Count the Words or Spaces in a String in JavaScript
Last updated: Mar 3, 2024
Reading time·6 min

# Table of Contents
- Count the words in a String using JavaScript
- Count the words in a String using
String.trim() - Count the words in a TextArea element using JavaScript
- Count the Spaces in a String in JavaScript
# Count the words in a String using JavaScript
To count the words in a string:
- Use the
String.split()method to split the string into an array of words. - Access the
lengthproperty on the array. - The
lengthproperty will return the number of words in the string.
function countWords(str) { const arr = str.split(' '); return arr.filter(word => word !== '').length; } console.log(countWords('bobby hadz com')); // 👉️ 3 console.log(countWords('This is a long string')); // 👉️ 5
We created a reusable function that takes a string as a parameter and returns the number of words in the string.
We used the String.split() method to split the string on each space.
The method returns an array containing the words in the string.
// 👇️ ['hello', 'world'] console.log('hello world'.split(' ')); // 👇️ [ 'bobby', 'hadz', 'com' ] console.log('bobby hadz com'.split(' '));
// 👇️ ['hello', '', 'world'] console.log('hello world'.split(' ')); // 👇️ ['one', '', 'two', '', 'three'] console.log('one two three'.split(' '));
We can use the Array.filter() method to make sure we don't count empty strings as words.
filter method enables us to remove the empty strings before accessing the length property on the array.The function we passed to the filter() method gets called with each element in
the array.
function countWords(str) { const arr = str.split(' '); return arr.filter(word => word !== '').length; } console.log(countWords('bobby hadz com')); // 👉️ 3 console.log(countWords('This is a long string')); // 👉️ 5
filter() method returns.We check if each element is NOT equal to an empty string and return the result.
const arr = ['one', '', 'two', '']; const filtered = arr.filter(element => element !== ''); // 👇️ ['one', 'two'] console.log(filtered);
The last step is to access the length property on the array to get the word
count.
Alternatively, you can use the String.trim() method.
# Table of Contents
- Count the words in a String using
String.trim() - Count the words in a TextArea element using JavaScript
- Count the Spaces in a String in JavaScript
# Count the words in a String using String.trim()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
String.trim()method to trim the string. - Use the
String.split()method to split the string by one or more spaces. - Access the
lengthproperty on the result.
function countWords(str) { return str.trim().split(/\s+/).length; } console.log(countWords('bobby hadz com')); // 👉️ 3 console.log(countWords('This is a long string')); // 👉️ 5
We used the String.trim() method to remove any leading and trailing whitespace from the string.
console.dir(' abc '.trim()); // 👉️ "abc"
The next step is to use the String.split() method to split the string by one
or more consecutive spaces.
We passed a regular expression to the String.split() method.
function countWords(str) { return str.trim().split(/\s+/).length; }
The forward slashes / / mark the beginning and end of the regular expression.
The \s special character matches spaces, tabs and newlines.
The plus + matches the preceding item one or more times (spaces).
In its entirety, the regular expression matches one or more consecutive spaces.
This way, we can be sure that we won't get multiple words if the string contains multiple spaces next to one another.
If you ever need help reading a regular expression, check out this regular expression cheat sheet by MDN.
It contains a table with the name and the meaning of each special character with examples.
# Table of Contents
# Count the words in a TextArea element using JavaScript
To count the words in a textarea element:
- Access the
valueproperty on thetextareaelement. - Split the value on each space.
- Use the
lengthproperty to get the word count.
Here is the HTML for the example in the article.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <textarea id="textarea" cols="30" rows="10"></textarea> <p> Number of words: <span id="word-count"></span> </p> <button id="btn">Count words</button> <script type="module" src="index.js"></script> </body> </html>
And here is the related JavaScript code.
