How to print Boolean values in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Print boolean values in Python
Use the print() function to print a boolean value in Python, e.g.
print(my_bool).
If the value is not of type boolean, use the bool() class to convert it to a
boolean and print the result, e.g. bool(0).
my_bool = True # ✅ print boolean value print(my_bool) # 👉️ True # ✅ print boolean value in a string print(f'is subscribed: {my_bool}') # 👉️ is subscribed: True # ✅ print integer representation of boolean value print(int(True)) # 👉️ 1 print(int(False)) # 👉️ 0 # ✅ print boolean value converted to lowercase print(f'{my_bool}'.lower()) # 👉️ true # ✅ Convert a value to a boolean print(bool('hello')) # 👉️ True print(bool(0)) # 👉️ False
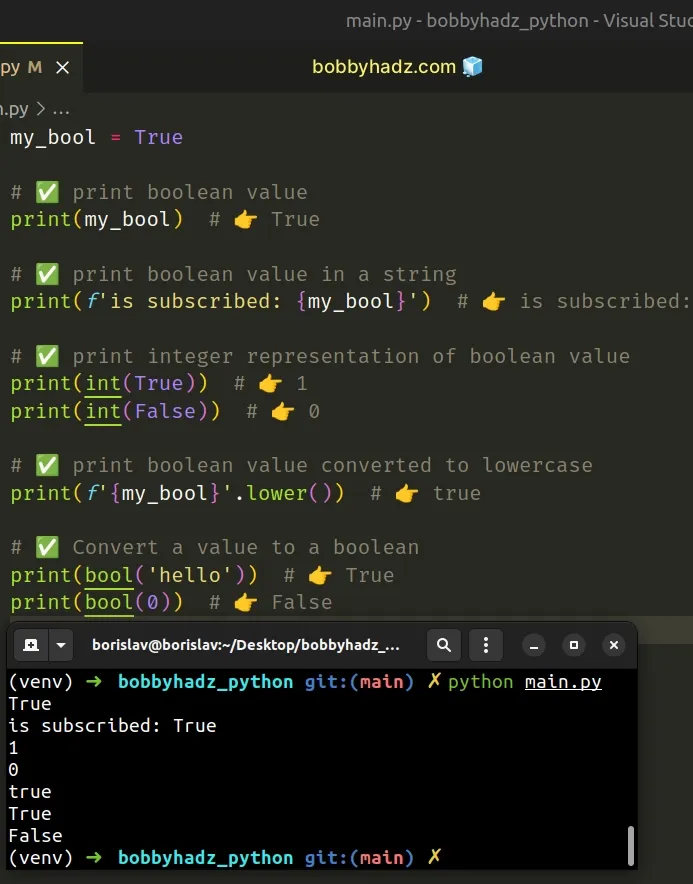
We used the print() function to print boolean values.
The print() function takes one or more
objects and prints them to sys.stdout.
If you have a boolean value, you can pass it directly to the print() function
to print it.
my_bool = True print(my_bool) # 👉️ True print(False) # 👉️ False
print() function returns None, so don't try to store the result of calling print in a variable.my_bool = True # ⛔️ BAD (print always returns None) result = print(f'is subscribed: {my_bool}') print(result) # 👉️ None
Instead, store the value in a variable and pass the variable to the print()
function.
my_bool = True result = f'is subscribed: {my_bool}' print(result) # 👉️ is subscribed: True
If you aren't sure what type a variable stores, use the built-in type() class.
my_bool = False print(type(my_bool)) # 👉️ <class 'bool'> print(isinstance(my_bool, bool)) # 👉️ True my_str = 'hello' print(type(my_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'> print(isinstance(my_str, str)) # 👉️ True
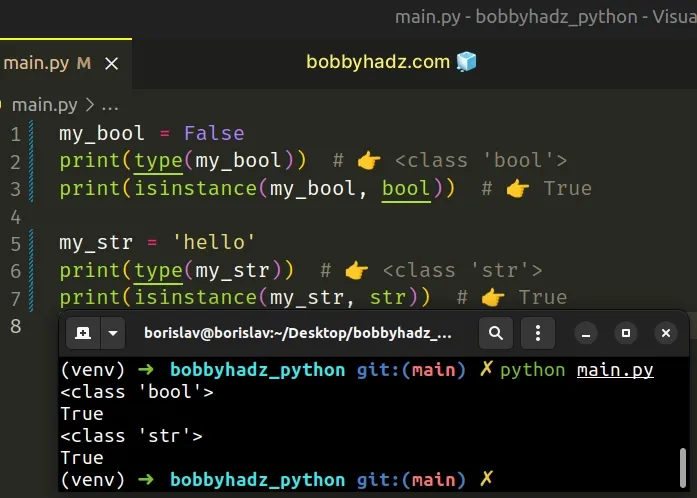
The type class returns the type of an object.
The isinstance function returns
True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the passed-in
class.
# Converting a value to a boolean and printing the result
If you need to convert a value to a boolean and print the result, use the bool() class.
print(bool('hello')) # 👉️ True print(bool(0)) # 👉️ False
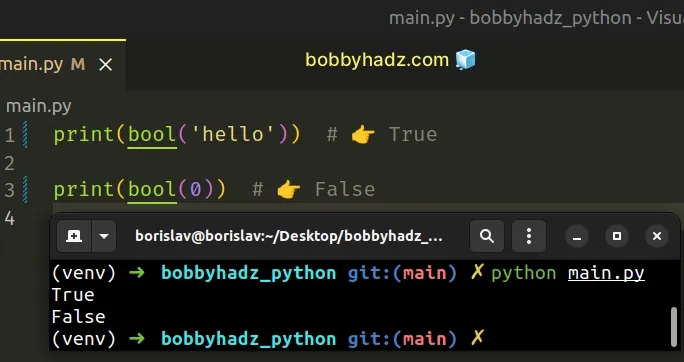
The bool class converts truthy values to True and falsy values to False.
All values that are not truthy are considered falsy. The falsy values in Python are:
- constants defined to be falsy:
NoneandFalse. 0(zero) of any numeric type.- empty sequences and collections:
""(empty string),()(empty tuple),[](empty list),{}(empty dictionary),set()(empty set),range(0)(empty range).
# Printing a boolean value in a String
If you need to print a boolean value or a variable storing a boolean value in a string, use a formatted string literal.
my_bool = True # ✅ print boolean value in a string print(f'is subscribed: {my_bool}') # 👉️ is subscribed: True
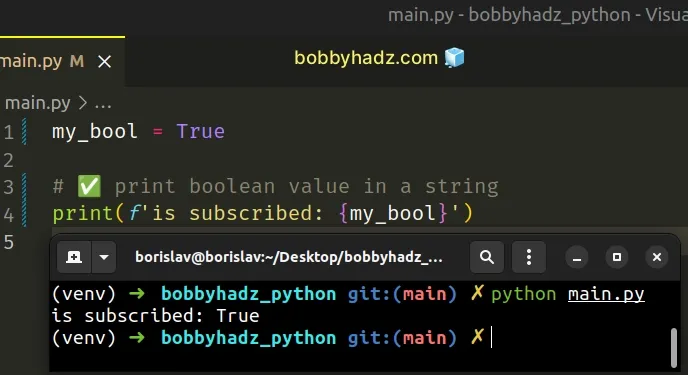
f.Make sure to wrap expressions in curly braces - {expression}.
# Passing multiple, comma-separated arguments to print()
Alternatively, you can pass multiple, comma-separated arguments to the print()
function.
# 👇️ is subscribed: True print('is subscribed:', True) # 👇️ is subscribed:True print('is subscribed:', True, sep='')
print() function, they get separated by a space.You can set the sep keyword argument to an empty string to remove the separator.
If you need to
convert a boolean value to its integer
representation, use the int() class.
print(int(True)) # 👉️ 1 print(int(False)) # 👉️ 0
The int class returns an integer object constructed from the provided number or string argument.
Conversely, if you need to convert an integer to a boolean value, use the
bool() class.
print(bool(1)) # 👉️ True print(bool(0)) # 👉️ False
The bool() class takes
a value and converts it to a boolean (True or False). If the provided value is
falsy or omitted, then bool returns False, otherwise it returns True.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Print alternate characters in a String in Python
- Print a Dictionary in Table format in Python
- How to Print on the Same Line in Python
- How to Print a Horizontal Line in Python
- How to print Integer values in Python
- How to Print a List in Columns in Python
- Print a List without the Commas and Brackets in Python
- Using nested Loops to print a Rectangle in Python

