Error: No default engine was specified and no extension was provided
Last updated: Apr 5, 2024
Reading time·5 min

# Table of Contents
- Error: No default engine was specified and no extension was provided
- Configuring your default view engine correctly
- If you need to send back an HTML file, use the
res.sendFilemethod - Using the res.send() method instead
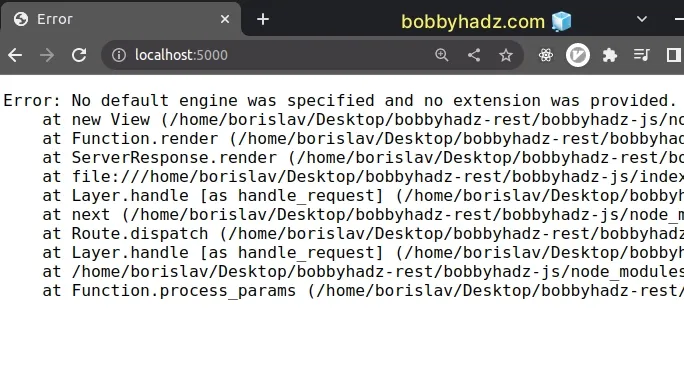
# Error: No default engine was specified and no extension was provided
The Express.js error "No default engine was specified and no extension was
provided" occurs when you use the res.render() method without setting a
default view engine.
To solve the error, use the app.set() method to set a view engine, e.g.
app.set('view engine', 'ejs');.
If you're trying to send back a JSON response to the client, replace the following:
res.render('home', { title: 'bobbyhadz.com', message: 'Example message: bobbyhadz.com', salary: 500, // ... some properties });
With the following:
res.status(200) res.json({ title: 'bobbyhadz.com', message: 'Example message: bobbyhadz.com', salary: 500, });
The res.render() method is used to render a view (HTML template) and send the rendered HTML string to the client.
The res.json() method is used to send a JSON response to the client.
The method sends a response with the Content-Type header set to
application/json and converts the passed value to a JSON string using
JSON.stringify().
# Configuring your default view engine correctly
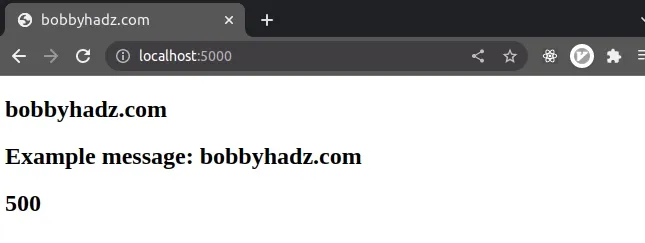
If you meant to render a view (HTML template) and send back the rendered HTML string, to the client, make sure to configure your view engine correctly.
import express from 'express'; // 👇️ if you use the CommonJS require() syntax // const express = require('express'); const app = express(); // ✅ Configure EJS as your view engine app.set('view engine', 'ejs'); app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.render('home', { title: 'bobbyhadz.com', message: 'Example message: bobbyhadz.com', salary: 500, }); }); const port = 5000; app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`); });
The code sample above uses the ES6 modules import/export to import express.
If you use the CommonJS require() syntax, use the following import statement
instead.
const express = require('express');
The example above assumes that you use ejs as your view (template) engine.
The error is resolved by adding the following line at the top of your entry
point file (e.g. app.js or index.js).
const app = express(); app.set('view engine', 'ejs');
Note that the line has to be added before any other route handlers.
Make sure that you have the ejs module installed.
# if you need to generate a package.json file npm init -y # 👇️ with NPM npm install express ejs # or with YARN yarn add express ejs
Now create a home.ejs file in views/home.ejs.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <h2>bobbyhadz.com</h2> <h2><%= message %></h2> <h2><%= salary %></h2> </body> </html>
Start your Express.js server with npx nodemon index.js and visit
http://localhost:5000.
npx nodemon index.js
By default, Express.js looks for your template files in a views/ directory.
We passed home as the first argument to the res.render() method and set the
view engine to ejs, so Express will look for a views/home.ejs file.
app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.render('home', { title: 'bobbyhadz.com', message: 'Example message: bobbyhadz.com', salary: 500, }); });
The example assumes that you use the following folder structure.
my-project/ └── index.js └── views/ └── home.ejs
As previously noted, Express will look for your template files in a views/
directory.
You can use the app.set() method if you need to specify a different path to
your template files.
Here is the default.
app.set('views', './views');
We used ejs as the template engine in the example, however, the same approach
can be used to set any other view engine.
For example, if you want to use pug as your view engine:
- Install the
pugmodule.
# with NPM npm install pug # or with YARN yarn add pug
- Create a
views/home.pugfile.
html head title= title body h1= message h2= salary
- Update your
index.js(orapp.js) file as follows.
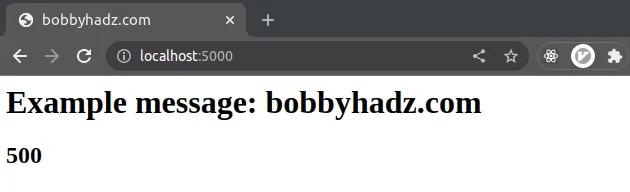
import express from 'express'; // 👇️ if you use CommonJS // const express = require('express') const app = express(); // ✅ Using the `pug` template engine app.set('view engine', 'pug'); app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.render('home', { title: 'bobbyhadz.com', message: 'Example message: bobbyhadz.com', salary: 500, }); }); const port = 5000; app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`); });
Start your Express.js server with npx nodemon index.js and visit
http://localhost:5000.
npx nodemon index.js
# If you need to send back an HTML file, use the res.sendFile method
If you need to send back a basic .html file, use the res.sendFile method.
Suppose that you have the following folder structure.
my-project/ └── index.js └── index.html
Here is the code for the index.html file.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <h2>bobbyhadz.com</h2> </body> </html>
And, here is the code for the index.js file.
import express from 'express'; import path from 'path'; import {fileURLToPath} from 'url'; const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url); const __dirname = path.dirname(__filename); const app = express(); app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, 'index.html')); }); const port = 5000; app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`); });
The example uses the ES6 modules import/export syntax.
If you use CommonJS require(), use the following code snippet instead.
const express = require('express'); const path = require('path'); const app = express(); app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, 'index.html')); }); const port = 5000; app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`); });
We passed the path to the index.html file to the res.sendFile() method to
send back an HTML file to the client.
I've written a detailed guide on how to use res.sendFile in Express.js.
# Using the res.send() method instead
You can also use the res.send() method in your route handlers.
For example, you could send a JSON response with the following line.
res.send({ site: 'bobbyhadz.com', age: 30, topic: 'Express.js', })
You can also use the res.send() method to send back an HTML string.
res.send('<h2>bobbyhadz.com</h2>')
You can also specify the status code.
res.status(404).send('Page not found!')
Or with a JSON response:
res.status(500).send({ error: 'Something went wrong', })
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Route.get() requires callback functions but got a object Undefined
- Cannot find module 'express' or 'cors' error in Node.js
- RangeError [ERR_HTTP_INVALID_STATUS_CODE]: Invalid status code
- How to ping a URL or a remote IP address using Node.js
- How to get the last modified Date of a File in Node.js
- How to Delete all Files in a Directory using Node.js
- DeprecationWarning: Buffer() is deprecated due to security and usability issues
- 413 Error: request entity too large in Node.js & Express
- body-parser deprecated undefined extended: provide extended option
- How to pass Variables to the next Middleware in Express.js

