Route.get() requires callback functions but got a object Undefined
Last updated: Apr 5, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Route.get() requires callback functions but got a object Undefined
The article covers how to solve the following related errors:
- Route.get() requires callback functions but got a object Undefined
- Route.post() requires callback functions but got a object Undefined
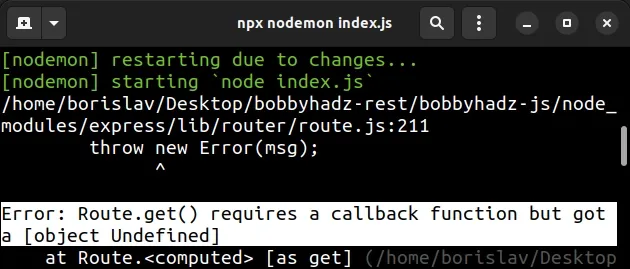
The error occurs when you pass a second argument of undefined to the
Router.get() or Router.post() methods.
import express from 'express'; const router = express.Router(); // ⛔️ Error: Route.get() requires a callback function but got a [object Undefined] router.get('/', undefined); // ⛔️ Error: Route.get() requires a callback function but got a [object Undefined] router.post('/', undefined); export {router as booksRouter};
This often happens when you misspell the name of the controller function you
have to pass as the second argument to Router.get() and Router.post().
You might have also imported the function incorrectly.
# Make sure to pass a function as the second argument to Router.get()
To solve the error, you have to make sure to pass a response handler function as
the second argument to the router.get() and router.post() methods.
import express from 'express'; const router = express.Router(); // ✅ Works router.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send('Home page of books route'); }); // ✅ Works router.post('/', (req, res) => { res.send('Adding a book to the DB'); }); export {router as booksRouter};
If you are
importing the function you
pass to router.get() and router.post() from another file, make sure to
import it correctly.
Here are some things to note:
- The function has to be exported from the other file, either using the
exportkeyword (ES6) or usingmodule.exports. - Make sure to spell the name of the response handle function correctly.
- Make sure the function exists and is defined in the file at the time you are trying to access it.
For example, assume you have the following folder structure.
index.js routes/ └── books.js controllers/ └── books-controller.js
# Using ES6 import/export statements
Here is the code for the controllers/books-controller.js module.
export function listBooks(req, res) { res.send('Home page of books route'); } export function createBook(req, res) { res.send('Adding a book to the DB'); }
The example uses the ES6 export syntax to export the two functions.
And, here is how you can import the functions in the routes/books.js file.
import express from 'express'; import { listBooks, createBook, } from '../controllers/books-controller.js'; const router = express.Router(); // Home page for this route router.get('/', listBooks); // Create book route router.post('/', createBook); export {router as booksRouter};
We used named imports to import the two functions and registered them on the
Router.
And here is how you can start your Express server in the index.js file.
import express from 'express'; import {booksRouter} from './routes/books.js'; const app = express(); app.use('/books', booksRouter); app.listen(5000, function () { console.log('Server listening on port 5000'); });
# Using the require() CommonJS syntax
Here is an example that uses the CommonJS require() syntax instead.
function listBooks(req, res) { res.send('Home page of books route'); } function createBook(req, res) { res.send('Adding a book to the DB'); } module.exports = { listBooks, createBook, };
And this is how you can import the functions in the routes/books.js file.
const express = require('express'); const { listBooks, createBook, } = require('../controllers/books-controller.js'); const router = express.Router(); // Home page for this route router.get('/', listBooks); // Create book route router.post('/', createBook); module.exports = { booksRouter: router, };
Alternatively, you can import the entire module and access the functions as properties on the module.
const express = require('express'); // 👇️ import the entire module const booksController = require('../controllers/books-controller.js'); const router = express.Router(); // 👇️ access functions as properties on the module router.get('/', booksController.listBooks); router.post('/', booksController.createBook); module.exports = { booksRouter: router, };
If you import the entire module, make sure to access the functions as properties
on the module, e.g. booksController.listBooks.
And here is how you can start your Express server in the index.js file.
const express = require('express'); const {booksRouter} = require('./routes/books.js'); const app = express(); app.use('/books', booksRouter); app.listen(5000, function () { console.log('Server listening on port 5000'); });
You can console.log the functions you are importing if the error persists.
Once you correct your import and export statements and pass a function as the
second argument to the Router.get() and Router.post() methods, the error
should be resolved.
I've written a detailed guide on how to import and export classes and functions using ES6.
# Defining your response handler functions inline
If none of the suggestions helped, you can always define your handler functions
in the same file as your Router.
const express = require('express'); const router = express.Router(); // 👇️ define Router.get handler function listBooks(req, res) { res.send('Home page of books route'); } // 👇️ define Router.post handler function createBook(req, res) { res.send('Adding a book to the DB'); } // 👇️ set Router.get handler function router.get('/', listBooks); // 👇️ set Router.post handler function router.post('/', createBook); module.exports = { booksRouter: router, };
You can also define the functions inline.
const express = require('express'); const router = express.Router(); // 👇️ define handler function inline router.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send('Home page of books route'); }); // 👇️ define handler function inline router.post('/', (req, res) => { res.send('Adding a book to the DB'); }); module.exports = { booksRouter: router, };
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