function countWords(str) { const arr = str.split(' '); return arr.filter(word => word !== '').length; } const button = document.getElementById('btn'); button.addEventListener('click', () => { const textarea = document.getElementById('textarea'); const wordCount = countWords(textarea.value); console.log(wordCount); const span = document.getElementById('word-count'); span.innerHTML = wordCount; });
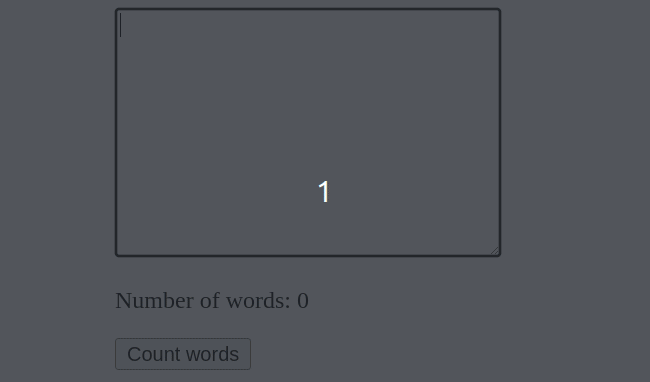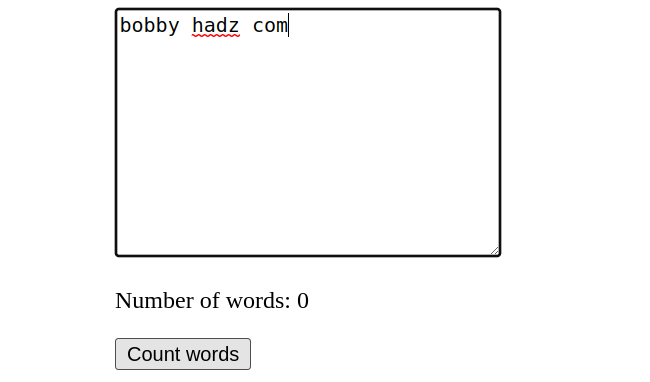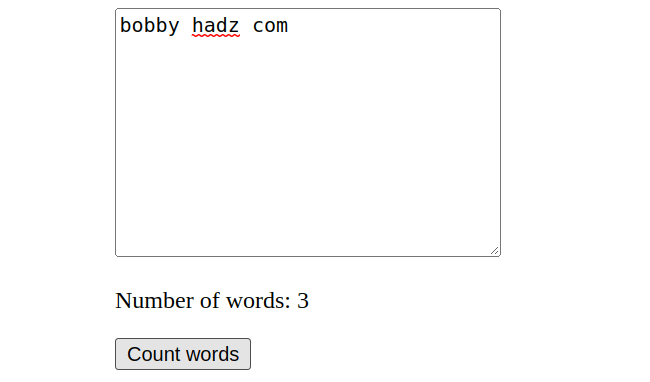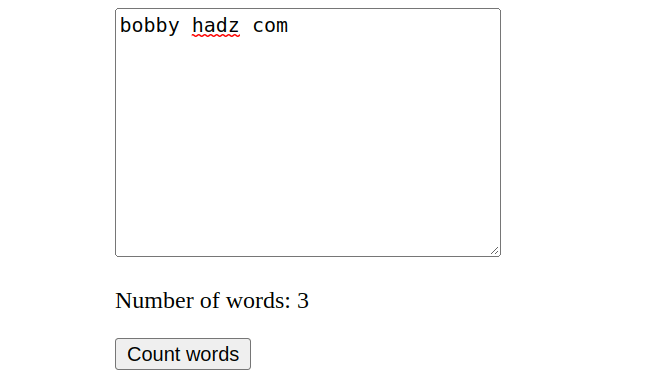
Every time the button is clicked, we log how many words are written in the
textarea element and show the result using a span element.
We added a click event listener to the button element, so every time it is clicked, a function is invoked.
We used the value property to
get the value of the textarea element
and used the previous function to get the word count.
The last step is to write the result to the screen by using the innerHTML
property on the span element.
# Count the Spaces in a String in JavaScript
To count the spaces in a string:
- Use the
split()method to split the string into an array on each space. - Subtract
1from the array's length. - The result will be the number of spaces in the string.
const str = 'bobby hadz com'; const spacesCount = str.split(' ').length - 1; console.log(spacesCount); // 👉️ 2
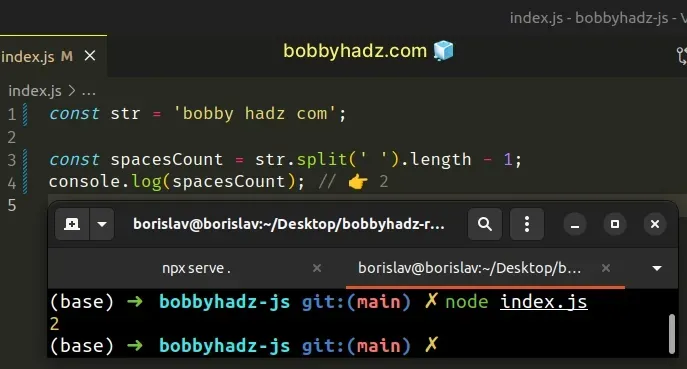
The String.split() method takes a separator and splits the string into an array on each occurrence of the provided delimiter.
