Convert Booleans to Integers and vice versa in Python
Last updated: Apr 9, 2024
Reading time·7 min

# Table of Contents
# Convert Booleans to Integers in Python
Use the int() class to convert boolean values to integers, e.g.
result = int(True).
The int() class will return 1 for True boolean values and 0 for False
values.
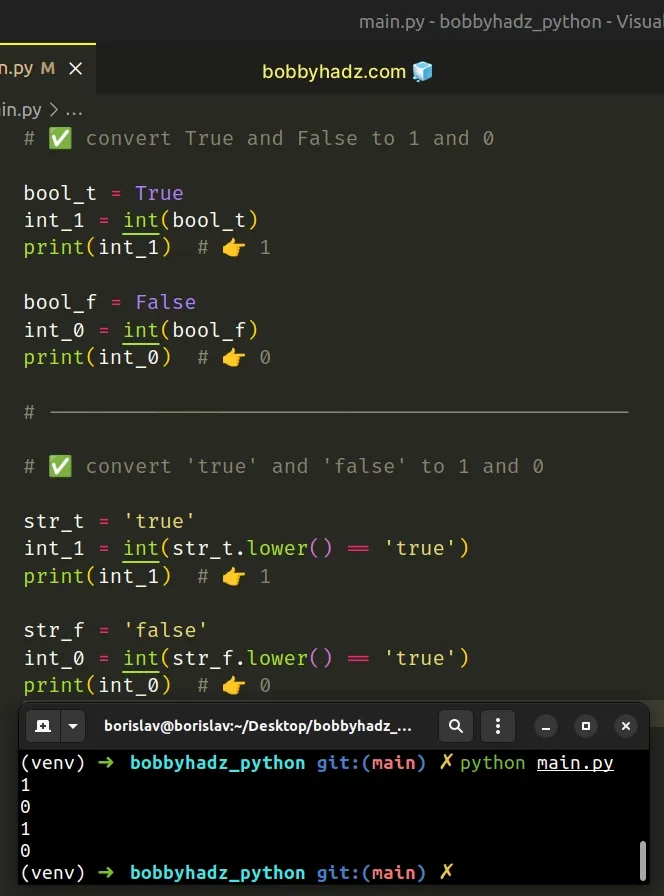
# ✅ convert True and False to 1 and 0 bool_t = True int_1 = int(bool_t) print(int_1) # 👉️ 1 bool_f = False int_0 = int(bool_f) print(int_0) # 👉️ 0 # ----------------------------------------------- # ✅ convert 'true' and 'false' to 1 and 0 str_t = 'true' int_1 = int(str_t.lower() == 'true') print(int_1) # 👉️ 1 str_f = 'false' int_0 = int(str_f.lower() == 'true') print(int_0) # 👉️ 0
If you need to convert integer values to booleans, click on the following subheading:
We used the int() class to convert True to 1 and False to 0.
result_1 = int(True) print(result_1) # 👉️ 1 result_2 = int(False) print(result_2) # 👉️ 0
The int class returns an integer object constructed from the provided argument.
The constructor returns 0 if no arguments are given.
True boolean values return 1 after conversion to integers and False values return 0.# Convert a list of Booleans to a List of Integers in Python
To convert a list of booleans to a list of integers:
- Use a list comprehension to iterate over the list.
- Use the
int()class to convert each boolean to an integer. - The new list will only contain integers.
list_of_booleans = [True, False, False, True] list_of_integers = [int(item) for item in list_of_booleans] print(list_of_integers) # 👉️ [1, 0, 0, 1]
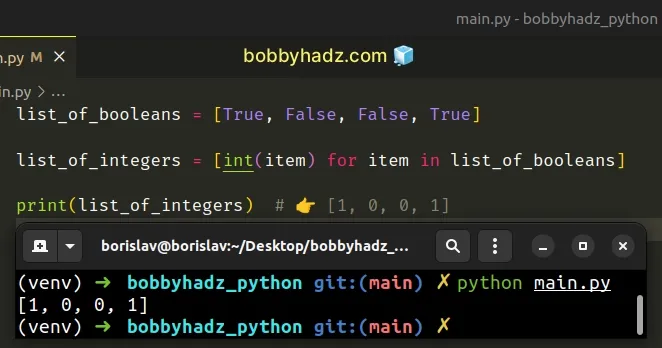
We used a list comprehension to convert a list of booleans to a list of integers.
