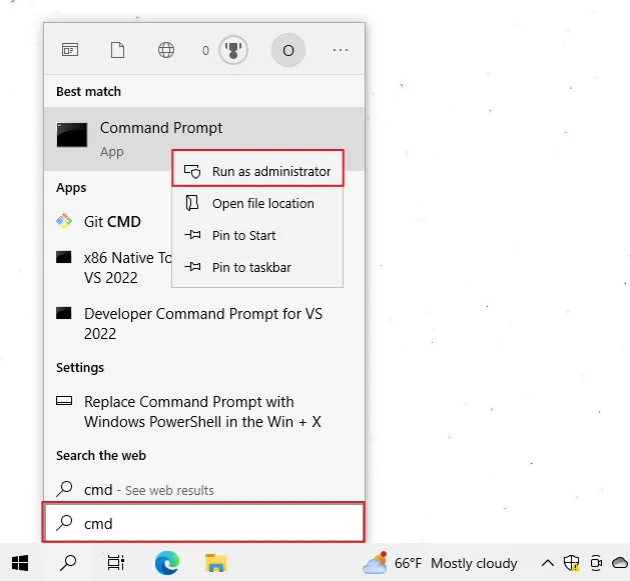
If the command doesn't succeed, try running CMD as an administrator.
If you get the error
'pip' is not recognized as an internal or external command,
use the python -m command when installing requests.
python -m pip install requests python3 -m pip install requests py -m pip install requests
# Installing a package on macOS or Linux
To install a package on macOS or Linux:
- Search for "terminal" and start the application.
- Type
pip install requestsand press Enter.
pip install requests # 👇️ with pip3 pip3 install requests
If you get an error that pip isn't found, use the python -m command.
python -m pip install requests python3 -m pip install requests
If you get a permissions error, prefix the command with sudo.
sudo pip install requests sudo pip3 install requests
If you need to install a specific version of the package, click on the relevant to you article:
- Pip install a specific version of a Python package
- Pip install a specific version of a Python package
# Importing and using the package in your Python file
After you install the specific package, you can import it and use it in your Python script.
Here is an example that imports and uses requests.
import requests def make_request(): res = requests.get('https://reqres.in/api/users', timeout=10) print(res.json()) make_request()
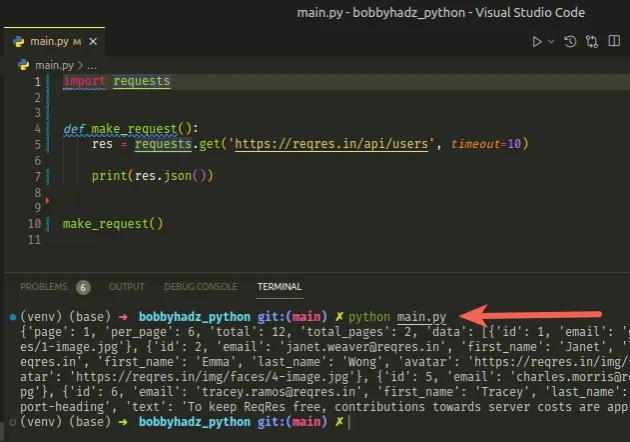
Once you import the package into a file that has a .py extension, e.g.
main.py, you can run your script with the python main.py command.
python main.py python3 main.py
# Installing a package in a Python script
If you need to install a package in a Python script, use the subprocess
module.
import subprocess import sys def install(package): subprocess.check_call([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", package]) install('requests')
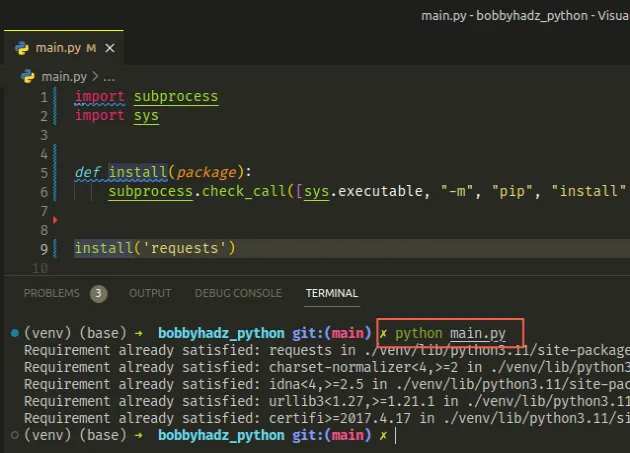
Make sure to replace requests with the name of the module you're trying to
install.
After adding the code to a file, e.g. main.py, you can install the package by
running the python main.py command.
python main.py
You can use a for loop if you need to install multiple packages.
import subprocess import sys def install(package): subprocess.check_call([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", package]) packages_to_install = ['requests', 'numpy'] for p in packages_to_install: install(p)
You can run the main.py file with python main.py to install the packages
from the list.
We stored the packages to be installed in a list and used a for loop to call
the pip install command for each package.
# Installing multiple packages in a single statement
An alternative way to install multiple packages is to use the iterable *
unpacking operator.
import subprocess import sys packages_to_install = ['requests', 'numpy'] subprocess.check_call([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", *packages_to_install])
We used the iterable * unpacking operator to unpack the list of packages in
the call to subprocess.check_call().
You can imagine that all of the packages from the list get passed as comma-separated arguments to the method and get installed.
# Checking if a package is installed before installing it
You can also check if the package is installed before trying to install it.
import sys import subprocess try: import requests print('The requests module is installed.') except ModuleNotFoundError: print('The requests module is NOT installed.') # 👇️ Install module python = sys.executable subprocess.check_call( [python, '-m', 'pip', 'install', 'requests'], stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL ) finally: import requests
We try to import the requests module and if it is not installed, a
ModuleNotFoundError is raised.
In this case, we install the module in the except block.
# Only installing packages that have not been installed
The following code sample checks if each package has been installed before
calling subprocess.check_call() with the missing packages.
import subprocess import sys import pkg_resources required = ['requests', 'numpy'] installed = [pkg.key for pkg in pkg_resources.working_set] packages_to_install = [ package for package in required if package not in installed] if packages_to_install: subprocess.check_call([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", *packages_to_install]) else: print('All packages have been installed')
We used a list comprehension to exclude all of the packages that have been installed.
On each iteration, we check if the current package is not in the list of installed packages.
The last step is to use the iterable * unpacking operator to unpack the list
of packages in the call to subprocess.check_call().
# Install the package in a virtual environment instead
If the suggestions didn't help, try creating a virtual environment by running the following commands from your shell.
# 👇️ Use the correct version of Python when creating VENV python -m venv venv # 👇️ Activate on Unix or MacOS source venv/bin/activate # 👇️ Activate on Windows (cmd.exe) venv\Scripts\activate.bat # 👇️ Activate on Windows (PowerShell) venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 # 👇️ Install any modules you need in your virtual environment pip install requests
If the python -m venv venv command fails, try the following 2 commands
instead:
python3 -m venv venvpy -m venv venv
Your virtual environment will use the version of Python that was used to create it.
# Upgrade your version of pip
If the error persists, try to
upgrade your version of pip by running the
following command.
Open your terminal and run the following command to install pip.
# 👇️ On Linux or macOS python -m ensurepip --upgrade # 👇️ Using python 3 python3 -m ensurepip --upgrade # 👇️ On Windows py -m ensurepip --upgrade
The ensurepip package enables us to bootstrap the pip installer into an
existing Python installation or virtual environment.
If the error persists, try upgrading pip by running:
# 👇️ on macOS or Linux python -m pip install --upgrade pip # 👇️ If you get a permissions error python -m pip install --user --upgrade pip # 👇️ for Python 3 python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip # 👇️ If you get a permissions error python3 -m pip install --user --upgrade pip # 👇️ on Windows py -m pip install --upgrade pip # 👇️ If you get a permissions error py -m pip install --user --upgrade pip
# Common causes of the error
The "SyntaxError: invalid syntax" error when using pip install occurs for
2 main reasons:
- Trying to use the
pip installcommand in a Python module, e.g. amain.pyfile. - Trying to use the
pip installcommand with the Python interpreter active in an interactive session.
If the error persists and you can't install the specific module, watch a quick video on how to use Virtual environments in Python.
This one is for using virtual environments (VENV) on Windows:
This one is for using virtual environments (VENV) on MacOS and Linux:
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Pip install multiple requirements files in Python
- How to pip install a package Globally instead of Locally
- Pip install and uninstall in silent, non-interactive mode
- Pip install a specific version of a Python package
- Pip list all available versions of a Python package
- The purpose of pip's
--no-cache-diroption