The String.split() method takes the following 2 parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
separator | The pattern describing where each split should occur. |
limit | An integer used to specify a limit on the number of substrings to be included in the array. |
The method returns an array of substrings.
const str = 'bobby hadz com'; // 👇️ [ 'bobby', 'hadz', 'com' ] console.log(str.split(' '));
We have to subtract 1 from the array's length to get the number of spaces in
the string because the space is the separator.
const str = 'bobby hadz com'; const spacesCount = str.split(' ').length - 1; console.log(spacesCount); // 👉️ 2
If you have to do this often, define a reusable function.
function countSpaces(str) { return str.split(' ').length - 1; } const str = 'bobby hadz com'; console.log(countSpaces(str)); // 👉️ 2
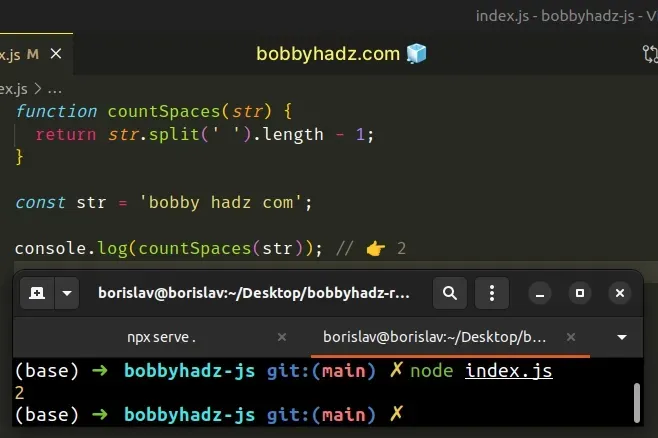
The countSpaces function takes a string as a parameter and returns the number
of spaces in the string.
Alternatively, you can use the String.replaceAll() method.
# Count the Spaces in a String using String.replaceAll()
This is a three-step process:
- Use the
lengthproperty to get the string's length. - Use the
replaceAll()method to remove all spaces from the string. - Subtract the length of the new string from the length of the original string.
const str = 'bobby hadz com'; const spacesCount = str.length - str.replaceAll(' ', '').length; console.log(spacesCount); // 👉️ 2
The String.replaceAll() method returns a new string with all matches of a pattern replaced by the provided replacement.
The method takes the following parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| pattern | The pattern to look for in the string. Can be a string or a regular expression. |
| replacement | A string used to replace the substring match by the supplied pattern. |
The String.replaceAll() method returns a new string with the matches of the
pattern replaced. The method doesn't change the original string.
Strings are immutable in JavaScript.
You can also define a reusable function.
function countSpaces(str) { return str.length - str.replaceAll(' ', '').length; } const str = 'bobby hadz com'; console.log(countSpaces(str)); // 👉️ 2
The function takes a string and returns the number of spaces in the string.
# Count the Spaces in a String using String.match()
This is a two-step process:
- Use the
String.match()method to match each space in the string. - Access the length property on the array.
function countSpaces(str) { return str.match(/\s/g)?.length || 0; } console.log(countSpaces('bobby hadz com')); // 👉️ 2 console.log(countSpaces('abc')); // 👉️ 0 console.log(countSpaces('a bc')); // 👉️ 1
The String.match method matches a string against a regular expression.
const str = 'bobby hadz com'; // 👇️ [ ' ', ' ' ] console.log(str.match(/\s/g));
The method returns an array containing the matches (if any) or null if no
matches are found.
We used the optional chaining (?.) operator to short-circuit if the method
returned null.
function countSpaces(str) { return str.match(/\s/g)?.length || 0; }
The optional chaining (?.) operator
short-circuits and returns undefined if the value to the left is nullish
(null or undefined).
If the String.match() method returns null, the function returns 0 as there
are no spaces in the string.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Count the Duplicates in an Array in JavaScript
- Count Elements in an Array that match a Condition using JS
- Count the Elements in Div or all elements with Class in JS
- Count Occurrences of each Element in Array in JavaScript
- Count the Number of Regex Matches using JavaScript
- Count the Unique Elements in an Array in JavaScript