On each iteration, we pass the current boolean to the int() class to convert
it to an integer.
list_of_booleans = [True, False, False, True] list_of_integers = [int(item) for item in list_of_booleans] print(list_of_integers) # 👉️ [1, 0, 0, 1]
The new list contains the integer representation of the booleans in the original list.
# Convert 'true' and 'false' to 1 and 0 in Python
To convert 'true' values to 1 and 'false' to 0:
- Use the equality operator to check if the value is equal to the string 'true'.
- Convert the result of the comparison to an integer.
- The conversion will return
1for 'true' values and0for 'false' values.
str_t = 'true' int_1 = int(str_t.lower() == 'true') print(int_1) # 👉️ 1 # ---------------------------------------- str_f = 'false' int_0 = int(str_f.lower() == 'true') print(int_0) # 👉️ 0
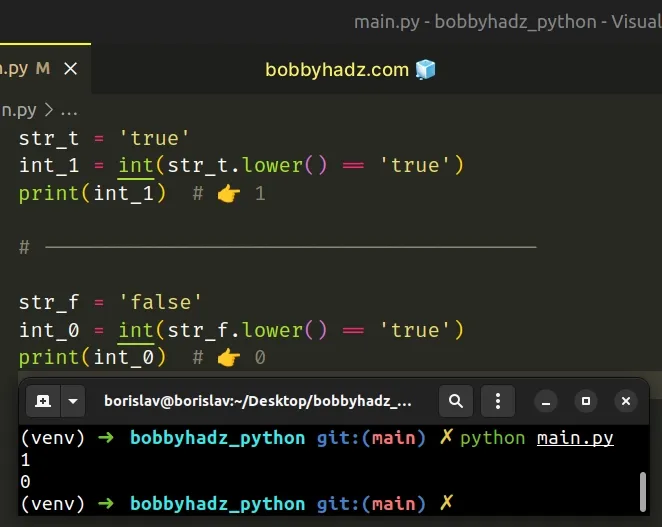
We used the lower() method to convert the string to lowercase before comparing
it to the string true.
The str.lower method returns a copy of the string with all the cased characters converted to lowercase.
The method doesn't change the original string, it returns a new string. Strings are immutable in Python.
True if the string stores a 'true' value and False otherwise.Converting True to an integer returns 1 and converting False to an integer
returns 0.
# Convert a list of 'true' and 'false' values to integers
If you need to convert a list of 'true' and 'false' strings to a list of 1 and
0, use a list comprehension.
my_list = ['true', 'true', 'false'] result = [int(item.lower() == 'true') for item in my_list] print(result) # 👉️ [1, 1, 0]
On each iteration, we compare the current string to the string 'true' and convert the result of the comparison to an integer.
Strings storing a 'true' value get converted to 1 and all other strings get
converted to 0.
# Convert a List of Booleans to List of Integers using map()
This is a three-step process:
- Pass the
int()class and the list to themap()function. - The
map()function will call theint()class with each boolean in the list. - Use the
list()class to convert themapobject to a list.
list_of_booleans = [True, False, False, True] list_of_integers = list(map(int, list_of_booleans)) print(list_of_integers) # 👉️ [1, 0, 0, 1]
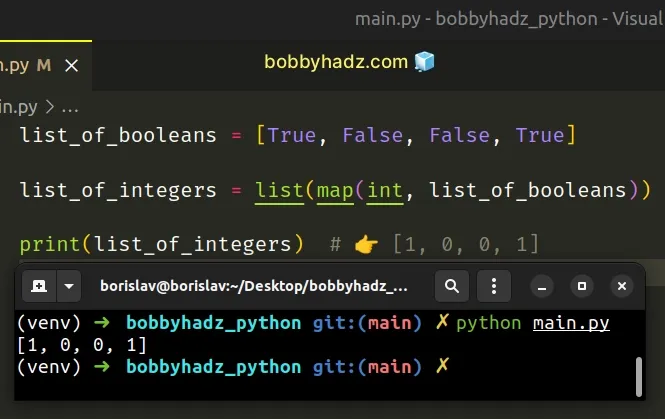
The map() function takes a function and an iterable as arguments and calls the
function with each item of the iterable.
int() class gets passed each boolean in the list and converts each value to an integer.Lastly, we used the list() class to
convert the map object to a list.
