Get all Elements by Type using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 5, 2024
Reading time·3 min
# Get all Elements by Type using JavaScript
Use the querySelectorAll() method to get all elements by type.
The method returns a NodeList containing the elements that match the
provided selector.
Here is the HTML for the examples.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <title>bobbyhadz.com</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" id="first_name" /> <input type="number" id="age" /> <script src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
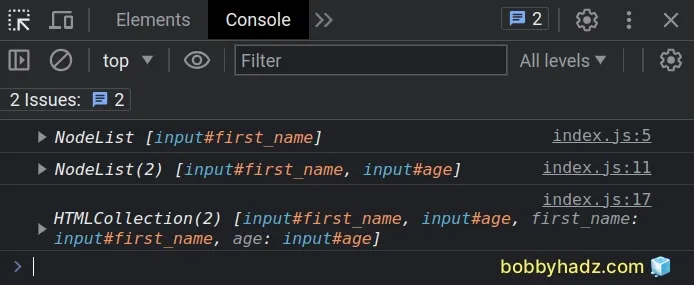
// ✅ Get all input elements with type = "text" const elements1 = document.querySelectorAll( 'input[type="text"]', ); console.log(elements1); // 👉️ [input#first_name] // ------------------------------------------------------- // ✅ Get all input elements const elements2 = document.querySelectorAll('input'); console.log(elements2); // 👉️ [input#first_name, input#age] // ------------------------------------------------------- // ✅ Get all input elements const elements3 = document.getElementsByTagName('input'); console.log(elements3); // 👉️ [input#first_name, input#age]
# Get all elements by type attribute
In the first example, we used the
document.querySelectorAll()
method to get all input elements that have a type attribute with a value of
text.
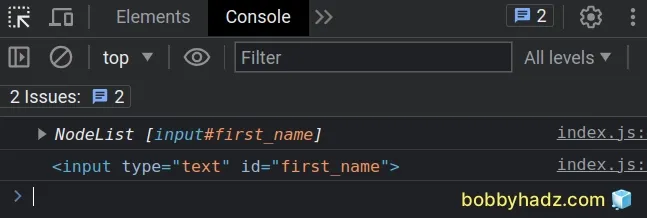
const elements1 = document.querySelectorAll('input[type="text"]'); console.log(elements1); // 👉️ [input#first_name] console.log(elements1[0]); // 👉️ input#first_name
If you want to get a specific element, you can access the NodeList at an index.
JavaScript indexes are zero-based, so the first element in the NodeList has an
index of 0.
# Select all elements that have a type attribute set to text
You can adjust the selector as needed, e.g. the following example selects any
type of element with a type attribute set to a value of text (not just
input elements).
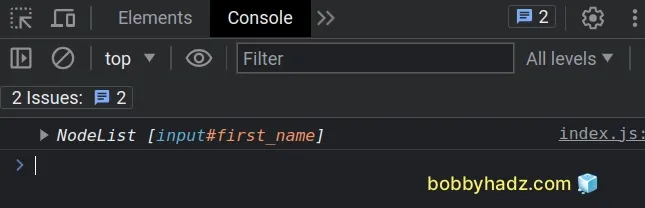
const elements = document.querySelectorAll('[type="text"]'); console.log(elements); // 👉️ NodeList [input#first_name]
# Get all input elements on the page
In the second example, we used the querySelectorAll method to get a NodeList
of all of the input tags.
const elements = document.querySelectorAll('input'); console.log(elements); // 👉️ NodeList(2) [input#first_name, input#age]
# Iterating over a collection of elements
If you need to iterate over the collection, use the forEach() method.
const elements = document.querySelectorAll('input'); console.log(elements); // 👉️ [input#first_name, input#age] elements.forEach(element => { console.log(element); });
# Get all elements by Type using getElementsByTagName
The third example uses the
document.getElementsByTagName()
method to select all input tags.
const elements = document.getElementsByTagName('input'); console.log(elements); // 👉️ [input#first_name, input#age]
querySelectorAll method and you might see the getElementsByTagName method used in older code bases.# Iterating over an HTMLCollection
The method returns an HTMLCollection, which you have to convert to an array if
you need to use methods like forEach().
const elements = Array.from(document.getElementsByTagName('input')); console.log(elements); // 👉️ [input#first_name, input#age] elements.forEach(element => { console.log(element); });
By converting the HTMLCollection to an array, we are able to use any of the
array-supported methods.
You can also use a for...of loop to iterate over the collection.
const elements = Array.from(document.getElementsByTagName('input')); console.log(elements); // 👉️ [input#first_name, input#age] for (const element of elements) { console.log(element); }
If you need to get a specific element, access the array at an index.
const elements = Array.from(document.getElementsByTagName('input')); console.log(elements); // 👉️ [input#first_name, input#age] console.log(elements[0]); // inptu#first-name console.log(elements[elements.length - 1]); // input#age
The first element in the array has an index of 0 and the last element has an
index of array.length - 1.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Get DOM Element(s) by Attribute using JavaScript
- Get element(s) by data attribute using JavaScript
- Get element by ID by partially matching String using JS
- Get Element(s) by their Name attribute using JavaScript
- Get Element by XPath using JavaScript - Examples
- Get Elements by multiple Class Names using JavaScript

