Get the Max of two Numbers using JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 4, 2024
Reading time·3 min

# Get the Max of two Numbers in JavaScript
Use the Math.max() function to get the max of 2 numbers, e.g.
Math.max(10, 5).
The function returns the largest of the provided numbers. If any of the
provided parameters is not a number and can't be converted to one, NaN is
returned.
console.log(Math.max(5, 10)); // 👉️ 10 console.log(Math.max(0, 20)); // 👉️ 20 console.log(Math.max(-10, 10)); // 👉️ 10 console.log(Math.max(-10, -15)); // 👉️ -10 console.log(Math.max('5', '15')); // 👉️ 15 console.log(Math.max('zero', 'five')); // 👉️ NaN
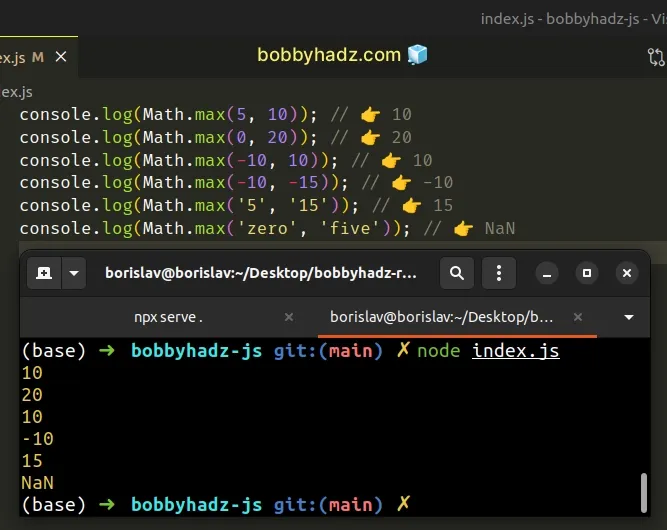
We used the Math.max() function to get the max of two numbers.
The function takes zero or more numbers as parameters and returns the largest number.
Therefore you could provide more than 2 numbers to the function.
console.log(Math.max(1, 3, 5, 7)); // 👉️ 7
If any of the provided values are not of type number, the function attempts to convert the value to a number before making the comparison.
If the function fails to convert the value to a number, it returns NaN (not a
number).
# Get the Max of two numbers using the ternary operator
You can also get the max of two numbers by using the ternary operator.
const num1 = 5; const num2 = 20; const highestNumber = num1 > num2 ? num1 : num2; console.log(highestNumber); // 👉️ 20
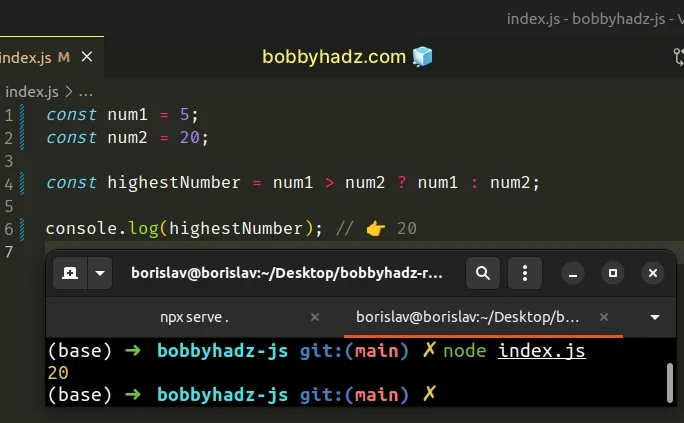
The ternary operator is
very similar to an if/else statement.
If the expression to the left of the question mark is truthy, the operator returns the value to the left of the colon, otherwise, the value to the right of the colon is returned.
If num1 is greater than num2, then num1 is returned, otherwise, num2 is
returned.
# Get the Max of two numbers using an if/else statement
You can also use an if/else statement.
const num1 = 5; const num2 = 20; let highestNumber; if (num1 > num2) { highestNumber = num1; } else { highestNumber = num2; } console.log(highestNumber); // 👉️ 20
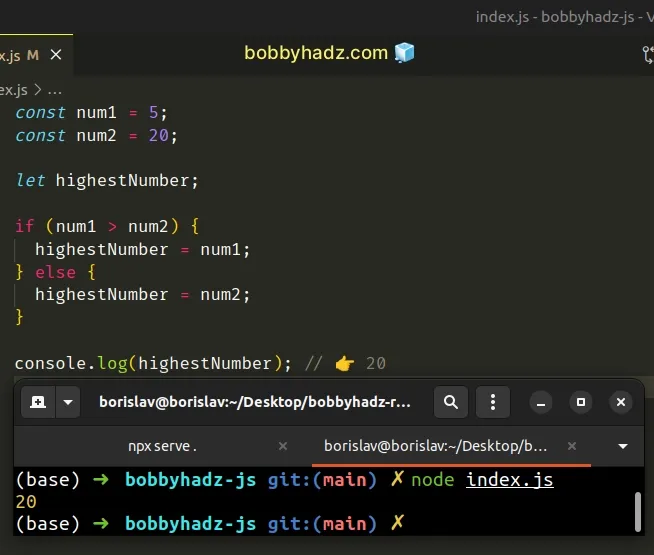
Notice that we used the let keyword to declare the highestNumber variable.
Variables declared using const cannot be reassigned.
In the if statement we check if num1 is greater than num2 and if the
condition is met, we set the highestNumber variable to num1.
Otherwise, we set the variable to num2.
# If you have the numbers stored in an array, use spread syntax (...)
The Math.max() function takes multiple, comma-separated numbers, so we can't
directly pass it an array of numbers.
const numbers = [5, 0, 20, 13, 35]; const result = Math.max(...numbers); console.log(result); // 👉️ 35
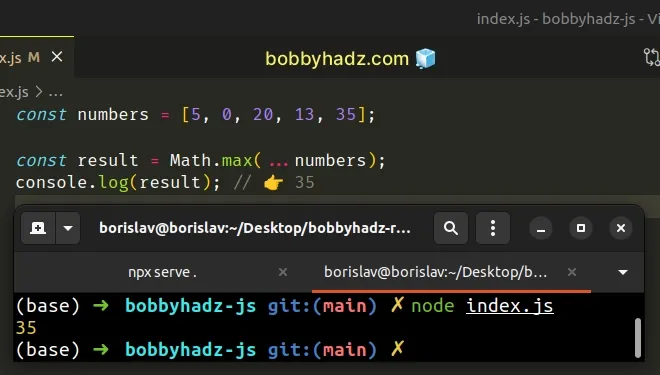
We used the spread syntax (...) to unpack the array in the call to the
Math.max() function.
You can imagine that the function got called with multiply, comma-separated arguments with the help of the spread syntax (...).
# Some non-numeric values convert to valid numbers
If the Math.max() function gets called with a value that is not a number, the
function attempts to convert the value to a number before making the comparison.
Note that some non-numeric values get converted to valid numbers in JavaScript. Here are some examples.
console.log(Number([])); // 👉️ 0 console.log(Number(null)); // 👉️ 0 console.log(Number(false)); // 👉️ 0 console.log(Number(true)); // 👉️ 1 console.log(Number('')); // 👉️ 0
If you pass any of these values to the Math.max() function, you might get
confusing results.
console.log(Math.max(null, -10)); // 👉️ 0 console.log(Math.max([], -10)); // 👉️ 0 console.log(Math.max(true, -10)); // 👉️ 1
In these examples, the Math.max() function converted the first value to a
number before comparing the values.
Since all of these successfully convert to a number, we got some unexpected results.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