The list class takes an iterable and returns a list object.
# Convert an Array of Booleans to an Array of Integers using NumPy
Use the astype() method to convert an array of booleans to an array of
integers.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([True, False, False, True], dtype=bool) int_arr = arr.astype(int) print(int_arr) # 👉️ [1 0 0 1]
The astype() method will return a copy of the array that contains the integer
representation of the values.
Make sure you have NumPy installed to be able to run the code sample.
pip install numpy pip3 install numpy
You can use the astype method on a NumPy array to copy the array and cast it to a specified type.
The only parameter we passed to the astype method is the data type to which
the array is cast.
To convert the array of booleans to an array of integers, pass the int class
to the astype() method.
# Convert Integers to Booleans in Python
Use the bool() class to convert the numbers 1 and 0 to boolean values.
The bool() class will return True when converting 1 to a boolean and False
when converting 0 to a boolean.
# ✅ convert 1 and 0 to boolean values result = bool(1) print(result) # 👉️ True result = bool(0) print(result) # 👉️ False # ------------------------------------------ # ✅ convert boolean values to integers result = int(True) print(result) # 👉️ 1 result = int(False) print(result) # 👉️ 0
We used the bool() class to convert the numbers 1 and 0 to booleans.
result = bool(1) print(result) # 👉️ True result = bool(0) print(result) # 👉️ False
The
bool()
class takes a value and converts it to a boolean (True or False). If the
provided value is falsy or omitted, then bool returns False, otherwise it
returns True.
All values that are not truthy are considered falsy. The falsy values in Python are:
- constants defined to be falsy:
NoneandFalse. 0(zero) of any numeric type.- empty sequences and collections:
""(empty string),()(empty tuple),[](empty list),{}(empty dictionary),set()(empty set),range(0)(empty range).
The bool() class returns True if passed any non-falsy value.
bool() class will return True when called with any number other than 0.If you need to convert a boolean value to an integer, use the int() class.
result = int(True) print(result) # 👉️ 1 result = int(False) print(result) # 👉️ 0
The int class returns an integer object constructed from the provided number
or string argument.
The constructor returns 0 if no arguments are given.
# Convert a list of Integers to a list of Booleans
To convert a list of integers to a list of booleans:
- Use a list comprehension to iterate over the list.
- Use the
bool()class to convert each integer to a boolean. - The new list will only contain boolean values.
list_of_integers = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1] list_of_booleans = [bool(item) for item in list_of_integers] # 👇️ [True, False, True, False, True, True] print(list_of_booleans)
We used a list comprehension to iterate over the list of integers.
On each iteration, we pass the current integer to the bool() class to convert
it to a boolean.
The new list contains the boolean representation of the integers in the original list.
The bool() class takes a value and converts it to a boolean (True or False).
If the provided value is falsy or omitted, then bool returns False,
otherwise it returns True.
All values that are not truthy are considered falsy. The falsy values in Python are:
- constants defined to be falsy:
NoneandFalse. 0(zero) of any numeric type.- empty sequences and collections:
""(empty string),()(empty tuple),[](empty list),{}(empty dictionary),set()(empty set),range(0)(empty range).
The bool() class returns True if passed any non-falsy value.
bool() class returns True.Alternatively, you can use the map() function.
# Convert list of integers to list of booleans using map()
This is a three-step process:
- Pass the
bool()class and the list to themap()function. - The
map()function will call thebool()class with each integer in the list. - Use the
list()class to convert themapobject to a list.
list_of_integers = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1] list_of_booleans = list(map(bool, list_of_integers)) # # 👇️ [True, False, True, False, True, True] print(list_of_booleans)
The map() function takes a function and an iterable as arguments and calls the function with each item of the iterable.
bool() class gets passed each integer in the list and converts each value to a boolean.Lastly, we used the list() class to convert the map object to a list.
The list class takes an iterable and returns a list object.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

