Split a String on Capital Letters using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Split a String on Capital Letters in JavaScript
Call the split() method with a regular expression to split a string on
capital letters, e.g. str.split(/(?=[A-Z])/);.
The regular expression uses a positive lookahead assertion to split the string on each capital letter.
const str = 'BobbyHadzCom'; const result = str.split(/(?=[A-Z])/); // 👇️ [ 'Bobby', 'Hadz', 'Com' ] console.log(result);
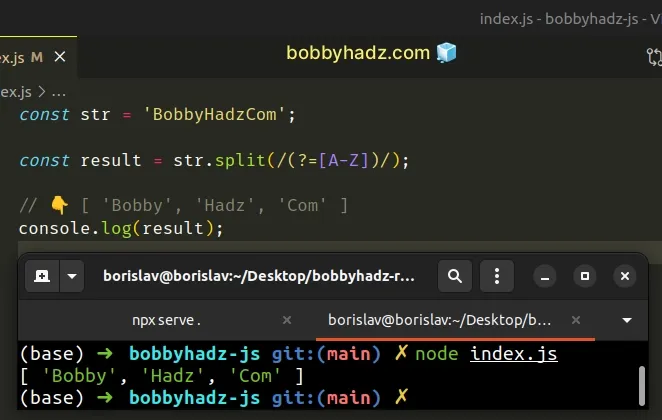
The only argument we passed to the String.split() method is a regular expression.
The forward slashes / / mark the beginning and end of the regular expression.
# Dealing with trailing spaces
If your string contains spaces, the substrings in the array will contain trailing spaces.
const str = 'Bobby Hadz Com'; const result = str.split(/(?=[A-Z])/); // 👇️ [ 'Bobby ', 'Hadz ', 'Com' ] console.log(result);
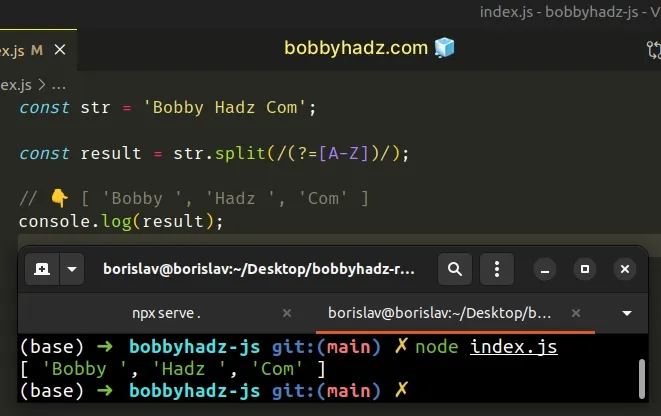
Similarly, if the string starts with a space, you will get an array element that contains a space.
const str = ' Bobby Hadz Com '; const result = str.split(/(?=[A-Z])/); // 👇️ [ ' ', 'Bobby ', 'Hadz ', 'Com ' ] console.log(result);
We can use the String.trim() and Array.map() methods to handle these edge cases.
const str = ' Bobby Hadz Com '; const result = str .trim() .split(/(?=[A-Z])/) .map(element => element.trim()); // 👇️ [ 'Bobby', 'Hadz', 'Com' ] console.log(result);
We used the trim() method to remove any leading and trailing spaces from the
original string.
// 👇️ "abc" console.log(' abc '.trim());
We then called the split() method to split the string on each capital letter.
Lastly, we used the Array.map() method to remove any leading or trailing
spaces from the strings in the array.
map() method gets called with each element in the array.On each iteration, we trim the string to remove the leading and trailing spaces and return the result.
The Array.map() method returns a new array that contains the values we
returned from the callback function.
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
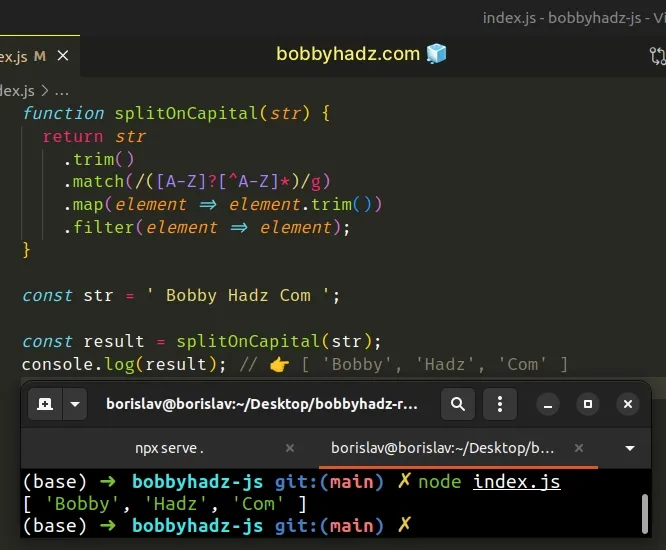
function splitOnCapital(str) { return str .trim() .split(/(?=[A-Z])/) .map(element => element.trim()); } const str = ' Bobby Hadz Com '; const result = splitOnCapital(str); console.log(result); // 👉️ [ 'Bobby', 'Hadz', 'Com' ]
The splitOnCapital function takes a string and splits it on each capital
letter.
# Split a String on Capital Letters using String.match()
Alternatively, you can use the String.match() method.
function splitOnCapital(str) { return str .trim() .match(/([A-Z]?[^A-Z]*)/g) .map(element => element.trim()) .filter(element => element); } const str = ' Bobby Hadz Com '; const result = splitOnCapital(str); console.log(result); // 👉️ [ 'Bobby', 'Hadz', 'Com' ]
The String.match() method matches a string against a regular expression.
The method returns an array containing the matches (if any) or null if no
matches are found.
The forward slashes / / mark the beginning and end of the regular expression.
The [A-Z] character class matches the capital letters from A to Z.
function splitOnCapital(str) { return str .trim() .match(/([A-Z]?[^A-Z]*)/g) .map(element => element.trim()) .filter(element => element); }
The question mark ? matches the preceding item (the capital letters) 0 or 1
times.
The caret ^ symbol means "NOT the following".
So, the [^A-Z] character class matches any character that is not a capital
letter.
The asterisk * matches the preceding item (non-capital letters) zero or more
times.
The g flag is used because we want to match all occurrences of the regular
expression and not just the first occurrence.
If you ever need help reading a regular expression, check out this regular expression cheat sheet by MDN.
It contains a table with the name and the meaning of each special character with examples.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Split a String and get First or Last Array Element in JS
- Split on the Last Occurrence of a String in JavaScript
- Split a String removing any Empty Elements in JavaScript
- Split a String at a specific Index using JavaScript
- How to Split a String by Newline in JavaScript
- How to Split a String by a Regex in JavaScript
- Split a String with multiple Separators using JavaScript
- How to Split a string by Spaces in JavaScript
- Split a String only on the First Occurrence of a Character
- Split a String by Special Characters in JavaScript
- Split a String every N characters in JavaScript

