Filter an Array of Objects based on a property - JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 1, 2024
Reading time·4 min

# Table of Contents
- Filter an Array of Objects based on a property
- Filter an Array of Objects based on a property using
Array.find() - Filter an Array of Objects based on a property using for...of
- Filter an Array of Objects based on a property using forEach
# Filter an Array of Objects based on a property in JavaScript
To filter an array of objects based on a property:
- Use the
Array.filter()method to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, check if the object's property points to the specified value.
- The
Array.filter()method will return an array with all objects that meet the condition.
const people = [ {name: 'Tom', age: 30}, {name: 'John', age: 40}, {name: 'Dillon', age: 30}, ]; const results = people.filter(obj => { return obj.age === 30; }); // 👇️ [{name: 'Tom', age: 30}, {name: 'Dillon', age: 30}] console.log(results);
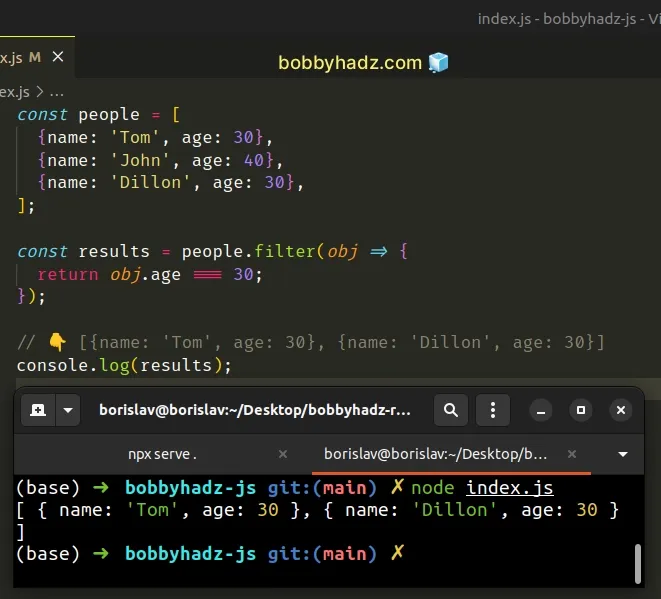
The function we passed to the Array.filter() method gets called with each element in the array.
On each iteration, we check if the object has an age property with a value of
30. If it does, the object gets added to the new array.
Array.filter() method returns an empty array.You can use the array's length to check if there is at least one object that meets the condition.
if (results.length > 0) { // 👉️ the condition was satisfied at least once }
If you only need to filter for a single object that meets a condition, use the
Array.find() method.
# Filter an Array of Objects based on a property using Array.find()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
Array.find()method to iterate over the array. - On each iteration, check if the object's property points to the specific value.
- The
find()method will return the first object that satisfies the condition.
const people = [ {name: 'Tom', age: 30}, {name: 'John', age: 40}, {name: 'Dillon', age: 30}, ]; const person = people.find(object => { return object.age === 30; }); // 👉️ {name: 'Tom', age: 30} console.log(person); if (person !== undefined) { // 👉️ the condition was satisfied }
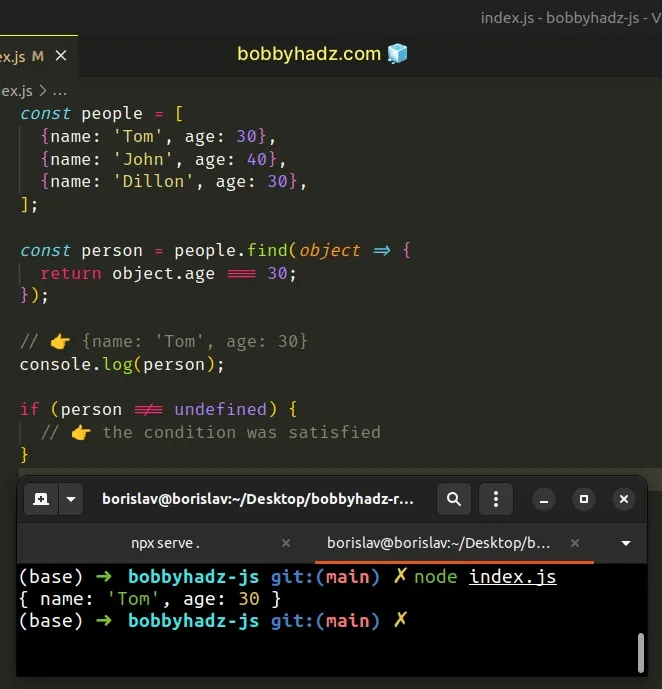
The function we passed to the Array.find() method gets called with each element in the array until it returns a truthy value or iterates over the entire array.
Once the callback function returns a truthy value, the corresponding array
element is returned from Array.find().
If the callback function never returns a truthy value, then Array.find()
returns undefined.
Even though there are multiple objects in the array that have an age property
with a value of 30, only the first object is returned before the
Array.find() method short-circuits.
# Filter an Array of Objects based on a property using for...of
You can also use a for...of loop to filter an array of objects based on a
property.
const people = [ {name: 'Tom', age: 30}, {name: 'John', age: 40}, {name: 'Dillon', age: 30}, ]; const results = []; for (const person of people) { if (person.age === 30) { results.push(person); } } // 👇️ [{name: 'Tom', age: 31}, {name: 'Dillon', age: 30}] console.log(results);
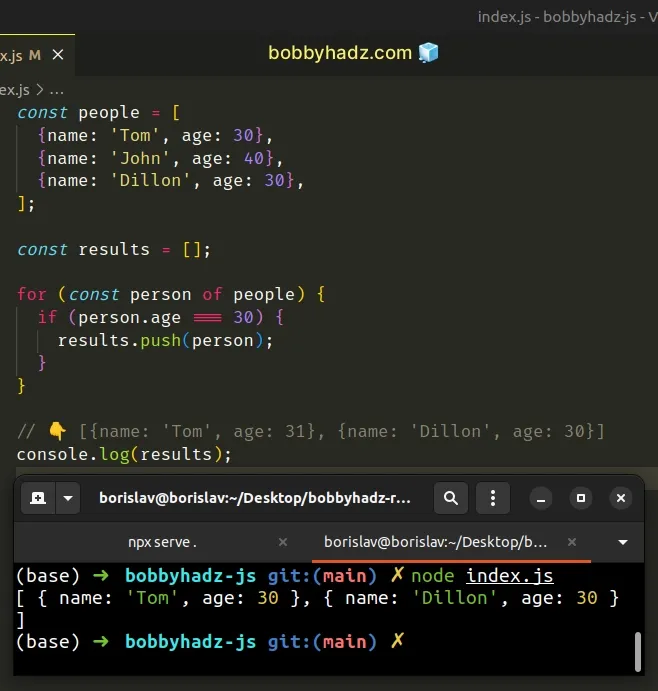
The for...of statement is
used to loop over iterable objects like arrays, strings, Map, Set and
NodeList objects and generators.
On each iteration, we check if the current object meets a condition and if the condition is met, we push the object into a new array.
If you only need to filter for a single object, use the break statement.
const people = [ {name: 'Tom', age: 30}, {name: 'John', age: 40}, {name: 'Dillon', age: 30}, ]; let result; for (const person of people) { if (person.age === 30) { result = person; break; } } // 👇️ { name: 'Tom', age: 30 } console.log(result);
We used the let keyword to declare a result variable that can be reassigned.
On each iteration, we check if the current object meets a condition.
If the condition is met, we set the variable to the object and break out of the loop.
The
break
statement terminates the current loop or switch statement.
# Filter an Array of Objects based on a property using forEach
You can also use the forEach() method to filter an array of objects based on a
property.
const people = [ {name: 'Tom', age: 30}, {name: 'John', age: 40}, {name: 'Dillon', age: 30}, ]; const results = []; people.forEach((person, index) => { console.log(index); // 👉️ 0, 1, 2 if (person.age === 30) { results.push(person); } }); // 👇️ [{name: 'Tom', age: 31}, {name: 'Dillon', age: 30}] console.log(results);
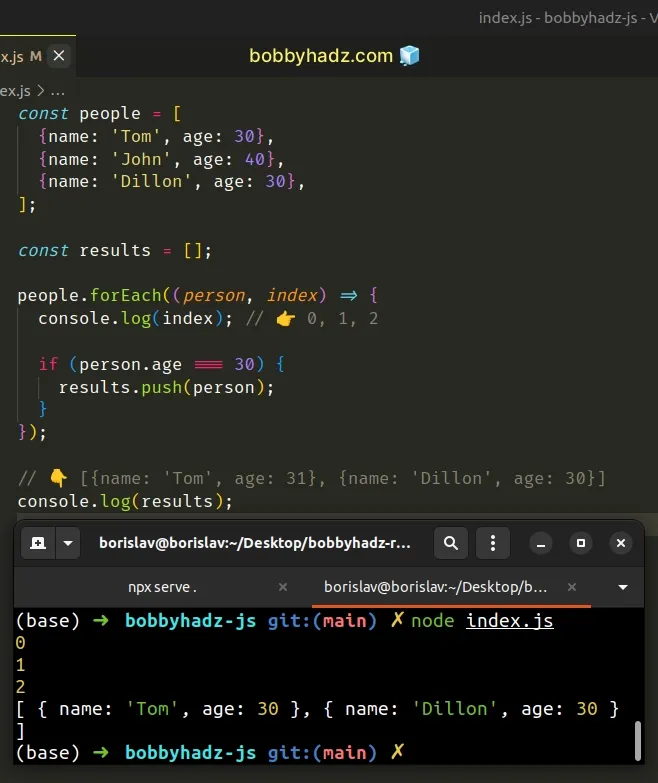
The function we passed to the Array.forEach() method gets called with each element in the array.
On each iteration, we check if the current object has a property equal to a specified value.
If the condition is met, we push the object into a new array.
You also have access to the index of the current iteration when using
forEach().
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:

